4⼀PULMONARY/ALLERGY/ENT Flashcards
What would you expect PFT for a patient with Asthma to be?
NORMAL PFT
but
[FEV1⬇︎ ≥20% (on methacholine challenge)]
“Either [BD → ⇪EVC] or [MC → ⬇︎EV]”

What are the recommendations regarding Influenza vaccine and [patients with “egg” allergy] ? (3)
pt s/p…
- [urticarial (egg rxn)]? → give [IM dead influenza vaccine]
- [SEVERE (egg rxn)]? → give [IM dead influenza vaccine] in healthcare setting under supervision
- [SEVERE (VACCINE rxn)]? → [INFLUENZA VACCINE❌CONTRAINDICATED]

Management for Asthma Exacerbation (3)

PIR

1st: [PAWSS respiratory failure?]
2nd: [Initial tx(SMC vs Mechanical Ventilation)
3rd: [Reassess q2-4h]
Whats the best medication for Awake Intubation induction?
_________________
why? (6)
Ketamine
_________________
“has a BAD RUP”
provides [BronchoDilation | Analgesia | Dissociative amnesia]
+
maintains [Respiratory drive | Upper airway tone | Protective reflex]
How is smoking/secondhand smoking a/w Chronic Sinusitis?
_________________
Name 3 other major causes of Chronic Sinusitis
cigarette smoke damage cilia ➜ ⬇︎mucus flow throughout the sinus ➜ chronic sinusitis
_________________
poorly treated acute sinusitis / [structural abnormality (nasal septum/palate)] / rhinitis
SMHHsx = [Snotty purulent nasal discharge/Maxillary facial pain/HA/Hot>39C]
Most epistaxis originate from the ⬜ in the ⬜
How do you manage this? -4
[Kisselbach Plexus] ; [ANTERIOR Nasal Septum]
________________
- try each tx until epistaxis resolved*
1st: Nostril pinching
2nd: [Topical Vasoconstrictor]
3rd: [Cautery (silver nitrate vs electrical)]
4th: [ANT nasal packing with bacitracin-sponge]

Tx for [Bacterial Aspiration PNA] -3
look for infiltrate in dependent portion of the lung
βMα
_________________
[CefTriaxone + Azithromycin](community acquired PNA)
+
[anaerobic abx if empyema or lung abscess present]

treatment regimen for GASP? -2
________________
What are the alternatives if a patient is allergic? -3
________________
Why is it important to treat GASP?
GASP = [Group A Strep Pyogenes]
[PO PCN VK]10d or [PO amoxicillin]10d
________________
allergy mild = Cephalosporin
allergy anaphylaxis = Azithromycin | Clindamycin
________________
prevention of Rheumatic Fever

What’s the most common cause of hemoptysis?
[Bronchial infxns (Bronchitis / Bronchiectasis)]

What are the most common organisms to cause Sinus infection (Rhinosinusitis)? - 3
________________
Tx?
Strep Pneumo > HFlu nontypeable > moraxella
________________
Tx = Amoxicillin/clavulanate
[Haemophilus Influenzae] Tx (5)
HaEMOPhilus
[FAT MC]
[Fluroquinolone vs. Ampicillin vs. Tetracycline vs. Macrolide(NOT ERYTHRO) vs. Ceftriaxone]
🄰. [Daily Cough with mucopurulent sputum and [Recurrent multiLobar PNA] likely indicates what dx?
________________
🄱 . How does this disease cause hemoptysis?
_________________
🄲. Explain why [Recurrent single lobe PNA] has a different workup
🄰 . Bronchiectasis
________________
🄱.
💥[multilobar poor ciliary clearance(2/2 Kartagener | CF | ABPA, etc) ] → *multilobar *bronchial wall infection ➜
💥[inflammatory bronchial wall thickening and permanent airway dilation]+ inflammation predisposes to repeat infections
💥➜ more bronchial wall thickening and dilation= [cycle of bronchial airway dilation + bronchial wall thickening+ bronchial wall inflammation]
💥➜chronic [bronchial wall inflammation] ➜ rupture of [bronchial wall superficial blood vessels] ➜ hemoptysis

