6 ⼀PREGNANCY II Flashcards
PreEclampsia = [Gestational HTN + Proteinuria]
What are the primary components for the Mechanisms of Disease in Preeclampsia? - 4
Ab complex mediated endovascular damage –>
- Hemolytic Anemia
- Platelet aggregation from ⬆︎Thromboxane
- Vascular constriction pervasively from ⬆︎Thromboxane

PreEclampsia = [Gestational HTN + Proteinuria]
Describe timeline for Postpartum preeclampsia
PreE presents anytime between
[20WGunless 2/2 Hydatidiform Mole → PreE can present <20WG - up to 12 weeks postpartum]
_________________

PreEclampsia –> SEVERE PreEclampsia –> HELLP and at anytime, Eclampsia is possible
Nipple discharge is pathologic if it is 1 of what 3 things?
________________
How do you workup breast nipple discharge?
spontaneous | uL | persistent

The most common cause of pathologic breast nipple discharge is ⬜
[Intraductal papilloma (from lining of the breast duct ) ]

Papillomas are usually benign but may have associated carcinoma(atypical|DCIS|Invasive) within the lesion
Which contraception should be given to a patient with PCOS?
_________________
why? -2
[Progesin IUD]
_________________
androgen excess in PCOS➜ unopposed estrogen ➜ anovulation, polycystic ovaries, irregular menses, endometrial hyperplasia/CA
Progesterone Protects the Endometrium

What is 1st line tx for Dysmenorrhea in sexually active pts?
________________
What about non-sexually active pts?
Combined OCPs
_________________
NSAIDs
Combined OCPs treat dysmenorrhea by ⬇︎endometrial proliferation ➜ atrophy which –> ⬇︎prostaglandin release –> ⬇︎painful uterine contractions
Diagnostic criteria for Primary Dysmenorrhea
_________________
etx
ITSO nml pelvic exampelvic cramping during first few days of menstruation
_________________
prostaglandin release from endometrial sloughing during menses
PreEclampsia –> SEVERE PreEclampsia –> HELLP and at anytime, Eclampsia is possible
_________________
what is the treatment for HELLP? (3)
(g): B
(p): BM
(s|h|e): BMX

🧭B=[BP control: (when ≥ 140/90) = Labetalol | Hydralazine]
🧭M=[IVMG SULFATE (SEIZURE PX)]
🧭X=[X“baby out now!” = STAT IMMEDIATE DELIVERY]
What is a Hydatidiform Mole? -3
_________________
How is HM related to CA?
★ abnormal fertilization of [empty ovum (complete mole)] by either 2 sperm or [1 sperm whose genome ultimately duplicates]
Or
★ abnormal fertilization of [normal “occupied” ovum by 2 sperm ( ➜ partial mole)]
★ Moles ➜ [hypertrophic and hydropic trophoblastic villi] that secretes βhCG > 100,000
_________________
❎HM can develop into [Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia]
_________________
tx = [D&C + contraception] ➜ [serial βhCG until undetectable x 6 mo]

Hydatidiform Mole is a precursor to ⬜
How do you manage Hydatidiform Mole ? (5)

[Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia]
_________________

Tx for Trichomoniasis is ⬜(2) . What are the precautions if female patient is breastfeeding?
{[2 gm metronidazole PO x 1] + [also treat sexual partner]}
_________________
after taking, breast milk should be expressed and discarded x 24h

Give brief descriptions that differentiate Postpartum
Blues vs Depression vs Psychosis
- Blues = onsets PPD1, peaking at PPD5 and subsiding PPD14, worst w/lactation
- Depression = onset between [1 month - 12 months after birth] Traditional s/s. Previous Depression hx is RF
- Psychosis = RARE but onsets IMMEDIATELY after birth
Explain how Breastfeeding is associated with iron deficiency
_________________
thalassemia< [MIX 13]< IDA
Breastfeeding only provides sufficient iron for first 6 months of life.
[infants ≥6 months] MUST be introducted [iron-rich solid foods (pureed meats/cereals)] to prevent iron deficiency anemia
_________________
(thalassemia < [Mentzer Index 13 (MCV/RBC)]< IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA)
There are 3 types of female Urinary Incontinence
Describe [Stress Urinary Incontinence]
urinary leakage with INC INTRAABDOMINAL STRESS (coughing / sneezing / laughing / lifting)

There are 3 types of female Urinary Incontinence
Describe [Urge Urinary Incontinence⼀Overactive Bladder]
URGE to urinate Suddenly / Overwhelmingly / Frequently

There are 3 types of female Urinary Incontinence
Describe [Overflow Urinary Incontinence]
constant OVERFLOWING DRIBBLE OF URINE and bladder distension 2/2 incomplete bladder emptying

(either from mechanical outlet obstruction or DM Detrusor hypOactivity)
There are 3 types of female Urinary Incontinence
dx for [Overflow Urinary Incontienence] -2
________________
tx for [Overflow Urinary Incontinence] -2
[⇪ post void residual] > 150 cc + neuropathy
________________
[intermittent self catherterization] + [correct underlying etx for incomplete bladder emptying]

If Pap Smear testing reveals [High Grade Squamous intraepithelial lesion], what is the next step in management? -2
COLPOSCOPY = cervix magnified to identify and BIOPSY abnormal areas
________or________
LEEP (loop electrosurgical excision procedure) = excision of cervical transformation zone and surrounding endocervix - [only if done with childbearing]

Trimester WG: [≤13|14-27 | ≥28]
Major causes of [1st trimester ≤14WG] bleeding - 3
- Spontaneous Abortion (inevitable vs threatened)
- Acute cervicitis (postcoital bleeding, Friable cervix with discharge)
- Molar Pregnancy
Differentiate the following spontaneous abortions:
Inevitable abortion
Threatened abortion
Missed abortion
Complete abortion
spontaneous abortion = occurs < 20 WG
- INEVITABLE = vaginal bleeding < 20WG with cervical os dilated –>abortion will inevitably happen soon
* * * - THREATENED = vaginal bleeding < 20WG with cervical os closed is clearly a threat to a STILL LIVING FETUS
* * * - MISSED = retained Fetal death <20WG with cervical os closed…which is why we Missed it - (pt will have pregnancy sx that just suddenly disappear out of nowhere)
* * * - COMPLETE = EXPELED FETAL DEATH <20WG WITH ALL PRODUCTS OF CONCEPTION COMPLETELY EXPELED AND THEN CERVIX CLOSES BACK UP
* spontaneous = occurs < 20 WG*

What are the 3 criteria options for diagnosing
Cervical insufficiency
[pp: ≥2 nonpainful {2nd trimester 14-27WG} spontaneous abortions]
OR
[Cp: Ultrasound showing short cervix ≤25 mm]
OR
[Cp: (early < 24WG ) nonpainful cervical Dilation]
_________________
pp = previous pregnancy
Cp = Current pregnancy
[⬜ placement] ⬇︎ risk of [2T14-27WG] loss in pregnant patients with cervical insufficiency.
What is it called when [pregnancy with cervical insufficiency] fails and prolapses?
and what’s the prognosis for this?
Cerclage;
[Previable Prolapsing amniotic membrane];
POOR PROGNOSIS (PPAM a/w imminent delivery/high risk preterm)
Lactational mastitis occurs ⬜(when?)
as a result of ⬜(etx -6)
[first 3 mo postpartum] ;
[breastfeeding difficulties(improved with lactation consultant)]➜[prolonged breast engorgement(diffuse BL TTP)]
➜ [inadequate milk drainage] ➜[clogged milk ducts & nipple pore]
➜ [Staph A Bacteria(from infant nasopharynx vs Mom skin) retrograde enter nipple pore & divide in stagnant milk]➜ Lactational mastitis
* * *
(**q**[Lies])

Lactational mastitis occurs ⬜(when?)
and presents with what 4 symptoms?
[first 3 mo postpartum] ;
(**q**[Lies])
quadrant[LAD& fever/ induration / erythema / swelling & Pain]

Lactational mastitis
tx -4
[(DicloxacillinPO) or (CephalexinPO)]
+
[KEEP BREASTFEEDING (frequent milk drainage)]
+
ibuprofen
— — — — —
+ [Needle Aspiration if ⊕abscess]

Breast engorgement presents as ⬜
Tx? (3)
diffuse BL breast TTP
_________________
BREAST PUMPING / NSAID / Cold Compress
Is it safe to direct breastfeed if Lactational mastitis is present?
YES!
(Interrupting breastfeeding can ➜ ⬇︎maternal milk production)

[(CAGS) Condyloma Acuminata Genital Skinwarts] is caused by ⬜2.
Since the [typical CAGS tx (⬜)] is contraindicated in pregnancy, how is delivery managed in pregnant patients with active CAGS? -2
[HPV 6] & [HPV 11] ;
[PodophyllumTOPICAL]
[Vaginal delivery(or CSection*)]
&
{NO [PodophyllumTOP]}
(Unfortunately, not even CSection prevents HPV vertical transmission so (unless large/obstructive*) Pregnant Women with [Condyloma Acuminata Genital Skinwarts] should proceed with vaginal delivery but WITH NO Podophyllum Topical tx

