Abdominal Catastrophes Flashcards
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Localised enlargement of the abdominal aorta
What is the pathology of the Abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Degeneration in the media of the arterial wall leading to slow continuous dilation of the lumen o the vessels
What is the clinical presentation o abdominal aortic aneurysm?
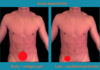
Asymptomatic unless ruptured If ruptured- sudden death or sudden severe abdominal pain, sudden collapse, Shock
What is bowel perforation?
Mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents normal movement of digestion products
What is the pathology of a bowel perforation?
Small bowel- adhesions due to previous surgery, femoral/inguinal hernia, volvulus, carcinoma of the caecum Large bowel- Carcinoma (left side usually) sigmoid volvulus, Diverticular disease
What is the clinical presentation of a bowel perforation?
Isotonic hypovolemic, vomiting and then metabolic alkalosis due to loss of HCl, Hypokalemia as compensation for alkalosis, Hypocholermic
What is bowel ischemia?
When blood supply through major arteries that supply intestines slows or stops When blood supply through major arteries that supply intestines slows or stops When blood supply through major arteries that supply intestines slows or stops
What can cause bowel ischaemia?
Embolism
What is clinical presentation of bowel ischemia?
Severe abdominal pain and tenderness, toxic and hypotensive, very high white cell count
What is the treatment of bowel ischemia?
Urgent laparotomy and resection of the dead bowel
What is cholangitis?
Infection of the bile duct
What is the pathology of cholangitis?
Gallstones obstructing the bile duct Ecoli
What is the clinical presentation of cholangitis?
Jaundice Biliary stasis Pain in Right upper quadrant Fever Biliary colic- history
What is the treatment of cholangitis?
remove gallstones
What is pancreatitis?
Disease in which the pancreas becomes inflammed
What is the pathology of pancreatitis?
Auto digestion by proteases of retro peritoneum May be due to alcohol or gallstones
What is clinical presentation of pancreatitis?
Significant dehydration due to vomiting Raised serum amylase Upper abdomen pain that radiates to the back Fever
What are the common causes of blood loss into the gut?
Bleeding oesphageal varices and bleeding peptic ulcer Bleeding diverticular disease Retroperitoneal bleeding
What is the clinical presentation of Bleeding oesphageal varices and bleeding peptic ulcer?
Haematemesis Bleeding massively from upper GI tract Melaena Due to alteration of blood by digestive enzymes and intestinal bacteria Occurs with bleeding anywhere from mouth to caecum Patients taking oral iron will have smelly black stool
What is the clinical presentation of Bleeding diverticular disease?
Bright red bleeding per rectum- Haematochezia Bleeding massively from upper GI tract
What causes retroperitoneal bleeding?
Due to ruptured AAA or torn retroperitoneal veins if on anticoagulants
Where would you feel pain in the small and where in the large bowel?

When would parietal peritoneum produce pain?
Inflammation causes pain
What would visceral pain be?
Reffered pain