c.
Focal bronchiectasis (involvement of single lobe/segment only) indicates airway blockage (malignancy/foreign body) ⼀ = Dx/Tx = FLEX bronchoscopy (since HRCT may not reveal/remove the obstructing lesion)
so…
🧠pts with [persistent Recurrent PNA] in:
[single lobe → 🔬FLEX BRONCHOSCOPY]
vs
[Multi lobe → 🔬HRCT]
Name the Causes of ARDS (10)
ARDS
A= Aspiration vs. [Acute Pancreatitis] vs. [Air Fluid Embolus (amniotic)]
R= Radiation
D= Drugs vs. DIC vs. Drowning
S= Sepsis vs. Smoking vs. Shock
ARDS is a restrictive pattern that –> [⬇︎Lung Compliance], [Group 3Pulm HTN] and impaired gas exchange
What are the 3 criteria for COPD Exacerbation
Co-P-D
[Cough ⇪ with SPUTUM ∆]
[Pulmonic WHEEZING BL]
[Dyspnea ( ➜respiratory acidosis)]
Out of the Tx for COPD Exacerbation
Which improves survival?
________________
Which ⬇︎future events?
“I’m having COPD Exacerbation! Give me DOPA! (but not really)”
[O2 PRN via BiPAP (goal: 90-94% O2 Sat)]
________________
Abx (Azithro-⬇︎future events or Levoflox or Doxy)
Tx for COPD Exacerbation-4
“I’m having COPD Exacerbation! Give me DOPA! (but not really)”
- Duoneb (albuterol + ipratropium)
- O2 PRN via BiPAP (goal: 90-94% O2 Sat)
- [Prednisone 40 mg qd x 5]
- Abx (Azithro-⬇︎future events or Levoflox or Doxy)
how is [PPSV 23 (Pneumococcal PolySaccharide Vaccine)] used in peds? (3)
PPSV23 in kids is used for peds at high risk for pneumococcal disease
- [Sickle Cell Anemia\Asplenia]
- Cardiac ❌
- cochlear implants
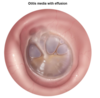
diagnostic criteria for Acute Otitis Media -2
________________
Which organisms cause AOM? -3
BULGING TM + [Middle Ear effusion with TM inflammation (fever/otalgia/erythema)]
________________
STREP PNEUMO = [HFLU NONTYPEABLE**] >> moraxella
________________
** also causes otitis conjunctivitis syndrome

Prophylactic abx tx and tympanostomy tube ⬇︎ [recurrent AOM],
and are recommended for which 4 patient groups?
[≥ 3 AOM in 6 mo] or
[≥4 AOM in 12 mo] or
[craniofacial DO] or
[neurodevelopmental DO = speech/hearing ❌]

How long does it take Malignant [Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodules] to double in size?
________________
How does this affect diagnostics?

1 month - 1 year

________________
Pt with stable Pulm Nodule > 1 year = NO CA!
Pt with hemoptysis comes in with [Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodule] on CXR
What are the 3 [preDiagnostic Mgmt] steps for SPN?

A: LOCATE PREVIOUS CXR ≥ 1y old!
_________________
b: If SPN unchanged = NO CA
C: If [(SPN ∆) OR (NO PRIOR CXR)] ➜ [Diagnostic Mgmt] (image)

Coin lesions = 80% chance malignancy
List 5 characteristics of [solitary pulmonary coin nodules] that help to determine their Malignancy & workup

Smoking hx | Location | Age | Border || size
-Smoking Hx
-Location: Endobronchial proximal extension/Local invasion/Satellite Nodules
-Age
-Border: : Spiculated / Retracted from surrounding tissue / irregular
-size: {≥8mm}

After the [SPN 3-step prediagnostic mgmt]
How do you workup [Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodule]?

Round, < 3mm, no LAD

[Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodule] DDx -5

- CA(hamartoma/metastasis/primary)
- Infectious [granulomatous/fungal (blasto,histo)]
- Pneumoconiosis
- Vasculitis
- Scar

How do you treat ANAPHYLAXIS ? -8
EPIC ➜ chag
[EPINEPHRINE {[IM ≤ 3x] ➜ [IVgtt if severe]}]
[Proair Albuterol + O2]
[INTUBATION ⼀early** for upper airway obstruction]
[Crystalloid IV/Trendelenburg for hypOtension]
________________
CTS / [Histamine1/2 R blockers] / [Admission to Hospital if severe|persistent]/ [Glucagon if on BBlocker]

peds epi = [0.01 mg/kg]
epinephrine MOA-2
alpha1🟢 → vasoconstriction
beta2🟢 → bronchoDilation
🟢 = receptor agonist
Acute Otitis Media
initial tx?
[AmoxicillinHD]10d