1 of the 3 Recommended [USPSTF Guidelines for Breast Cancer Screening] is to give [Genetic test/counsel to pts with [⊕High Risk Familyhx (breast CA)*]
_________________
io\Breast CA , name 4 criteria that qualify a patient as [⊕High Risk Family hx]
- [**⊕High Risk Familyhx (breast CA)</sub>**] =
- [ GOE3___(1stºor 2ndº ⼀breast)]*
- *
- or*
- [ 2__(1stº⼀breast) (1_under50yo)+ (1_anyAge)]*
- *
- or*
- [1__(1stº⼀BILATERAL BREAST)]*
- *
- or*
- [ 1__(1stºor 2ndº ⼀< breast AND ovarian >)]*

What are the 3 Recommended [USPSTF Guidelines for Breast Cancer Screening]? (3)
- ⊕[(50-74yof) → mammogram q 2y](<50 yo depends on individual)
- ⊕[(HRFHx)* → Genetic test/counsel(only if ⊕HRFHx!)]
-
❗️ ❗️NOSELF BREAST EXAMS! ❗️ ❗️
* * *
* *HRFHx = [HIGH RISK(CA)⼀Family history]*

Postpartum endometritis cp -4
_________________
tx (2)
RF: CESAREAN / GBS+ / prolonged ROM / protracted labor / operative vaginal delivery
postpartum: [uterine fundal tenderness] , vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding, fever
_________________
Clindamycin + gentamicin
polymicrobial infection
In pregnancy, c/f appendicitis can be ruled out using ⬜ and presents atypically with ⬜
graded compression abd ultrasound ; [R abd pain with NO peritoneal signs or McBurney TTP]
Pt’s Pap Smear reveals [Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance]
Mngmt? - 5
- Pap smear revealing [ASCUS-(Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance)].. →*
1st: HPV typing - –if high risk HPV(16 or 18)—>*
2nd: Colposcopy - –if Colposcopy abnml –>*
3rd: Cervical biopsy
There are several causes of abnormal uterine bleeding. give differentiating factors for each:
Pelvic organ Prolapse
_________________
Cervical CA
_________________
endocervical polyp
_________________
endometritits
_________________
leiomyoma
eroded and bulging mass at introitus +/- incontinence, constipation, dyspareunia
_________________
exophytic cervical lesion
_________________
smooth vermiform appearance visibily protruding thru cervical os
_________________
uterine and cervical motion tenederness
_________________
enlaged irregularly shaped uterus
Urethral diverticula etx
_________________
s/s (3)
repeated infection and urethral trauma (vaginal delivery) ➜ distension of diverticulum with purulent fluid
_________________
- ANT vaginal wall mass
- postvoid dribbling
- dysuria
* diagnosis confirmed with pelvic MRI or TVUS*

What are the 2 medical managements for elective spontaneous abortion
- [misoPROSTol (PROSTaglandin analogue) 800 mcg vaginally]expels ≤2W
* * * - [MiFepristone antiprogestin]

What’s the time limit for pregnant women in [Latent labor Stage 1A] if they’re nulliparous?
________________
What about if they’re multiparous?
Labor = (LA)PD
1A: Latent labor phase = Strong Contractions q3-5 min (should be <20 hrs for nulliparous pts and <14 hrs for multiparous pts)
1B: ACTIVE labor phase = Cervix is now 6 cm Dilated, [growing @ 0.5cm / hr] and effacing
________________
2 : Pushing Time! since Cervix is now 10cm FULLY DILATED (should be ≤3 hrs for nulliparous and ≤2 hrs for multiparous)
________________
3 : Delivery of Baby! and then Deliver Placenta
What’s the time limit for pregnant women to deliver the Placenta?
Labor = (LA)PD
3 : Delivery of Baby! and then Deliver Placenta (<30 min)
What is the first manifestation of pubety for females?
BREAST –(2.5 years later)–> Menarche by 15 yo

What is the workup for Primary Amenorrhea ?-3
-{girls of nml growth with: [no menses by 13 yo] or [no menses by 15 yo with breast]}

What’s the time limit for pregnant women in [stage3:”pUSH!”labor] if they’re
Multiparous?
________________
What about if they’re Nulliparous?
[MULTIPAROUS ≤2h (add 1 hour if +epidural)]
[nulliparous ≤3h (add 1 hour if +epidural)]
________________
- Labor = (LA)pd*
- 3 : PUSH! baby out ! since Cervix is now 10 cm FULLY DILATED ([MULTIparous≤2 hrs] and [nulliparous≤3 hrs] (add 1 hr if +epidural))*

What are the stages of Labor?
Labor = (LA)pd
[stage1: <u>L</u><u>atent</u>LABOR(Mn1420)]
= Strong Contractions q3-5 min ([MULTIparous≤14h] | [nulliparous≤20h])
_________________
[stage2:<u>A</u><u>CTIVE</u>LABOR]
= Cervix 6 cm Dilated, [growing @ 0.5-(1-2) cm/hr] and effacing
[stage3:”pUSH!”labor(Mn23)]!
= pUSH out Baby since Cervix is now [10 cm FULLY DILATED] ([MULTIparous≤2h] | [nulliparous≤3h])+epidural= add 1h
[stage4:”dELIVER”labor({p0.5})]
delivery baby➜ [placenta ≤0.5h]
https: //www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation_563008&feature=iv&src_vid=Xath6kOf0NE&v=ZDP_ewMDxCo

What are the 4 clinical features for diagnosing [stage1B:ACTIVELABOR]?
- Labor = LApd*
1. [stage1: <u>L</u><u>atent</u>LABOR(Mn1420)] = [StrongContractionsq 3-5 min] - *
PLUS:
- [Cervix Dilation ≥ 6 cm]
- [Cervix growing at 0.5-(1-2)cm/hr] {grows 1-2 cm/hr normally – with No less than 0.5 cm/hr }
- [Cervix effaced]
* Fetal Heart Tracing is IRRELEVANT in diagnosing [s1B Active LABOR]

For pregnant women in [stage2ACTIVE LABOR], when is the patient considered to be in [labor protraction]?
________________
How do you treat this? (2)
Labor = (LA)pd
NORMAL s2AL: Cervix is now 6 cm Dilated, [growing @ [GOE 0.5 cm/hr and effacing]
* * *
[s2ALPROTRACTION] = cervical dilation[LOE 0.5 cm/hr]
_________________
[s2AL PROTRACTION] Tx :
Oxytocin + Amniotomy
(since most common cause of [stage 2ACTIVE LABOR PROTRACTION] = contraction inadequacy)
Criteria for Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
[≥3 consecutive < 20WG spontaneous abortions]
How are migraines associated with Pregnancy?
Migraines commonly start [2T14-27WG] of Pregnancy
But also be suspicious of [Pseudotumor Cerebrii]
How does Obesity commonly cause amenorrhea?
Obesity –> anovulation without affecting LH/FSH levels which–> Amenorrhea
What is Mittelschmerz?
Mittelschmerz = “Middle of the cycle” uL pelvic pain that occurs when blood released from rupture of follicle during ovulation irritates peritoneum

order: LH surge –> 36 hrs will pass –> Ovulation
How does [Pregnancy Induced Pruritus] present?- 2
- [Benign FOCAL Abdominal PiP(Pregnancy Induced Pruritus)
- WITH NO RASH
* * *
{PiP and iCP have NO RASH vs [Pemphigoid Gestationis ⊕abd rash]}

[Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy] = A/W IUFD, GZD PRURITUS INCLUDING PALMS/SOLES, BUT STILL ALSO NO RASH
[Pregnancy Induced Pruritus] Tx- 3
- Oatmeal baths
- UV light
- Antihistamines
{PiP and iCP have NO RASH vs [Pemphigoid Gestationis ⊕abd rash]}
Pemphigoid Gestationis occurs during the __ or __ trimester
CP- 3?
[2T14-27WG] OR [3T28-42WG]

[prodromal Pruritus]
→ [Periumbilical papules + plaques](both sparing mucus membranes)
→ [Bullae Eruption]
Pemphigoid Gestationis occurs during the __ or __ trimester
Dx?- 2
Tx?- 3

2nd OR 3rd
Clinical , Biopsy
Tx = [topical CTS], Antihistamines, Delivery

Guidelines for PAP Smear Cervical CA Screening - 3
[PAP Cervical Screening starts at 21 yo]
- [Age 21 - 65 PAP every 3 years (cytology only)] ≥ 3x consecutively before stopping after 65
________________
OR
- [Age 30-65 can PAP every 5 years if they add HPV testing] ≥ 2x consecutively before stopping after 65
________________
BUT
- Risk Groups (immunocompro/CIN2, 3 or CA hx) need more frequent PAP screening = voids out #1 and 2 if present
What are the main side effects of [LevoNorgestrelprogestin IUD]- 2
- Breast tenderness
- HA

