Anatomy (Nervous System) Flashcards
Homeostasis (2)
- Tendency of an organism or cell to maintain internal equalibrium by adjusting its physiological processes
- Maintained by autonomic nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System (1) & Controls (3)
- Visceral motor functions
- Contorls:
1. Cardiac muscle
2. Smooth muscle
3. Glands
What controls BV’s and how?
- Sympathetic contracts BV’s and turning it off dialates BV’s
Sympathetic Autonomic Ganglia
- Paravertebral ganglion (sympathetic chain ganglia)
- Prevertebral ganglia are assoicated with large BV’s in abdomen
Parasympathetic Autonomic Ganglia
- Intramural ganglion are distributed in the wall of the target organ
- Parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
Superior Cervical Ganglia
- Inervates all of the head and neck for sympathetic NS
Cranial Nerve 10 (Vegas Nerve) (9)
Preganglionic fibers in brain stem
Innervates:
- Lungs
- Heart
- Liver
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Pancreas
- Large Intestine
- Small Intestine
Sacral Nerves 2-4 (5)
Innervate:
- Large Intestine
- Small Intestine
- Rectum
- Bladder
- Genitalia
Sympathetic Chain Ganglia (4)
- Contains 2 neurons
- 1 in CNS (T1-L2 Region)
- 1 in paravertebral ganglia (next to vertebra) or in prevertebral ganaglia
- Always enter spinal nevre via white matter and leave via gray matter
Pre/Postganglionic Sympathetic & Pre/Postganglionic Parasympathetic Cell Bodies
Pre Symp - T1-L2 region of CNS
Post Symp - Paravertebral ganglia or prevertebral ganglia
Pre Para - Brain stem or S2-S4 region of CNS
Post Para - Inner wall of target organ
Sympathetic Option 1
Preganglionic fibers - Intermediolateral gray area of T1-L2 -> ventral root into spinal cord -> 2nd neuron in paravertebral ganglion via white ramus communicans
Postganglionic fibers - paravertebral ganglion -> spinal nerve via gray ramus communicans -> dorsal & ventral ramus for distribution

Sympathetic Option 2
Preganglionic Fibers - Neurons in Intermediolateral gray matter in T1-L2 -> spinal nerve via ventral root -> paravertebral ganglion via white ramus comminicans -> up or down sympathetic chain to synapse at specific paravertebral ganglion
Postganglionic Fibers - Neurons in paravertebral ganglion -> spinal nevre via gray ramus communicans n-> dorsal and ventral ramus for distribution
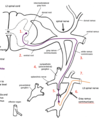
Sympathetic Option 3
Prevertebral fibers - Neurons in Intermediolateral gray area of T1-L2 -> spinal nerve via ventral root -> paravertebral ganglion via white ramus communicans -> exit chain as splanchnic nerve into prevertebral ganglion
Postganglionic fibers - Neurons in prevertebral ganglia -> target organ via following BV’s or autonomic plexus

Parasympathetic Pathway
Preganglionic fiber:
Brain stem - Vegus nerve -> organs in thorax or abdomen until splenic flexure of colon
Sacral Spinal Cord (S2-S4) - Intermediolateral gray area -> spinal nerve via ventral root -> ventral ramus -> decending colon or organs of pelvis or erectile tissue
Postganglionic fibers - neurons in target organ
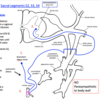
Visceral Sensory Pathway
Visceral fibers from target organs via following sympathetic fibers -> Dorsal root ganglia
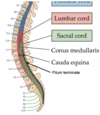
Conus Medullaris
- Narrowed end of spinal cord
- Around L1/L2