Recurrent AOM should raise concern for ⬜, and warrants treatment with ⬜
beta-Lactamase producing [Strep Pneumo or HFlu NT] ➜ resistance ; amoxicillin/clavulanic acid

normal AOM tx = [AmoxicillinHD]10d
How do you treat [Acute Otitis Media with PCN allergy]? -2
Azithromycin or Clindamycin
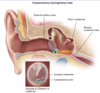
How do you treat [Acute Otitis Media refractory persistent]?
[Tympanostomy with tympanocentesis]
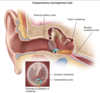
Out of the 3 organisms that cause Acute Otitis Media, which is unique? why?
HFLUnontypeable
________________
can also cause [otitis conjunctivits syndrome] in which purulent conjunctivitis occurs at same time as AOM

Acute Mastoiditis is a complication of ⬜ and is caused by [ ⬜ microbe]
________________
clinical presentation? -2
Acute Otitis Media ; [middle ear infection(with Strep Pneumo) ] spreads to [mastoid air cells]
________________
- AURICLE DISPLACEMENT
- mastoid TTP
tx = [amoxHD]10d
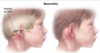
other sx: otalgia, fever
Paradoxical Emboli are a more common cause of ⬜ in young than elderly
_________________
explain etiology of Paradoxical Emboli
stroke
______________
emboli from venous system (DVT) travels thru intracardiac shunt into arterial system ➜ stroke
dx = TTE and bubble study
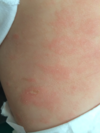
[Eczema Atopic Dermatitis] cp -4
________________
Where do you find this cp in infants? -3
________________
where in Adults/Kids?
“Eczema making you [PPP →P]sx? needs LEGITtx”
________________
{acute [Pink(Erythematous) Patch & Papules] →CHRONIC[ Plaqueswith LICHENIFICATION]}

[infant = face, trunk, extensor surfaces]
________________
[Adults/Kids = flexor surfaces]
[Eczema Atopic Dermatitis] MOD (4)

1) [skin barrier dysfunction]
2) + [Th2 skewed immune response]
3) + INC production of IgE
4) = chronic inflammatory skin disorder
________________
This [Th2 skewed immune response] can be balanced by a [Th1 cytokine profile] built only from EARLY MICROORGANISM EXPOSURE

“Eczema making you [PPP →P]sx? needs LEGITtx“

(fill-in-Blank)

[Eczema Atopic Dermatitis] Tx -5

“Eczema making you [PPP →P]sx? needs LEGITtx”
- [Lifestyle ∆ (avoid hot/dry climate, harsh soaps, harsh detergents)]
- [EmollientsTOP(skin hydration) + antihistaminesPO]
➜
- [GlucocorticoidsTOP (low potent = hydrocortisone / medium = triamcinolone / HIGH = Betamethasone) – contraindicated on face and flexural surfaces]use only in acute exacerbations
- [Inhibitors of CalcineurinTOP {i.e. Tacrolimus} = for face and flexural surfaces]
- [Therapy ⼀phototherapy vs immunosuppressants = SEVERE]
“Eczema making you [PPP →P]sx? needs LEGITtx“
Classic Sx of Sarcoidosis-8
CCuBBeDD
Cardiomyopathy Restrictive
HYPERCalcemia: elevated ACE and 1-25VitD production –> HYPERCalcemia and HYPERCalciuria
uveitis –> Vision loss
Bilateral Hilar LAD! = COMMON = CXR is 1st screening test!
Bell’s Palsy
erythema Nodosum (SubQ Fat lesions)
[Dry cough & Dyspnea]
Diffuse interstitial fibrosis

- Image showing b/l Hilar LAD. Hepatosplenomegaly and generalized LAD also occur*
What is the 1st screening test for Sarcoidosis? Why?
_________________
What is the confirmatory test for Sarcoidosis? (2)
CXR ; [>90% of patients have Bilateral Hilar LAD]
_________________
[Lymph Node Biopsy revealing noncaseating granulomas] –(if no lymph node accessible)–> [Lung biopsy via bronchoscopy]
_________________
CCuBBeDD
Image showing b/l Hilar LAD