When does [Fetal Postmaturity Syndrome] occur?
GOE42WG
[fetal Postmaturity syndrome]
________________
s\s -4
- occurs GOE 42WG*
1. long fingernails
2. meconium-stained placenta
3. [wrinkled peeling skin]
4. small for gestational age
[Transient Tachypnea of Newborn]
cp -4
[Retained Fetal Lung Fluid (from Cesarean/prematurity/Maternal DM)]➜
1. [prominent Interlobar fissure fluid]
2. [Tachypnea (retractions/nasal flaring) with clear breath sounds]
3. lung hyperinflation
4. cardiomegaly
Cause of [Transient Tachypnea of Newborn] (3)
[CESAREAN/PREMATURITY/MATERNAL DM] ➜ [Retained Fetal Lung Fluid]
Tx for [transient tachypnea of newborn]
SPONTANEOUSLY RESOLVES IN 1-3d
risk factors for [transient tachypnea of newborn] -3
- Cesarean
- Maternal DM
- Prematurity
caused by Retained fetal lung fluid
Clinical criteria for diagnosing PMS (PreMenstrualSyndrome) relies on PMS sx
What is the mngmt for PMS? - 5
PMS sx: [PMS BEGIN] –(1 week)→[MENSES] –(
[begin 1 week before menses]LUTEAL
and
[resolves during the 1 week after menses]FOLLICULAR
1st: Sx Diary reveal PMS sx timing occured over ≥ 2 menstrual cycles
2nd: Order TSH to r/o hypOthyroidism as cause
3rd: Exercise w/NSAIDs
4th: SSRI
5th: Combined OCP if SSRI don’t work and there’s no cxd
What are the causes of [Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea]?-6
Functional hypOthalamic amenorrhea ; these pts have low FSH and therefore NO postmenopausal sx
- Excessive Exercise
- Starvation(very low calorie diet)
- underweight(low BMI/Anorexia/Wt loss)
- Stress
- Depression
- Chronic illness
note: these pts will NOT have normal menstrual cycles

Explain how [Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea] causes amenorrhea
Stress → [(⬇︎Leptin) & (⇪GGBNC)] →
⬇︎GnRH → ⬇︎FSH/LH → No follicle maturation/menopausal sx/ovulation → ⬇︎Estrogen = Amenorrhea
- GGBNC = Ghrelin/GABA/BetaEndorphins/NeuropeptideY/CRH*
- Functional hypOthalamic amenorrhea ; these pts have low FSH and therefore NO postmenopausal sx*
- note: these pts will NOT have normal menstrual cycles*

Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea
What’s the most common long term complication for these pts?
Osteoporosis from lack of estrogen
- note: these pts will NOT have normal menstrual cycles*
these pts have low FSH and therefore NO postmenopausal sx

What are the options for Mngmt of Spontaneous Abortion - 4
- Expectant: Watchful Waiting for products of conception to expel naturally in 2-6 weeks
- Surgical: [Dilitation & Curettage (D&C) (cant be done during infection)] or [Manual Vacuum Aspiration]
- Medical: 800mcg Vaginal Misoprostol - takes up to 2 weeks for expel

ALL REQUIRE 1 WEEK FOLLOW UP
How do you anticoagulate a pregnant patient? -3
[1T < 14WG] = [LMW Enoxaparin]
_________________
[2T14-27WG] = WARFARIN
_________________
[3T28-42WG = WARFARIN
Clinical criteria for diagnosing PMS (PreMenstrualSyndrome) relies on PMS sx
What is the Clinical Criteria for PMS?
PMS sx begin 1 week before menses (luteal phase) and resolves during week after menses (follicular phase) for ≥ 2 menstrual cycles
(IF BBC HH)sx
Clinical criteria for diagnosing PMS (PreMenstrualSyndrome) relies on PMS sx
Name the 7 main PMS sx
IF BBC HH
- IRRITABILITY/MOOD SWINGS
- Fatigue
- Bloating
- Breast TTP
- Concentration ⬇︎
- Hot Flashes
- HA
[Polyhydramnios ( AFI ≥24 cm)] is a risk factor for Placenta Abruptio
What are the risk factors for Polyhydramnios? - 2
- Maternal DM - poorly controlled
- [swallowing_fetal anomalies (esophageal atresia)]
Amniotic Fluid Index for Polyhydramnios
≥ 24cm
RF = Maternal DM, congenital swallowing malformation
Polyhydramnios can –> placenta Abruptio
patients who are high risk for preeclampsia should receive what prophylaxis?
[12 WG ASA low dose]
risk factors for preeclampsia -4
- prior severe preeclampsia
- chronic HTN
- DM
- CKD
* px = [12 WG ASA low dose]*
For Antepartum patients, their NST (Non Stress Test) should be reactive
What is the Fetal Heart Tracing criteria for this?-4
_________________
Does this happen in pts in labor?
reactive = appropriate [fetal cerebral oxygenation]
- within a 20 min period there are
- at least two HR accelerations that are
- 15 bpm over baseline
- 1.5 small boxes long (15 sec)
_________________
THIS IS NOT REQUIRED FOR PTS IN LABOR
Criteria for PreEclampsia is Gestational HTN + [Proteinuria or End Organ Damage]
What are the clinical requisite for Gestational HTN dx? -6
- NO previous HTN
- ≥ 20 WG
- Systolic > 140
- Diastolic > 90
- At least 2 readings taken > 6 hrs apart
- BP taken in seated or semi-reclined position
requires all 6 for Gestational HTN dx
FYI: PreEclampsia can still occur superimposed on Chronic HTN
PreEclampsia dx = [Gestational HTN + Proteinuria]
How do you clinically diagnose Proteinuria for pregnant women - 4
1.[≥300 mg protein on 24 hr urine]
OR
2.[≥ 30 mg/dL on dipstick]
OR
3.[At least 1+ on dipstick]
OR
4.⭐[ Protein:Creatinine ratio > 0.3 ]⭐
Must occur [(≥2x) ( each ≥6H apart)]
Full term infant = 37- 42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor 34 to 36+6 WG - 3
“Pregnant Bitches”
+
(DELIVER NOW)

1
Full term infant = 37 -42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor 32 to 33+6 WG - 4
Pregnant Bitches Take
+

(deliver at 34WG)
Gestational sacs normally implant in the _____
Describe a Cornual Interstitial ectopic pregnancy
upper uterine fundus ;
implantation in outer “cornual” areas of uterus
dx = transVaginal US // tx = MTX or surgery if severe

Name the major risk factors for Ectopic Pregnancy - 6

- previous ectopic
- previous Pelvic
- previous Tubal surgery
- PID
- Bicornuate heart shaped uterus (causes cornual interstitial ectopic pregnancy)
- In Vitro Fertilization (causes cornual intersitital ectopic pregnancy)

tx = MTX or surgery if severe
Hyperemesis Gravidarum is a normal part of pregnancy that resolves by 20 WG
What are the risk factors for getting this? - 3
- Multiple Gestation
- GERD hx
- Hydatidiform Mole (note: elevated βHCG can stimulate thyroid and –> thyrotoxicosis of hyperemesis!)
HG is usually unresponsive to PO antiemetics, and can cause Thiamine Deficiency
When is a NST indicated? - 2
- [Movement from fetus ⬇︎]
OR
- [HRp 32-34WG]
* * *
HRp: High Risk pregnancy
the most common cause of NONreactive NST is fetal sleep cycle so be sure to allow at least 40 min testing and use vibroacoustic stimulation to wake them up!

