Anatomy: Overview of the Lower Limb Flashcards
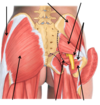

what are the superficial gluteal muscles
gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae
what are the superficial muscles of the gluteal region innervated by
gluteal nerves:
gluteal maximum: inferior gluteal
all other: superior gluteal
what are the deep muscles of the gluteal region innervated by
nerves from the sacral plexus
what is the function to the superficial muscles of the gluteal region
extensors (gluteus maximus)
abductors and medial rotators of thigh(gluteus med and min)
what is the function of the deep muscles of the gluteal region
-lateral rotators of thigh and hip stabilisers
Trendelenburg’s gait
when the pelvis drops on opposite side of the raised limb - indicates that the abductor muscles on the standing limb are weakened or paralysed (superficial muscles)
due to lesion in sup gluteal nerve

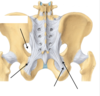

what quarter of the gluteal region would you use for injections
lateral upper
what are the greater and lesser sciatic foramens formed by
sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments
what forms the sciatic nerves
L4-S3
what forms the pudendal nerves
S2-S4
what forms the -Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
S1-S3
what is the principal nerve to the perineum
pudendal nerve
what is the largest nerve in the body
sciatic (L4-S3)
what does the posterior cuatenous nerve of the thigh supply
skin over posterior thigh, popliteal fossa, lateral perineum and upper medial thigh
the sciatic nerve


where does the sciatic nerve usually exit
inferior to piriformis

what does the sciatic nerve supply in the gluteal region
nothing
what 2 nerves does the sciatic nerve consist of
tibial nerve and common fibular bunched together - separate in distal posterior thigh
what is the superior boundary of the femoral triangle
inguinal ligament
what is the medial border of the femoral triangle
lateral border of the adductor longus
what is the lateral border of the femoral triangle
medial broder of the sartorius
what forms the floor of the femoral triangle
iliopsoas laterally and pectineus medially
what forms the roof of the femoral triangle
deep fascia (fascia lata)
name the contents of the femoral triangle from lateral to medial
femoral nerve
femoral artery
femoral vein
lymphatics
what is the femoral triangle surrounded by
connective tissue - femoral sheath
what forms the inguinal ligament
inferior edge of the external oblique aponeurosis
what is not found in the femoral sheath
femoral nerve


compartment syndrome
swelling of tissue or increase in fluid (bleeding) causes increased pressure, as the fascia creates an enclosed compartment.
affects the function of muscles of nerves in the compartment.
can be acute or chronic
how is the pressure form compartment syndrome relieved in an emergency
fasciotomy
must be done ASAP to reduce risk of irreversible ischaemia

what 4 muscles are found in the anterior compartment of the thigh
flexors of the thigh: pectinues, ilipsoas and sartorius
extensor of the thigh: quadriceps femoris

what nerve are the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh supplied by
femoral nerve (L2-L4)
psoas major nerve (L1-L3) supplies the iliopsoas
what 5 muscles are found in the medial compartment of the thigh
adductors of the thigh: adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, gracilis, obturator externus

what nerve are the muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh supplied by
obturator nerve (L2-L4)
the hamstring part of adductor magnus is supplied by the tibial nerve
what muscles are in the posterior compartment of the thigh
extensors of thigh and flexors of the leg: semitendinosus, semimembranosus & biceps femoris

what nerve are the muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh supplied by
tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2)
the short head of biceps femoris is supplied by common fibular divison of sciatic nerve
what is the function of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg
dorsiflexors of ankle & extensors of toes
what muscles are found in the anterior compartment of the leg
tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, fibularis tertius

what are the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg supplied by
deep fibular nerve (L4, L5)
what is the function of the muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg
foot eversion and weakly plantar flex ankle
what muscles are found in the lateral compartment of the leg
fibularis longus and brevis

what are the muscles in the lateral group of the leg supplied by
superficial fibular nerve (L5, S1, S2)
what muscles are in the superifical group of the posterior compartment of the leg
gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris

what muscles are in the deep group of the posterior compartment of the leg
popliteus, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior
what are the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg supplied by
tibial nerve
what type of joint is the hip joint
synovial
what is the ‘socket’ of the hip joint
acetabulum
what are the hip joint ligaments formed from
thick part of fibrous layer of joint capsule
what are the 3 ligaments around the hip joint
- iliofemoral, pubofemoral and ischiofemoral
- note: the iliofemoral is an upside down Y shape

what is this ligament

iliofemoral
what is this ligament

ischiofemoral
describe the head of the femurs arterial supply
has its own arterial supply that runs to the head of the femur in the ligamentum teres


what do the medial and lateral circumfex arteries do
anastomose around the femur
where do the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries usually come from
deep femoral artery
what do the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries give off
retinacular arteries

what does the artery to the head of the femur branch off from
obturator


what type of joint is the knee joint
synovial
name the 3 articulations of the knee joint
2 x femerotibial and 1 x femeropatellar

how is the knee joint strenghtened
by ligaments
L - M, anterior view


extracapsular ligaments of the knee


what are minisci
fibrocartilage
waht are the extracapsular ligaments of the knee
patellar
fibular (lateral collateral)
tibial (medial collateral)
what are the intra articular knee ligaments
within joint
ant and pos cruciate
what are the menisci in the knee joint
medial and lateral mensici
types of meniscal tear

name the borders of the popliteal fossa

superolaterally – biceps femoris
superomedially – semimembranosus
inferiorly – gastrocnemius
roof – popliteal fascia

what is another name for the calcineal tendon
achilles tendon


what is the achilles tendon formed from
tendons of soleus and gastrocnemius together
where does the achilles tendon attach
-attaches to calcaneal tuberosity of the calcaneus
what does the ankle jerk reflex result in and what nerves does it test
plantar flexion
S1 and S2 nerve roots
what arteries around the hip joint are susceptible to damage in intarcapsular fractures
retinuacular arteries

what can corticosteroids cause in the femoral head
avacular necrosis
what are the small end arteries in the head of teh femur susceptible to
blockage eg fat, thrombus, nitrogen gas


what muscle can be used as a tendon graft eg for ACL reconstruction
semitendinosus

what must be examined in patients that present with knee pain
HIP
- obturator nerve can refer pain from hip pathology to knee
what is the adductor canal also called
Hunter’s canal
where does the adductor canal extend to and from
apex of femoral triangle to adductor hiatus of adductor magnus
what does the adductor canal contain
femoral vein, artery and saphenous nerve (branch of femoral nerve)
where do the femoral artery and vein become the popliteal artery and vein
adductor hiatus (adductor magnus)
which menisci if fixed and which is mobile
MM fixed
LM mobile
which way does the patella always dislocate
and what test is performed to detect patellar instability
laterally
patellar apprehension test

what resists valgus stress
MCL
what does the ACL resist
internal rotation and anterior translation of tibia

what does the PCL resist
posterior translation of the tibia or anterior translation of femur
also hyperextension of the leg
what does the LCL do
resist varus stress and helps to resist external rotation
what is our tibiofemoral angle on average
6 degrees valgus
what do people with genu varum have increased risk of
medial OA
- converse for genu valgum



what will cause increased synovial fluid in the knee joint
acute meniscal tear and degenerative conditions
what causes lipohaemarthrosis in the knee joint
fracture
what movements comprise pronation of the forefoot
eversion, abduction, dorsiflexion

abduction and adduction of the hindfoot

what movements comprise supination of the foot
inversion, adduction and plantar flexion

what happens if the tibial posterior tendon elongates
flat foot

what is another name for flat foot
pes planus
quadriceps muscles

movement of the tibia during flexion and extension of the knee
knee pivots on medial compartment (medial minisci fixed) during flexion and extension
tibia interally rotates on flexion and externally rotates on extension
describe the lymphatic drainage of the lower leg
- superficial lymphatics to superficial ingiunal nodes
- deep lymphatics to deep inguinal nodes
- then to external iliac nodes
- common iliac
- lumbar



what do the PCL and LCL resist
external rotation