Sarcoidosis Etx-2 (Etiology)
[CD4 Helper T] inappropriately respond to environmental triggers + Suppressed TRegs –> Non-Caseating Granulomas in Lung = [Asx vs pulmonary sarcoidosis(give 1 year CTS)] ➜
75% sarcoidosis is self-limited and non-reocurring
Image showing b/l Hilar LAD

[Sarcoidosis: sxCCuBBeDD | txSCAM ]
Sarcoidosis Tx-4
“Sarcoidosis is a SCAM”
[Steroids1y]
Cyclosporine
Azathioprine
MTX
Image showing b/l Hilar LAD

[Sarcoidosis: sxCCuBBeDD | txSCAM ]
Chronic Cough is defined as ⬜
Initial evaluation for Chronic Cough is with ⬜ – and this helps to rule out/in [Obstructive Airway Disease (asthma)]
idiopathic cough > 4 weeks
________________
Pulmonary Function Test Spirometry
Exposure to ⬜ is an important risk factor for Acute Otitis Media
________________
How do you reduce frequency of recurrent Acute Otitis Media -4
smoking
_________________
NO ❌SMOKING
NO ❌DAY CARE
NO ❌ PACIFIER
✅give breastfeeding
[Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria]
MOD
________________
tx -2
[(Spontaneous idiopathic)urticaria episodes] > 6 wks
________________
2nd gen[H1 R blocker]
+
[avoid NSAIDs]
[non-sedating 2nd gen H1 R Blocker] = loratadine / cetirizine
ABPA occurs in patients with ⬜ or ⬜
_________________
clinical features of ABPA? (4)
[ABPA (Allergic BronchoPulmonary Aspergillosis)]
[preexisting asthma] or
[preexisting cystic fibrosis]
with
BACH
- -[Brown sputum cough with fever]*
- [Asthma exacerbations recurrently]
- -[CXR fleeting infiltrates* (transient & different parts of lung)**]
- -[HRCT central bronchiectasis]*
ABPA occurs in patients with ⬜ or ⬜
_________________
MOA?
[ABPA = (Allergic BronchoPulmonary Aspergillosis)]
pts with [preexisting asthma or preexisting cystic fibrosis] may develop
noninvasive colonization of of airways by Aspergillus -→ [EXAGGERATED IgG and IgE mediated response -→ BACH sx
Dx for [ABPA (Allergic BronchoPulmonary Aspergillosis)] -4
- initial = [skin testing for Aspergillus]
- [elevated total IgE]
- [elevated Aspergillus IgE]
- [elevated Aspergillus IgG]
________________
BACH = [Brown sputum cough with fever] [Asthma exacerbation recurrently] [CXR fleeting infiltrates (transient & different parts of lung)] [HRCT central bronchiectasis]
tx for [ABPA (allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis)] -2
[Systemic CTS + itraconazole]
________________
tx = directed at acutely stopping underlying inflammation and reducing Aspergillus burden
Patients s/p smoke inhalation have ⇪ risk for ⬜, and thus warrant low threshold for ⬜ if +signs of airway injury
_________________
For pts s/p smoke inhalation, but [stable with NO signs of airway injury] what’s the alternative initial mgmt?
airway injury = oropharyngeal blistering/hypoxia
progressive airway edema and obstruction ; intubation
_________________
[bedside fiberoptic laryngoscopy] to evaluate
Guidelines for Lung CA screening - 3
low dose annual CT if fits all 3 criteria:
- [55-80 yo]
- smoked for ≥20 pack years
- still smoking or quit within last 15 years
_________________
Pack Year = [# of packs/day x # of years smoking]
ex: [4 packs/ day x 30 years smoking = 120 pack years]
what’s the cause of hypoxemia in COPD patients?
poor elastic recoil + bronchitis/bronchospasm/mucus plugs ➜ ⬇︎ventilation = [low V/Q ratio] = poor oxygen delivery to well perfused areas
supplemental O2 ⇪ delivery of O2 to (and ergo) ⇪ oxygen exchange in lung regions with low V/Q
SOLC is associated with LEMS and ⬜ syndrome?
_________________
When this occurs, how is it treated?
SIADH
( ➜ euvolemic hypOnatremia)
_________________
Water Restriction
Pts p/w anaphylaxis can be discharged or admitted
What determines if a pt with anaphylaxis should be admitted for observation? (2)
1.SEVERE (hypOtension | upper airway edema | respiratory distress)
or
2.PERSISTENT (REQD MULTIPLE EPI DOSES)