What is the most accurate method of determining gestational age?
FIRST trimester US with crown to rump length (since there is minimal variability of fetuses when they first start off)
Dx for Ovarian Torsion
Pelvic US revealing adnexal mass with absent Doppler flow
Ovarian Torsion is more common amongst _____[pre/post] menopausal women
PREmenopausal
Untreated ovarian torsion –> sepsis, chronic pelvic pain and infertility
What is Culdocentesis? ; What is it used for?
centesis of intraperitoneal fluid thru the cul-de-sac via vaginal aspiration ; No longer used and has been replaced by US for identifying pelvic free fluid
How do you diagnose Endometriosis?
LAPORASCOPY to biopsy & remove endometriotic lesions

1st, treat empirically with NSAIDs tho
What is the MOST IMPORTANT intervention for preventing vertical HIV transmission from Mom to baby?
What are 2 other less important methods?
Triple Antiretroviral therapy (2 NRTI + [1 NNRTI or 1 PI])
Also, [c/s if viral load is > 1000] and [Zidovudine given to neonate for ≥6 wks after birth] are also good but not most important
What is the precaution in a pregnant woman with Graves’ disease?
Mom’s HYPERactive Thyroid stimulating Ab (anti-TSH R Ab) can cross the placenta and stimulate the baby’s thyroid gland –> [fetal Thyrotoxicosis]
Baby’s tx = methimazole + Beta Blcoker
Mode of inheritance for Hemophilia A
X-linked recessive
What’s the time limit for pregnant women in [stage1: <u>L</u><u>atent</u>LABOR] if they’re
multiparous?
_________________
nulliparous
[stage1: <u>L</u><u>atent</u>LABOR(Mn1420)]
= Strong Contractions q3-5 min ([MULTIparous≤14h] | [nulliparous≤20h])
What’s the time limit for pregnant women in [stage4:”dELIVER”labor] ?
Labor = LApd
[stage4:”dELIVER”labor({p0.5})]
baby now pushed out → deliver baby → deliver [placenta ≤0.5h]
Why is there no use in getting a D-dimer in a pregant woman for DVT workup?
D-dimer is already naturally elevated in pregnant woman due to their physiological ⬆︎ fibrinogen
What is the disadvantage of using Progestin only OCP for contraceptive?
You have to take it every day DOWN TO THE EXACT HOUR or it will fail! = compliance issues
What’s the most common cause of [unilateral breast discharge (serous or bloody])?
Intraductal Papilloma

CP of Fat necrosis of Breast - 4
- s/p previous breast trauma →
- MassFIRM
- MassiRREGULARLY SHAPED
- Mammogram: Oil cyst +/- calcifications that appear malignant but has fat globules and foamy macrophages on bx

CP for Fibroadenoma - 5

- nonpainful mass
- firm mass
- solitary mass
- mobile
- ~2 cm

Fibrocystic changes of the breast are common in ____(pre/post) menopausal women
How does this typically present? - 2
PREmenopausal
- cyclical bilateral breast pain
- diffuse nodularity
This [Fibrocystic cyclical BL breast pain] is exacerbated with caffeine!
CP for Inflammatory Breast CA - 7
- Peau d’orange appearance (superficial dimpling & pitting)
- Diffuse breast erythema
- breast edema
- breast pain
- nipple changes (retraction, flattening)
- Axillary LAD
- +/- nipple discharge

often confused with infectious process, but difference is IBC has NO FEVER and DOESN’T RESPOND TO ABX
CP for Lobular breast carcinoma - 3
- FIXED palpable mass
- Irregular borders
- +/- Bilateral
Paget Disease of the Breast is a form of ____(type of CA) that presents how? - 3
Ductal ADC
- crusty eczematous or ulcerating nipple & areola
- +/- bloody nipple discharge
- +/- nipple retraction
85% of Paget Disease of Breast is 2/2 underlying DCIS of glandular rissue which migrate thru mammary ducts to nipple surface. Dx = Mammogram and biopsy

How do you discern pharyngitis 2/2 Neisseria Gonorrhea from pharyngitis 2/2 infectious mononucleosis?
N. Gonorrhea = non-exudative pharyngitis, and has PID lower abd pain
vs.
Mono = exudative pharyngitis and has fatigue
otherwise, presentation is similar
Describe Lichen Sclerosis MOD
autoimmune chronic inflammatory condition of anogenital region that affects women of any age that –> vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
THIS DOES NOT AFFECT THE VAGINA!
dx = vulvar punch biopsy

Sx of Lichen Sclerosis - 5
- Pruritus SEVERE
- Dyspareunia
- White Grayish pale vulva (distinguishes from postmenopausal vaginal atrophitis)
- Cigarette paper texture of vulva (thin, crinkled)
- loss of vulvar anatomy (introitus, labia minora, clitoral hood)

dx = vulvar punch biopsy
Risk factors for Endometrial adenocarcinoma -3
- EEE - Excess Estrogen Exposure (HRT, neoplasm, [menstruation outside of 12-52], Nulliparity, Anovulation/PCOS)
- Tamoxifen
- Obesity (excess insulin–> ⬆︎androgen release from ovarian theca –> excess androgen is converted into estrone –> EEE)

Smoking and Progestin OCP ⬇︎Endometrial CA Risk
How does Vaginal CA (SQC or Clear cell ADC) present?-4
Who usually gets Vaginal SQC?
Where does Vaginal SQC occur in the vagina?
- Malodorous vaginal discharge
- Vaginal irregularity aesthetically (mass, plaque, ulcer)
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Postcoital bleeding
Vaginal SQC = > 60 yo
Vaginal SQC = POSTERIOR Upper 1/3 of vaginal wall

What are the risk factors for Vaginal SQC?
same as Cervical CA risk factors

(cervical CA migrates to vagina)
In Ovarian CA, why is the specificity for CA-125 much higher in older women?
CA-125 can be elevated in younger women who have leiomyomata or endometriosis, so elevated CA-125 is only associated w/ovarian CA in POSTmenopausal women
For ovarian CA, what can CA-125 be used for? -2
Postmenopausal women have ⬆︎risk of ovarian CA
- Monitors for recurrence after ovarian CA tx
- used in initial w/u of an ovarian mass to determine if it is malignant or benign
DO NOT DO NEEDLE ASPIRATION ON OVARIAN MASS PTS SINCE CA STATUS IS UNKNOWN AND MAY BE IATROGENICALLY SPREAD DURING ASPIRATION
Pt comes in with Postmenopausal bleeding
How do you evaluate them? (4)

Describe the clinical progression of primary syphilis chancres
single papule that turns into shallow, nonpainful, nonexudative ulcer with indurated edges, accompanied with BL inguinal LAD
THESE ARE EXTREMELY INFECTIOUS!

What are the features of [ChancROID?]?-4
Is it painful?
What organism causes this?
- [Deep ulcers with Exudative Grayish yellow Base]
- PAINFUL inguinal coalesced bubo nodes
- Organisms clump in long strands like a “school of fish”
* * *
PAINFUL
- Haemophilus Ducreyi*

What are the features of a Genital Herpes?-3
_________________
Is it painful?
“sssssSS… Ouch, GenHerpes”
1. [Several SOUR(painful) Small Shallow Sores(ulcers) ]
2. [Sangra base (Erythematous base)]
3. [Swollen LAD}

PAINFUL
What are the features of [Lymphogranuloma Venereum?]?-3
Is it painful?
What organism causes this?
- Multiple small shallow ulcers (similar to herpes)
- Large PAINFUL coalesced inguinal lymph nodes = Buboes
- Intracytoplasmic chlamydial inclusion bodies
** Initial lesion is NOT painful but Buboes are **
- Chlamydia Trachomatis*

Bechet Syndrome CP-2
Recurrent [Vasculitis-mediated aphthous and genital Ulcers]
What are the features of [Donovanosis granuloma inguinale]?-4
Is it painful?
What organism causes this?
- Extensive Granulation-base ulcers
- NO LAD
- Deeply staining gram neg (intracytoplasmic cyst = Donovan bodies)
- Mostly in India
▶nonpainful
▶Klebsiella Granulomatis

What do you do if a pt with clinical s/s of syphilis has a negative RPR?
Empiric PCN G IM!

RPR false negatives are a thing so you should repeat serology in 2 weeks to see if tx reduced titers. Also, Treponemal Pallidum can NOT be cultured so don’t do it!
THESE ARE EXTREMELY INFECTIOUS!
What is the DDx for Stress urinary incontinence - 2
Incontinence with coughing/lifting/sneezing
{⭐① vs ②a/b/c → URETHRAL HYPERMOBILITY → SUI⭐}
_________________
①{[⬇︎urethral tone] < bladder neck bulking tx > } and
②.[⬇︎pelvic floor muscle]
2a. [from injury|weakening] < kegel exercise tx >
2b. →urethral prolapse < urethral sling tx >
2c. →[Pelvic Organ Prolapse (bladder/uterus ⼀ a/w vag bulge)]</sub> < pessary tx >

What is the DDx for Overflow incontinence - 2
- DM neuropathy
- mechanical obstruction
⬇︎Detrusor activity or mechanical outlet obstruction –> Overdistended bladder –> involuntary dribbling and incomplete empyting (⬆︎PVR)
Normal Post Void Residual for Men
< 50 cc
Explain why clinicians no longer should empirically treat both Chlamydia and Gonorrhea if only one is Positive and the other is negative
Since NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test) (as compared to culture) is much more specific and sensitive = little chance of NAATfalse negatives =
empiric tx of both Gonorrhea and Chlamydia (iTSO 1 having ⊕NAAT and 1 having ⊝NAAT) … is no longer needed = only treat the ⊕NAAT test result
TLDR: (if using NAAT)→TRUST and TREAT only ⊕ [GC/Chlam NAAT]
(empiric tx of both was done in the past either because [Culture ➜ INC delay for pending result] or because [Culture –> INC chance of false negative]
Tx for Stress Urinary Incontienence - 4
- URETHRAL SLING
- Kegel exercise physical therapy
- Vaginal pessary
- Bladder neck Injectable bulking if etx is related to sphincter deficiency
What are bodily signs of ovulation - 3
- CLEAR thick cervical mucus discharge (looks like uncooked egg white) - starts thin and then becomes thick after ovulation
- ⬆︎temperature
- Mittelschmerz mid-cycle (day 14) pelvic pain
order: LH surge –> 36 hrs will pass –> Ovulation

