Anatomy: Foot Flashcards
name the bones of the foot


what joint is between the talus and calcaneus
subtalar joint

what movement do the tibialis ant and pos cause
inversion of the foot
what movement do fibularis muscles cause
eversion
what are the 2 midtarsal joints
calcaneocuboid and talocalcaneonavicular

What joint is between the cuneiforms/cuboid proximally and the metatarsals
tarsometatarsal joints

what are the main movements of the mid tarsal joints
inversion (tibialis ant and pos) and eversion (fibularis muscles)
what type of joints are the midtarsal joints
synovial
what type of joints are the MTP
synovial
what type of joints are the interphalangeal joints
synovial hinge joints - flexion and extension of the toes
what is the function of the arches of the foot

shock absorption, push off spring function, inc weight bearing capacity by weight redistribution across the whole foot
what are the arches supported by
plantar aponeurosis and plantar ligaments
what also protects against puncture wounds
plantar aponeurosis

what is the plantar aponeurosis
thickened central area of plantar fascia - deep fascia of the sole of the foot

what is the medial longitudinal arch formed from
calcaneus, talus, navicular, 3 cuneiforms and 1-3 metatarsals
what is the medial longitudinal arch supported by
flexor hallicus longus
attachment of tibials ant
attachment of fibularis longus

what is the lateral longitudinal arch formed by
calcaneus, cuboid and metatarsals 4 and 5
what arch is usually weight bearing on standing
lateral longitdunal arch
what plane of the foot is the transverse arch located in
coronal

what is the transverse arch formed by
cuboid, cuneirforms and the bases of all 5 metatarsals
what is the transverse arched supported b
fibularis longus and tibialis posterior
what action do the sole muscles produce
flexion of the toes
what action do the interosse muscles produce
abduction/adduction of the toes
what is the dorsalis pedis artery a branch of
anterior tibial artery

where is the pulse of the dorsalis pedis artery taken
lateral to extensor hallicus longus tendon
what does the dorsalis pedis artery branch to
arcuate artery on the dorsum of the foot

what do the medial and lateral plantar arteries branch from
pos tibial artery

what arch do the med and lat plantar arteries contribute to
deep plantar arch
what arises from the deep plantar arch (artery)
metatarsal arteries which branch into digital arteries
how many digital arteries per toe
4
superficial veins: what does the dorsal venous arch give rise to
small and great saphenous vein

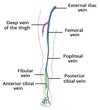
describe th deep veins of the foot
follow arteries
drain into ant and pos tibial and fibular veins - join to form the popliteal vein
describe the motor supply to the foot
tibial nerve to the muscles of the sole of the foot
deep fibular nerve to the muscles of the dorsum
sensory nerve supply to the dorsum of the foot
mainly superficial fibular with deep fibular nerve supplying the first interdigital cleft
sural nerve supplying the proximal lateral border
saphenous nerve supplying the medial border

what is the sural nerve formed from
a sensory nerve formed from tibial and common fibular nerves
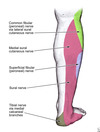
sensory nerve supply to the plantar surface of the foot
Mainly tibial nerve to the heel and majority of sole (medial and lateral planter nerves)
sural nerve supplying the proximal lateral border
saphenous nerve supplying the proximal medial border (borders as for the dorsum)

describe the lymphatic drainage of the foot
lymphatic vessels accompany the great and small saphenous veins