EPIC ➜ chag
these pts have ⇪ risk for potentially fatal biphasic anaphylaxis (recurrence of sx after initial resolution)
PE classification is based on the clinical presence of ⬜ and ⬜
When is a pulmonary embolism considered submassive? -2
_________________
treatment? (2)
(R& H)
[RV dysfunction = hypOkinesis vs Dilation]
[HypOtension SBP less than 90]
“MASSIVE PE diagnosis Require Haste!”

[⊕R : ⊝h = subMassive] → [(UFH anticoag) vs (catheter-thrombolysis)]tx
PE classification is based on the clinical presence of ⬜ and ⬜
When is a pulmonary embolism considered MASSIVE? -2
_________________
treatment? (2)
(R& H)
[RV dysfunction = hypOkinesis vs Dilation]
[HypOtension SBP less than 90]
“MASSIVE PE diagnosis Require Haste!”

[⊕R : ⊕H = MASSIVE] → [(Embolectomy) vs (systemic thrombolysis)]tx
PE classification is based on the clinical presence of ⬜ and ⬜
When is a pulmonary embolism considered low risk? -2
_________________
treatment?
(R& H)
[RV dysfunction = hypOkinesis vs Dilation]
[HypOtension SBP less than 90]
“MASSIVE PE diagnosis Require Haste!”

[⊝r : ⊝h = low risk] → [(UFH anticoag)unless CTX]tx
Explain why Obstructive sleep apnea is important in assessing if patient can have surgery or not?
OSA ⇪ risk for periOperative RESPIRATORY FAILURE if pharmacologic hypOventilation [sedation/neuromuscular blocker/opioids/anesthesia] occurs
will p/w HYPERCapnia and hypoxia
Criteria for Pulmonary HTN
Pulm Arterial presure ≥25(normal = 20)

Pulm HTN = [≥25 Pulm Arterial Pressure ] (nl=20)
What are the causes of Pulmonary HTN?-4
What’s most common cause?
①{pulmARTERY (intrinsic)(Idiopathic, [Limited CREST Scleroderma], HIV, Schistosomiasis, SLE)</sup>
② ⭐{LHEART❌= MOST COMMON CAUSE}⭐
③LUNG(Chronic Lung Dz/Hypoxemia/OSA)
④ pulmVEIN(CTEPE)
[(pulmonary HTN ≥25 PAP) females] should AVOID PREGNANCY!

🔎CTEPH = Chronic ThromboEmbolic Pulm HTN
Acute Bronchitis sx (4)
the bronchitis CAWS
1. [COUGH (+/- productive) 5D-3W ⼀self-limited]
_________________
- ALS
- [Wall (chest wall tenderness)]
- [SYSTEMIC SX ABSENT (FEVER = C/F bPNA)]
aLS = Adventious Lung Sounds (wheezing/rhonchi) / bPNA = bacterial PNA

Acute Bronchitis MOD
_________________
How is Acute Bronchitis treated? (3)
[precedingviral URI]➜ bronchial epithelial sloughing ➜ bronchial inflammation
➜{[COUGH (+/- productive) 5D-3W ⼀self-limited] (CAWS sx)} 2/2 lung’s attempt to clear slough debris
_________________
- bronchoDilators
- NSAIDs
- NO ABX

Acute Bronchitis MOD
_________________
How is Acute Bronchitis diagnosed? (2)
[precedingviral URI]➜ bronchial epithelial sloughing ➜ bronchial inflammation ➜ {[COUGH (+/- productive) 5D-3W ⼀self-limited] (CAWS sx)} 2/2 lung’s attempt to clear slough debris
_________________
Clinical
(CXR if PNA suspected)

What paraneoplastic syndromes is Squamous cell lung carcinoma associated with?
sCa++mous cell carcinoma!
⬆︎⬆︎PTHrelatedProtein –> HYPERCALCEMIA

Which bacteria cause Community Acquired PNA-8
- Strep Pneumo
- H. Flu
- Moraxella
- MRSA
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae-AT (ATypical)
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae-AT
- Chlamydophila Psittaci-AT
- Legionella-AT