How does high androgen levels affect fertility for Women?
high Androgen (such as PCOS) –> ⬇︎GnRH release from feedback inhibition –> ⬇︎FSH –> ⬇︎ovarian maturation –> 2°follicle atresia –>
- Anovulation chronically
- Amenorrhea
- Polycystic Ovaries
Adenomyosis CP - 3
- symmetrically enlarged TENDER uterus (> 12 weeks in size)
- Menorrhagia
- Dysmenorrhea eventually –> Chronic Pelvic Pain

etx: glands invade uterine myometrium –> blood deposition inside myometrium during cycle –> dysmenorrhea from irregular contractions and menorrhagia from extra deposited blood
Adenomyosis dx
True dx = pathological exam of tissue after hysterectomy

etx: glands invade uterine myometrium –> blood deposition inside myometrium during cycle –> dysmenorrhea from irregular contractions and menorrhagia from extra deposited blood
What’s the most common sign of Endometrial Polyps

nonpainful intermenstrual bleeding
Most common causes of Intermenstrual bleeding - 5
“I’m seeing some spotting in between my periods”
- Endometrial Polyps - nonpainful and light
- Endometrial ADC/hyperplasia - Older women
- Adenomyosis
- Cervicitis(from PID)
- Cervical CA
Leiomyomata uterine Fibroids CP - 5
- Pelvic pressure –> urinary incontinence/incomplete voiding/constipation
- irregularly enlarged NONTENDER uterus
- Menorrhagia (especially with submucosal)
- Dysmenorrhea (especially with submucosal)
- Progressively longer menses due to deformity of the uterus from fibroids

Submucosal and Pedunculated are the worst!
Clinical definition of Primary Amenorhhea
girls with no menses by age 15 but who have normal growth and secondary sex characteristics
Why do pts with Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome have NO ovaries/fallopian tubes/uterus/cervix but DO have breast?
they actually have functioning Testes that secrete AntiMullerian Hormone & Testosterone and this –> regression of Mullerian ducts. Breast comes from the aromatization of testosterone into estrogen
Wolffian ducts also degenerate and fetal urogenital sinus does not differentiate into a penis and scrotum –> default of external female genitalia
CP of congenital 5α reductase deficiency
ambiguous genitalia at birth 2/2 undervirilization
these pts can not convert Testosterone –> DHT
Difference in CP between Androgen insensitivity syndrome and Mullerian agenesis pts
AIS pts will have NO pubic or axillary hair since they don’t respond to testosterone (which is what causes axillary/pubic hair in both sexes!)
but
Mullerian agenesis pts have normal testosterone levels so will have pubic and axillary hair
Both obvi have no mullerian duct organs
What are the common side effects of OCPs - 6
- HTN
- Breast Tenderness
- ⬆︎TriAcylGlycerides
- Bloating with Nausea
- Breakthrough bleeding = most common (usually with lower estrogen doses)
- Venous thromboembolism (Migraine w/aura is a ctd for Combined OCPs)
Wt Gain is NOT a side effect of combined OCPs and OCPS actually ⬇︎risk of Endometrial and Ovarian CA
Why is Intrauterine Copper device relatively contraindicated in dysmenorrhea pts
its uterine inflammatory rxn actually –> ⬆︎pain
Why is Medroxyprogesterone depot relatively contraindicated in young pts - 2
- it causes ⬇︎ of bone mineral density
- it ⬆︎body fat and ⬇︎lean muscle mass
in addition to Breast tenderness and bleeding for 1st 6 months
Why can pts with PID sometimes present with RUQ pain?
uterine infxn extends from fallopian tubes (salpingitis) –> diffuse abd –> Liver capsule–> RUQ pain exacerbated with deep inspiration = Fitz Hugh Curtis perihepatitis
PID causes salpingitis and cervicitis
What’s the gold standard method to diagnose Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia? ; What’s tx for this?
Colposcopy (even if they’re pregnant! - DO IT) ; Cervical Conization (via cold knife conization or loop electrosurgical excision procedure)

conization inevitably –> short cervix and cervical stenosis due to scar tissue
What is Asherman syndrome
INTRAUTERINE ADHESIONS (could be from infxn or uterine surgery)
this can cause 2° Amenorrhea (normal ovulation and hormone levels but mechanical amenorrhea)

CP for [Bartholin gland Duct] cyst-4
_________________
What causes this?
- 4 or 8 o’clock position - base of labium majora
- egg shaped
- CYSTIC mass
- nonpainful
_________________
[Bartholin gland Duct] obstruction
can develop into abscess which presents with fluctuance

Describe Gartner duct cyst
_________________
Where do they come from?
single or multiple submucosal cyst on the lateral aspects of the upper ANT vagina
_________________
incomplete regression of Wolffian duct

Tx for
asymptomatic Bartholin duct cyst
_________________
symptomatic Bartholin duct cyst? -2

OBSERVATION if asx since it will spontaneously drain :-)
_________________
If symptoms are present –> Incision and Drainage f/b word catheter ⬇︎ recurrence
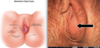
What would you expect symptom presentation for this to be?
_________________
What would you expect pelvic US to reveal?

Mature dermoid cystic teratoma of ovary
mostly asx but sometimes with long standing lower abd/pelvic pain
_________________
hyperechoic ovarian cyst with calcifications(from teeth and bone)

What are the 4 CA associated with Lynch Syndrome
- proximal Colorectal
- Ovarian
- Endometrial
- Skin
Germline mutation in mismatch repair protein
Mngmt for [Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma (ovarian CA)]- 2 steps
1st: XLap to remove pelvic mass, dissect pelvic and paraAortic lymph nodes, inspect entire abd cavity
2nd: Platinum based Chemotherapy
* this comes from ovarian, tubal or peritoneal abnormal proliferation*
What is Choriocarcinoma?
_________________
What other organ does it involve?
aggressive form of [gestational trophoblastic neoplasia]
_________________
metastasizes to LUNGS –> cp/dyspnea/hemoptysis
When does [GTNChoriocarcinoma] occur?
Choriocarcinoma is an aggresive subtype of GTN
occurs after ANY TYPE OF PREGNANCY
Choriocarcinoma is an aggresive subtype of GTN
🔎GTN = [Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia]
BRCA mutation is associated with Breast and Ovarian CA(Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma)
How can pts reduce their risk of developing [Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma]?-5
- BL Salpingo-Oophorectomy
- OCP (only ⬇︎ovarian CA but actually ⬆︎breast CA risk)
- 1st gestation < 30 yo
- Breastfeeding
- Tubal ligation
Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma comes from Ovarian, Tubal or Peritoneal abnormal proliferation
What is the most common complication of an untreated [Mature dermoid cystic teratoma of ovary]?

OVARIAN ISCHEMIA 2/2 TORSION
mass on the ovary –> ⬆︎risk for torsion around its support ligaments which contain ovarian blood supply
It is NOT common for [Mature dermoid cystic teratoma of ovary] to rupture

Pt has just been hospitalized for PID
Now that she’s hospitalized, what are the inpatient abx options for PID?-3
Inpatient:
- CeFOXitin IV + Doxy PO
- Cefotetan IV + Doxy PO
- [Clindamycin IV + Gentamicin IV]
Remember: PID is actually POLYmicrobial

What is the outpatient abx regimen for treating PID (2)
IMCefTriaxone
+
PODoxy
make sure these pts can tolerate and comply with PO abx
What are the risk factors for Cervical CA? - 6
- Smoking (impairs immunity)
- STI hx
- HPV 16/18(early/frequent sex)
- ImmunoCompro
- [VaginalSQC CA] hx(Vaginal SQC CA) and (Cervical CA) share SAME RISK FACTORS
- Vulvar CA hx
(Vaginal SQC CA) and (Cervical CA) share SAME RISK FACTORS
What are the risk factors for Toxic Shock Syndrome - 3
organisms = staphA and GASP
- Tampons
- [Sinus/Nasal Surgery]
- [Skin lesions or Burns]
CP for Toxic Shock Syndrome - 5
organisms = Staph A and GASP
- Generalized “sunburn” macular rash INVOLVING palms & soles
- hypOtension
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea

[CAGS -Condyloma Acuminata Genital Skinwarts] are caused by _____ & _____.
Describe its appearance - 2
HPV 6 & 11
Could Either be:
1.multiple skin-colored exophytic(cauliflower-like) lesions +/- friability
OR
2.multiple skin colored smooth sessile(broad & flat) papules +/- friability

Condyloma Lata is caused by ⬜ .
_________________
How would you describe these lesions?-2
Treponema Pallidum **SECONDARY** syphilis
1. **FLAT**
2. **VELVETY**
* * *
“**CLTS** get *syph*!”
[**C**<sub>ondyloma</sub> **L**<sub>ata </sub>**T**<sub>reponema</sub>P<sub>allidum </sub>**S**<sub>yphilis</sub>]
Which hormone prepares the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg?
Progesterone Prepares endometrium via decidualization
Which hormone induces prolactin production during pregnancy?
postpartum DROP ofEstrogen

Which hormone is responsible for myometrium relaxation during pregnancy?
Progesterone
How should pts with PCOS go about restoring ovulatory cycles 1st?
What’s the next 2 options if that doesn’t work?
1st: WEIGHT LOSS!
2nd:[Clomiphene citrate (GnRH🟢)]
3rd: so_k
PCOS Tx = [*Wt loss →soCk]

Why do women who’ve recently delivered and are breastfeeding have no menstrual cycles?
Elevated Prolactin (responsible for mammogenesis and galactogenesis) inhibits GnRH release –> anovulation and amenorrhea for ≤ 6 months

after 6 months, even with breastfeeding women will start to ovulate again and even before then, this is not a reliable form of contraception
Lichen Sclerosus and Atrophic Vaginitis can present similarly
What is the major distinguishing feature?
Both have thin & pale tissue
Lichen Sclerosus does NOT affect the vagina
Atrophic Vaginitis affects both and can be a result of menopause (2/2 natural, chemotherapy, radiation, surgical or lack of estrogen replacement therapy)
Describe the appearance of Lichen Planus
Ulcerated Glazed Erythematous Vulva

Who should be the only demographics to receive BRCA/HER2 testing - 3
- Women with Breast CA < 50 yo
- Women with Ovarian CA at any age
- Women with first degree relatives with #1 or #2
CP of ovarian CA - 3
- early satiety (from ascities)
- abd/pelvic pressure (from ascities)
- GI sx (constipation/diarrhea/bloating/anorexia) - (from ascities)
What is the most common pelvic tumor in women?
Leiomyomata uterine fibroids

Submucosal and Pedunculated are the worst!
[T or F] Posterior Cul-De-Sac fluid accumulation in a pregnant woman is an abnormal finding
FALSE

(this is a normal finding for preggos along with corpus luteum ovarian cyst UNLESS IT’S IN THE SETTING OF ECTOPIC. THEN IT MEANS HEMOPERITONEUM FROM RUPTURE OR OVARIAN CYST RUPTURE)
DDx for Free fluid in the pelvis of a woman - 3
- Normal pregnancy change
- Ruptured Ectopic –> hemoperitoneum
- Ruptured Ovarian cyst

[T or F] Combined OCPs ⬆︎ risk for Endometrial CA ; Explain
FALSE ; Combined OCPs ⬇︎risk for Endometrial CA because the progestin differentiates endometrial cells
[T or F] Combined OCPs ⬇︎ risk for Ovarian CA ; Explain
TRUE ; Combined OCPs ⬇︎risk for Ovarian CA because it suppresses chronic ovulation which causes chronic damage to surface
Why are Combined OCPs contraindicated in pts with [Migraine with aura] hx?
There is a rare but serious RISK OF STROKE with use of combined OCs in women with migraine/HA hx, especially if they smoke or are > 35 yo
What’s the first steps in w/u for Bilateral breast discharge with no lumps, LAD or nipple changes?-4 ; Why?
Hyperprolactinemia is most common cause of galactorrea
- PROLACTIN levels - Prolactinoma could –> Hyperprolactinemia
- TSH levels - hypOthyroidism could –> ⬆︎TRH & TSH –> Hyperprolactinemia since TRH stimuales prolactin release
- PREGNANCY test - Pregnancy could –> Hyperprolactinemia since TSH shares same α-subunit Is this as bHCG
- MED REVIEW - D2🟥Antidepressants/Opioids all –> Hyperprolactinemia

When should the HPV 3 dose vaccine be given to females?
Between 11-26 yo regardless of anything
*they receive 3 doses spread out*
**this INCLUDES women with genital warts, positive HPV and abnormal cytology hx!!!!**
When should the HPV 3 dose vaccine be given to males?
Between 9-21 (or 26 if HIV+ and/or gay) yo
*they receive 3 doses spread out*
In a +bHCG pt who comes in with RLQ pain, vaginal bleeding and a negative Transvaginal US
why would we wait and repeat the bHCG & transvaginal US in 2 days if at the time it was already 1000
Intrauterine pregnancy is not detectable via transvaginal US until 1500-2000 bHCG. There should be SOMETHING on transvaginal US at that time (whether normal pregnancy or ectopic)

βhCG levels have to be ____ for pregnancy to be detected via transvaginal US, and usually _____ when transabdominal US can finally detect it
What are βhCG levels during:
A: Ectopic Preg/Miscarriage
B: Molar Pregnancy
βhCG levels have to be 1500-2000 for conclusive pregnancy detection via transvaginal US and usually >5000 for transABDominal US to finally detect it
A: Ectopic Preg/Miscarriage = low βhCG
B: Molar Pregnancy = > 100,000 βhCG!!!
βhCG should double every 2 days in normal pregnancy for first 7 weeks

How does Obesity commonly cause amenorrhea?
Obesity –> anovulation without affecting LH/FSH levels which–> Amenorrhea
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) are used for _______(indications)-3 ; What are the main side effects of SERMs? - 3
1.[Breast CA px]
2.[Breast CA tx adjuvant (Tamoxifen)]
3.[Postmenopausal Osteoporosis (Raloxifene)]
SIDE EFFECTS
A: Hot Flashes
B: Venous Thromboembolism (all estrogen agonist ⬆︎resistance to protein C)
C: Endometrial Hyperplasia/ADC
note: SERMs not only modulate estrogen receptors but they actually block estrogen binding competitively
🄰 What would you expect the following hormones (prior to hypothalamus shut down) to be in PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome)?
GnRH
FSH
Estrogen
🄱 . Explain each
PCOS= [⇪GnRH] , [nml FSH], [⇪⇪⇪Estrogen]

PCOS (initially)=
🍟[⇪GnRH] (from [DM/ObesityHYPERinsulinemia] stimulating ([HYPER GnRH⼀LHwsx] …
_________________
🍟[nml FSH] …(whilst FSH secretion stays normal/unchanged)
_________________
🍟[⇪Estrogen] ([HYPER GnRH⼀LHwsx ] → ⇪ ⇪HYPERandrogen secretion from Ovarian Theca → converted into ⇪ ⇪ ⇪HYPEREstrone (HYPEREstrone eventually → GnRH hypothalamus shut down via neg feedback)
___________________________x____________________________________
{🔎wsx = Weighted secretion = [(LH>FSH) or (FSH>LH) ]secretion}
[🔎BSX = BALANCED SECRETION = (LH = FSH)]secretion*
What would you expect the following hormones to be in Hypothalamic hypogonadism (functional hypothalamic amenorrhea)?
GnRH
FSH
Estrogen

What would you expect the following hormones to be in [Primary Ovarian Insufficiency]?
GnRH
FSH
Estrogen
POI main sx = [amenorrhea ≤40 yo(unless POI cause = Menopause)]

How does estrogen deficiency cause stress AND URGE incontinence? -5
▶⬇︎estrogen –> [ atrophyVulvoVagina
▶and atrophy[BUM(Bladder trigone/ URETHRA/Muscles of PelvicFloor)] –>
[atrophyU → Urethral closure –> ⬆︎bladder pressure]→ URGEi
[(atrophyM → ⬇︎Urethral compliance) →UTI] → URGEi (rule this out first!)
[atrophyM → ⬇︎Urethral compliance]→ STRESSi
“ estrogen maintains her VBUM”
What are the causes of Primary Ovarian Insufficiency? - 8
- Menopause
- [Chemotherapy - targets rapidly dividing granulosa/theca cells]can cause <u>Premature </u>POI
- [Radiation - targets rapidly dividing granulosa/theca cells]can cause <u>Premature </u>POI
- oophorectomy
- Turner syndrome
- fragile X syndrome
- hypOthyroidism
- adrenal insufficiency