Which NON-bacteria cause Community Acquired PNA-3
- Flu
- TB
- Histoplasmosis
Vancomycin is not typically used for empiric CAP tx
When would Vancomycin be used in CAP? (4)
- septic shock
- respiratory failure
- [MRSA imaging (multilobar PNA with cavitation)]
- [MRSA colonization (HD, HF, MRSA colonization hx)]

How do you determine disposition for Community Acquired PNA ?
CURB 65
Confusion
BUN > 20
Respiratory Rate > 30
BP < [(90) / (60)]
65 y/o +
________________
[0-1 = outpatient with f/u] | [2 = inpatient] | [3+ = ICU]

Treatment for ICU CAP (2)
_________________
Community acquired pneumonia
βF | βM

Treatment for Inpatient CAP (2)
_________________
Community acquired pneumonia
F | βM

Treatment for Outpatient CAP (4)
_________________
Community acquired pneumonia
A | D | F* | βM*

What is an Auricular hematoma?
_________________
What’s the management for it? (3)
blunt ear trauma → hematoma between [outer ear cartilage] and perichondrium
_________________
- [STAT hematoma evacuation]to avoid infection, avascular necrosis and permanent cauliflower ear deformity]

also:
2. POabx
3. Pressure dressingto prevent re-accumulation of blood s/p evac
PE mgmt is based on HDS vs HDUS. [PE HDUS = ⬜]
How do you workup [HDSPulmonary Embolism]?
PE HDUS{[(SBP< 90)x ≥15m]
or
[requires vasopressor|inotrope support]}

PE mgmt is based on HDS vs HDUS. [PE HDUS = ⬜]
How do you workup [HDUSPulmonary Embolism]?
(PE) HDUS = {[(SBP< 90)x ≥15m]
or
[requires vasopressor|inotrope support]}

HDUS patient (SBP < 90) with suspected obstructive shock 2/2 massive pulmonary embolism
How do you manage this? (2)
[ThrombolysisSystemic]
and/or
Embolectomy

pt w suspected PE → HDS →[no RV_TTE❌]→ pretest probability
describe how to determine pretest probability for suspected HDS Pulmonary Embolism? (3)
wells: “ Don’t Die | Tell Team To | Calculate Criteria “
[HIGH ≥6]
_________________
[3-5 = INTERMEDIATE]
[ low ≤2]

What are the EKG signs for Pulmonary Embolism? (3)
“for PE EKG use RST”
1. RAD👇🖐🏾
2. [S1Q3T3]
3. [TWIin precordial V1-V6]

What are the 3 different ways you can diagnose ANAPHYLAXIS?
rapid onset of…
1. [🅂 + (🆁↔🆅)any antigen]
2. [≥2 🅂 🅲 🆁 🅶{+🄽**} Likely antigen]
3. [🆅KNOWN antigen]
_________________
[🅂kin/mucosa] [🅲 ardio] [🆁 espiratory] [🅶I] [🆅ascular low BP]
these pts should be prescribed self-injectable epinephrine!
** add 🄽euro ⼀if peds

tx = EPIC ➜ chag
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
dx? (5)
- skin bx (to exclude urticarial vasculitis or mastocytosis)
- CBC
- UA
- [CRP or ESR]
- LFT

a Chronic spontaneous urticaria patient has been given [2nd gen H1 R blocker] with no relief
What therapies can be tried next? (4)
- [1st gen H1 R blocker] at bedtime
- [Leukotriene R blocker (montelukast)]
- H2 R blocker
- CTS PO
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
prognosis?
self-limited to 2-5 years
chronic Cough is a common (and sometimes the only) symptom of ⬜ and is treated with ⬜ weeks of PPI
GERD; 8
What is the MOST RELIABLE method for verifying ETT placement?
_________________
What are the less reliable methods of verifying ETT placement? (4)
[CO2 CAPNOGRAPHY] - (CO2 analysis) either via [waveform (quant vs rectangular) analysis] or [colorimetric litmus (purple ➜ yellow) analysis]
_________________
[bs Auscultation], [chest rise], [ETT passing thru vocal cord visualization], [ETT fogging]
HIV+ pts have higher risk for [Active TB Infection]
Explain how CD4 count is specifically related to TB -2
_________________
- ⇪ CD4 = Cavitary apical lung TB
- ⬇︎CD4 = [Lobar/Pleural/Disseminated] TB

clinical findings for [TB pleural effusion] (5)
commonly found in advanced HIV
- ⇪ Adenosine DeAminase
- lymphocyte predominant
- exudative
- negative smear
- dx = [pleural biopsy demonstrating histopathologic pleural granuloma]