List the numerous contraindications to Combined OCPs - 11
- Migraine with aura
- Smokes ≥15 cig/day and ≥35 yo
- HTN ≥160/100
- Heart disease
- DM with end organ damage
- Breast CA (estrogen AND progesterone may have proliferative effects on breast tissue)
- Liver Cirrhosis/CA
- Thromboembolism hx
- Prolonged immobilization
- Antiphospholipid syndrome hx
- ≤3 wks postpartum
What is [PGVD -(Penetration Genitopelvic Vaginismus Disorder)]
_________________
tx?-2
pain with any vaginal penetration (penis, tampon, gyne exams)
_________________
tx = Vaginal Dilators, Kegel exercises
this is AKA Vaginismus
In pts with Pudendal neuralgia, where do they have superficial pain? - 3
- Vulva
- Perineum
- Rectum
these are the pudendal n distribution areas
What are the causes of Hydrosalpinx (fluid accumulation in fallopian tubes) - 2
- Adhesions (PID, surgery)
- Tubal ligation
What is the 1st line tx for Postmenopausal hot flashes? ; What can you use if that doesn’t work?
WEIGHT LOSS ; Combined OCPs
HEY! HRT IS NO LONGER RECOMMENDED FOR [CAD, DEMENTIA OR OSTEOPOROSIS POSTMENOPAUSE PX]!!!!!!!
How does the Levonorgestrel progestin IUD work as a contraceptive? - 3
- thickens cervical mucus
- thins the endometrium when present outside of pregnancy which –> implantation impairment AND ⬇︎menstrual bleeding
- prevents withdrawal bleeding altogether –> amenorrhea
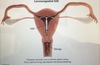
What is the main side effect of Copper IUD
Menorrhagia
What is the main side effect of Medroxyprogesterone injections
Weight Gain
Pelvic US reveals
Hyperechoic ovarian cyst with calcifications
Dx?
[Mature dermoid cystic teratoma of ovary]

Pelvic US reveals
Homogenous cystic ovarian mass
Dx?
[Endometrioma (Endometriosis of ovary)]

Ovarian hyperThecosis is usually diagnosed in ____[pre/post] menopausal women
What is it?
POSTmenopausal;
⬆︎Theca cell activity –>
⬆︎androgen –> virilization,
and ⬆︎insulin resistance → hyperglycemia, acanthosis nigricans
this does NOT affect LH and FSH and ovaries are enlarged but not cystic
DDx for Menorrhagia (abnormal uterine bleeding) - 10
“Bleed Uteri in the [Coagulopathic COVE PLACE]!
Coagulopathic
_________________
Cervical CA
Ovulatory dfxn
Vaginal CA
[Endometrial hyperplasia/ADC (get bx if risk factors present)]
_________________
Pregnancy
Leiomyomata uterine fibroids
Adenomyosis
Copper IUD
Endometrial Polyps
Pregnancy, Structural, NonStructural, Meds
What does [Fat necrosis of breast] show on mammography -2
[oil cyst +/- calcifications ]
that may initially appear to be malignant(until malignancy r/o by bx revealing fat globules and foamy macrophages)

What does [Fat necrosis of breast] show on core biopsy - 2
fat globules and foamy macrophages

When is MRI of the breast indicated? - 5
- [breast CA BRCA carrier]
- [breast CA BRCA carrier … in 1st degree relative]
- [breast CA Dz assessment]
- [breast CA Tx assessment]
- breast/chest radiation between 10-30 yo
In a woman with normal menstrual cycles, what is usually the cause of infertility if she is > 35 yo?
diminished Ovarian reserve
oocytes are of finite number and quality
What is an ovarian Fibrothecoma
sex cord-stromal tumor that secretes both but Estrogen > testosterone
[inclusion cyst of Vulva] usually result because of ⬜, whereas [epidermal cyst of Vulva] result from ⬜
injury local→ [inclusion cyst of Vulva]
_________________
exit duct of sebaceous gland obstructed→ [epidermal cyst of Vulva]
of Vulva
What are 4 major s/s of Pregnancy
FAWN
- Fatigue +/- insomnia
- Amenorrhea
- Weight gain
- NV
these sx can overlap with Perimenopausal sx so be careful not to quickly dismiss an older pt who’s actually pregnant!
Tx for Condyloma Acuminata - 5
- Trichloroacetic acid
- [Cryotherapy c liquid nitrogen or cryopr obe]
- [Imiquimod 5% cream {pt application}]
- [Podophyllum resin] Pregnancy C❌D
- [PodoFilox 0.5% gel{pt application}]Pregnancy C❌D
[(HPV6 & HPV11)CAGS-Condyloma Acuminata Genital Skinwarts]

[T or F] It is ok to perform a Colposcopy in a pregnant woman whose pap recently resulted abnormal
TRUE (Colposcopy is indicated when pap is abnormal even if pt is pregnant! - DO IT) ; So is Cervical bx if a lesion has high-grade features

Endocervical curettage is contraindicated
[T or F] It is ok to perform a Cervical biopsy on a pregnant woman whose pap recently resulted abnormal
TRUE - after Colposcopy, if lesion has high-grade features
Endocervical curettage is contraindicated
[Atypical Glandular Cells] on a Pap may be due to either [____ CA] OR [____ CA]
What should you do to work this up? - 3
Endometrial ; [cervical(from Endometrial glands migrating to cervical area)]
perform…
- Colposcopy(evaluates Ectocervix)
- Endocervical curettage(evaluates endocervix)
- Endometrial biopsy(evaluates Endometrium)
- With AGC on Pap you need to evaluate Ectocervix, endocervix and Endometrium*
What is Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
Ovulation inducing medications –> excessive follicle development –> ovarian enlargement, ascities, SOB and abd pain
Secondary Amenorrhea occurs when women stop having menses for ≥6 months
What is the full workup for Secondary Amenorrhea?
Evaluate FLAT PiG for 2° Amenorrhea

In a pt with hypothyroidism, why do you need to _____[decrease/increase] her [levothyroxine T4] when she becomes pregnant? -3
INCREASE (with monitoring of T4);
- Estrogen from pregnancy usually ⬆︎Thyroid binding globulin AND bHCG stimulates thyroid –> ⬆︎total thyroid hormone in mom for the baby.
- BUT hypOthyroid Moms won’t produce adequate thyroid hormone and this can –> congenital hypOthyroidism.
- So give hypOthyroid Moms more [Levothyroxine T4] when pregnant
Levothyroxine = T4 / Liothyronine = T3
A friable cervix is one that easily _____ when touched. This is usually a sign of cervicitis secondary to _____
bleeds “crumbles” ; [N. Gonorrhea PID]
bHCG shares an ___subunit with which other 3 hormones?
ALPHA;
- FSH
- LH
- TSH–> Pregnant woman naturally have more T3 and T4 (also because Estrogen ⬆︎thyroid binding globulin which ⬆︎total thyroid levels) - these pts are still clinically euthyroid
How do you confirm a female pt has urinary retention?
_________________
male?
urinary catheterization [≥150ccFEMALE] [≥50ccmale]
Bladder can hold up to 400 cc
Indications for Pessary - 2
- Pelvic organ prolapse
- Stress urinary incontinence
What are risk factors for Osteoporosis? - 9
Bone Mineral Density (T-score) ≥ 2.5 SD BELOW the YAM
- OSTEOPOROTIC FX HX(personal OR family)
- ⬇︎Estrogen (postmenopause)
- LOW BMI (malnutrition/malabsorption)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Poor Ca+ intake (body needs [1000mg/dayPREmenopausal] and [1200 mg/dayPOSTmenopausal])
- Smoking
- EtOH abuse
- White race
- CTS
What are the major risk factors for PreMenstrual Syndrome? - 5
- FAMILY HX OF PMS
- [Pyridoxine VitaminB6] deficiency
- Ca+ deficiency
- Mg deficiency
- Age > 30
Dx for [Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea]?
⬇︎FSH

Which substance actually exacerbates the cyclical bilateral pain associated with Fibrocystic changes of breast?
Caffeine
Raloxifene MOA
Indications-2
[SERM-(Selective Estrogen R Modulator)]
- Breast CA
- Osteoporosis
* * *
* SE = Venous Thromboembolism*
Why do [pt < 21 yo] NOT require PAP Smear Cervical CA screening?
Immune System in patients < 21yo clears HPV on its own
CP for TTP -3
________________
When does this occur during pregnancy?
“preggos can always get the TTPTAN!”
- Thrombocytopenia ➜ Petechial Rash
- Anemia hemolytic
- Neurologic ∆
________________
In pregnancy can occur [ANYTIME (even Postpartum)]
What’s Major difference between TTP and HELLP during pregnancy?
TTPTAN = can occur anytime from [1st trimester <-thru-> PostPartum]
vs
HELLP (and [Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy]) = [3rd Trimester 28-42WG] ONLY
CP for Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy - 3
________________
When does this occur?
[3rd trimester 28-42WG]
- ⬆︎LFTs
- hypOglycemia
- NV
Gestational sacs normally implant in the _____
upper uterine fundus

Gestational sacs normally implant in the _____
What is the “typical” triad for Ectopic Pregnancy? - 3
upper uterine fundus ;
i\⊕UPTVAL had an ectopic the other day!
- Vaginal bleeding/spotting
- Adnexal Tenderness (if implanted in tube)
- Lower abd pain
dx = transVaginal US / tx = MTX or [surgery if severe]
(in the setting of ⊕UPT)

Preeclampsia is typically diagnosed ____ weeks gestation.
What is the exception to the rule?
GOE20WG! ; Preeclampsia as a complication of Hydatidiform mole (which may occur < 20WG)
- PreEclampsia –> SEVERE PreEclampsia –> HELLP and at anytime, Eclampsia is possible*
- ________________*
Tx -2
- STAT DELIVERY
- MgIV
PostMenopause [Hormone Replacement Therapy] ⇪ DVT/PE risk
________________
What are 2 alternative tx for Postmenopause sx?
- SSRI
- SNRI
________________
50-70% f endorse sx reduction
how long after discontinuing contraception does it take for ovulation to return?
LOE1month
What’s the FIRST step in working up Infertility?
SEMEN ANALYSIS
definition of
Infertility ?
[GOE12mo timely unprotected intercourse] ➜ still no conception
Endometriosis
________________
physical exam findings -2
- immobile uterus
- [pelvic nodules (w/chronic pelvic pain)]
primary ovarian insufficiency
main presenting sx
[secondary amenorrhea ≤40 yo]
(for all POI causes <u>except Menopause)</u>

Source of Estrogens (3)
- Ovaries
- Liver (from Estriol)
- Peripheral tissue (from androgens)
Source of Progestins (4)
- Ovaries
- Testis
- Adrenal Gland
- Placenta during pregnancy
comes from Cholesterol
List the natural estrogens (3). Which is most estrogenic?
- Estrone (E1)
- Estradiol (E2) = MOST ESTROGENIC
- Estriol (E3) = not very active

List the [synthetic steroidal estrogens] (3)
- Ethinyl estradiol
- Mestranol
- Quinestrol
Aromatase MOA (2)
Converts…
- Androstenedione –> e1e1 can transform to [eE3 estriol] (think: A is 1st letter)
_________________ - Testosterone –> E2 (like :”test-es”)
only can e1 possibly later convert to Ee3

Ee3 = E3 = EsTriol
How do Steroid Hormones molecularly work?
Hormone diffuses into target cell and binds to receptor. [Hormone-receptor complex dimerizes in nucleus] and binds to specific DNA regions (activators/repressors) –> Gene tx
Describe the Name and Hormone levels during the Menstrual cycle
A: Days 1-14
B: Day 14
C: Days 14-28
A: [Follicular Proliferative Phase] = low E2 with INC FSH and LH receptors on Dominant follicle
B: Ovulation (FSH & LH peak with LH surge)
C: [Luteal Secretory Phase]= Progesterone INC

Reproductive actions of Estrogen (5)
- Female Secondary Sex characteristics
- Puberty & Adolescent changes (epiphyseal closure)
- Menstrual cycle (gonadotropin secretion)
- Uterine Endometrial proliferation
- [Thin Cervical Mucus] secretion for sperm facilitation
Metabolic actions of Estrogen (7)
- [INC HDL] :-)
- INC Bile saturation into cholesterol –> DEC cholelithiasis
- Stimulates Renin substrate release –> INC BP
- INC Clotting
- DEC Bone Resorption
- DEC LDL
- DEC free thyroid hormone (via INC TBG)

CNS actions of Estrogen (2)
- Positive mood, cognition, memory
- Protects against Neurodegenerative DO
Estrogen Clinical Indication (5)
“We Use Estrogen for OPRAH”
- OCP component (ethinyl estradiol)
- [HRT Menopausal (Premarin)]
- [Perimenopause/Oligomenorrhea/Dysmenorrhea]
- [Really behind (♀delayed Puberty | ♀hypOgonadism)]
- Acne (Estrostep)
Estrogens SE (6)
Beware of Estrogen’s CAVE
- Breast tenderness
- Venous Thrombosis
- Constitutional (HA/NV)
- Edema
- [Endometrial Hyperplasia/Carcinoma (Estrogen when taken alone)]
- Adenocarcinoma in offspring of pts who’ve taken DES
SERM = ____. What is its MOA (2)
SERM = Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator
- Estrogen BLOCKER in some tissues
- Estrogen Agonist in other tissues
Tamoxifen Indication
Pre AND POSTMenopausal Breast CA that are (ER/PR +). Serves as [Adjuvant Hormonal Therapy]
Tamoxifen Contraindications (2)
- DVT/PE Hx
- Pregnancy
Drug class of Clomiphene
SERM
Clomiphene Indication
Female Infertility 2° to ovulation DO

Clomiphene MOA (2)
SERM”[❌ at TOP] … [tickles down below]”
- Estrogen Blocker @ hypothalamus & pitutiary–> INC LH & FSH
- Partial agonist @ ovaries

- [hypOthalamus& ANT PitEstrogen🟥] →”tricks” hypOthalamus into thinking Estrogen is low → ⇪ LH & FSH [used for IVF]
- OVARY [Estrogen PARTIAL🟢]
Raloxifene Indication (2)
Osteoporosis & [Postmenopausal Breast CA Px] only
Raloxifene MOA (2)
- Estrogen R Agonist @ Bone
- Estrogen R BLOCKER @ Uterus & Breast
Name the [Aromatase inhibitors] (4)
Anastrozole
Letrozole
Exemestane - (Covalently Irreversible)
Formestane - (Covalently Irreversible)
[Aromatase inhibitors] indication (2)
[ER⊕ Breast CA (Tx and Px)]

[Aromatase inhbitors] SE (8)
“Don’t FETCH Vile aRomas”
- [Fractures & Arthralgia]
- Thrombophlebitis
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Vaginal Bleeding (profuse)
- Edema-Peripheral
- Constitutional (HA/Nausea)
- Dyspnea
- Rash
Physiological actions of Progesterone (7)
- Menstrual cycle: Negative feedback during [Luteal secretory phase]
- Endometrial transformation –> [Luteal Secretory phase]
- Reverts [thin cervical mucus] back to [THICK cervical mucus] which inhibits any further sperm transport
- INC body temp at Ovulation
- Maintains Pregnancy: Inhibits Uterine contraction and suppresses immune system
- Mammogenesis
- Blocks and enhances actions of estrogens

Progestin Indication (6)
- OCP alone or [OCP componenent]
- Menopausal Endometrial Protection (medroxyprogesterone)
- Oligomenorrhea
- Amenorrhea
- PCOS
- Endometriosis
Name the [Progestin only OCP] (5)
- Levonorgestrel
- Norgestrel
- Norethindrone
- Medroxyprogesterone (injectable)
- Etonogestrel (Implant)

How do [Progestin only OCP] perform their action (4)
Alters …
- GnRH pulsation and DEC ANT Pit responsiveness to GnRH
- Tubal Peristalsis
- Cervical Mucus Secretions
- Endometrial Receptiveness

[Progestin only OCP] SE (3)
- Irregular periods
- Breast tenderness
- Constitutional (HA / Nausea / Dizziness)

Name the [Progestin only OCP] and its dosage given for [spotting, irregular periods, oligomenorrhea]
Medroxyprogesterone given via injection q3 mo.

Which [Progestin only OCP] is used for Emergency contraception (morning after)
Levonorgestrel (Blocks LH surge and impairs surge transport)

[Combined OCP] MOA (2)
- Negative feedback on Gonadotropin secretion –> No ovulation
- Progestin thickens Cervical mucus

[Combination OCP] SE (9)
BirthControl Gives Ladies A Home Without Terrible, Bawling Babies
- Breast Tenderness (don’t use in Breast CA)
- Gallbladder Dz
- Liver Neoplasm
- Abnormal Menstruation
- HTN
- Weight change
- Thromboembolism
- Bloating
- Breakthrough Bleeding
Why is estrogen always coadministered with progestin in [women with uterus]
Estrogen, given alone, –>Endometrial CA
MiFepristone
[MOA] -2
- [Progesterone R Blocker] and
- [Glucocorticoid R blocker at high dose]

MiFepristone
Indication (2)
- Abortion (only with pregnancy ≤49 days)
- Refractory Cushing’s Syndrome

Name and Describe which drug MiFePriStone is co-adminstered with for [Abortions LOE49d]
mi(S)oPROStol = (S)imulates PROStaglandin = [PROStaglandin analogue] that (S)Timulates uTerus ➜ [uTerus contraction w/ NVD]
“(S)imulates PROStaglandin to (S)queeze the uTerus “

Dosage Regimen for Emergency Contraceptive
1st: Within 72 hours of intercourse take 2 T [0.75 mg of levonorgestrel]
2nd: Wait 12 Hours
3rd: Repeat Step 1

Menopause Dx (2)
1 year since last menses + [FSH > 25]
Menopause sx come from ___ deficiency and includes what 4 main EARLY sx?
Menopause sx come from Estrogen deficiency:
- Mood Changes (95%) (HRT Tx indicated)
- Fatigue (95%)
- Vasomotor instability –> Hot Flashes (70%) (HRT Tx indicated)
- Insomnia (55%)