Meniere disease
clinical presentation (5)
[24VATH]
- 24m - 24Hepisodes
- Vertigo
- Aural fullness
- Tinnitus
- Hearing loss uL (low freq sensorineural)

Meniere disease
etx?
defective inner ear endolymphatic resorption ➜ ⇪ [endolymph volume/pressure distension = endolymphatic hydrops] ➜ vestibular and auditory damage ➜ [24VATH]</subMeniere sx

Meniere disease
dx? -2
- comprehensive audiogram
- MRI(to r/o other central vertigo etx)

“Meniere must”DABtx on **24*VATHsx *”
Meniere disease
Tx? (5)
- [(D)iet ∆(⬇︎Salt, ⬇︎Caffeine, ⬇︎EtOH)]
- RxMaintenance[HCTZ | (B)etahistine]
- RxACUTE[(A)ntiemetics | vestibular suppressants]

“Meniere must”DABtx on **24*VATHsx *”
BPPV
MOD
Ca+ otoliths accumulated within semicircular canals –>
[brief < 1 min] episodes ([triggered by head position ∆ie Dixhall-Pike] ) of:
-Nauseous
-Dizzy(Vertigo)
-Nystagmus
“BPPV gave me…Nauseous Dizzy Nystagmus”

What does pulmonary contusion look like on radiograph?
localized irregular lung opacification - up to 24h s/p blunt chest trauma

how do you treat pulmonary contusion? (2)
- supplemental O2
- pain control

patient with suspected PE, CTA CTD ➜ abnormal V/Q
How do you interpret V/Q scan? (4)

What is Pulmonary Cachexia Syndrome? (2)
- loss of lean muscle mass 2/2 SEVERE COPD (⇪ WOB ➜ energy imbalance ➜ wt dysregulation)
- and (systemic inflammation ➜ ⬇︎appetite)
tx = optimize lung function and nutrition
In patients with impaired renal function, ⬜ is most appropriate to evaluate for acute PE. How is acute PE positively confirmed using this modality?
V/Q scan;

[T or F] Fever is not a symptom of Pulmonary Embolism
FALSE! ⼀15% of PE has fever
(= abx not indicated if no other infectious s/s)

“Flash” pulmonary edema occurs from ⬜
▶For FLASH pulmonary edema, between Furosemidediuretic IV and [NTGvenoDilator IV )], which takes priority?
▷why?
[HTN Emergency > 180/120]
_________________
[NTG venoDilator IV]
◁⼀venoDilation by NTG rapidly DEC cardiac preload (which rapidly DEC intracardiac filling pressures)➜ rapid “flash” pulmonary edema improvement
What condition is a/w hyperacute stridor after extubation?
_________________
Explain
Laryngeal edema
_________________
direct mechanical damage from intubation ➜ laryngeal inflammation/edema ➜ does not symptomatically present until pt extubated and breathing on their own = PostExtubationStridor ➜ REINTUBATE TX
a. In acute PE, What is the [most important predictor of INC PE Mortality]?
b. explain why
a.[HDUS severe hypOtension✳]
_________________
b.
▶{[HDUS severe hypOtension] ⬅︎ [RV❌] ⬅︎ [MASSIVE (Obstructive) PE = INC PE Mortality]}
▶so… [HDUS severe hypotension] is an important predictor for INC PE Mortality
INC short term PE mortality

✳{[SBP < 90 x ≥15m] |vasopressor💊|inotrope💊}
🔎RV❌ = RV Dilation|RV hypOkinesis
📖 {[HDUS severe hypOtension] likely indicates [RV❌] which likely 2/2 a [MASSIVE* (Obstructive) PE] which → INC PE Mortality*}
⬜ is the MOST IMPORTANT predictor of increased short term mortality in acute PE patients
_________________
Name other predictors (7)
[HDUS severe hypOtension([SBP < 90 x ≥15m]|vasopressors|inotropes)
_________________
- Age
- AMS
- CA
- Tachypnea
- Tachycardia
- hypOthermia
- hypOxemia severe

Describe the 4 treatment options for patients with acute PE

Describe [Exercise Induced Bronchoconstriction] (3)
_________________
MOD?
-{[asthma-like reaction] to exercise}
-WITH OR WITHOUT PREEXISTING ASTHMA
-in mostly athletes
_________________
[Hyperventilation shortens time for humidification] ➜ cool dry air stimulates mast cell degranulation ➜ bronchoconstriction
EIB = asthma-“LIKE” rxn during exercise ( +/- hx of asthma)
How do you diagnose [Exercise Induced Bronchoconstriction]?
_________________
How is it treated?
[Exercise challenge ➜ (FEV1 ⬇︎ GOE15% from baseline)] = EIB
_________________
[bronchoDilator 10m before exercise]
Usually, Influenza treatment consist of {⬜ +/- [O|Z]}
Which patients are eligible for [Oseltamivir|Zanamivir]? (3)
APAP(symptomatic care)
+/- [O|Z] if…
1. [ < 48h exposure(w/wo sx)]
2. pt presenting AT sx onset
3. {[High risk comorbidities(DM, CardioPulm❌, prior flu hospitalization) = add [PNA CXR r/o] }
What causes Snoring?
_________________
What factors increase Snoring? (3)
[relaxed upper airway during sleep (habitual vs OSA)]➜ respiration induced soft tissue vibrations
\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_
1. EtOH before bed
2. smoking
3. [obese BMI>35]
For patients p/w Snoring, how can you initially screen them for OSA?
[STOPBang] ≥3 = ⊕OSA

Dx Criteria for screening test of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
[STOPBang] ≤ 2 = not OSA
a/w mild cognitive impairment in elderly
_________________
Other causes of sleepiness: narcolepsy, restless leg, depression, drugs

List for confirmation test for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
POLYSOMNOGRAPHY

Other causes of sleepiness: narcolepsy, restless leg, depression, drugs
Why does INC respiratory drive in a patient receiving chronic Opioids concerning?
chronic opioids should ➜ DEC respiratory drive, and since Opioids blunt respiratory response … breakthrough [INC respiratory drive] in the setting of chronic Opioids likely indicates abnormal NON-opioid process (SUCH AS Pulmonary Embolism)
The Centor Criteria is used to differentiate Patients with Acute Pharyngitis
Recite the Criteria
_________________
Explain the Interpretation
*old AGE: [add 1pt← (15-44) → subtract 1pt]

(malignant) Mesothelioma
Sx (4)
- [PLEURAL EFFUSION
- with [pleuritic chest pain, cough and SOB]
- Night sweats
- Wt loss

(malignant) Mesothelioma
How is it diagnosed? (3)
-
Chest Imaging [PLEURAL CALCIFICATION and THICKENING]
* * * - [Thoracentesiswith Cytology]
- [Thoracotomy bxOpen vs VATS]

(malignant) Mesothelioma
occurs typically from ⬜ but arises ⬜ after exposure.
_________________
Tx includes ⬜3 and median survival after dx is ⬜
[occupational asbestos(cement/tile/ships) exposure]; 15-30y
_________________
[Palliative, Surgery, Chemoradiation] ; 9-13 months
Thoracic duct obstruction can cause ⬜. Diagnosis is supported by ⬜ lab
chylothorax ; [pleural fluid TAG > 110]
from milky white lymph leaking out of the thoracic duct into lung

Chronic silicosis is an occupational lung disease that commonly affects which job professions? (4)
_________________
What would you expect on CXR? (2)
Miners | sandblasters | foundry workers | masons
_________________
upper lobe nodules + lower lobe emphysema
What are the following measurement values for EXUDATIVE pleural fluid :
[Pleural:Serum Protein]
________________
[Pleural:Serum LDH]
________________
Usually caused by ⬆︎capillary or pleural membrane permeability
Pleural:Serum protein >0.5
________________
Pleural:Serum LDH >0.6

What are the following measurement values for transudative pleural fluid :
[Pleural:Serum Protein]
________________
[Pleural:Serum LDH]
________________
Pleural:Serum protein ≤0.5
________________
Pleural:Serum LDH ≤0.6

What are the following measurement values for EXUDATIVE pleural fluid :
pH
________________
Glucose
________________
Usually caused by ⬆︎capillary or pleural membrane permeability
pH<2
________________
Glucose<60

What are the following measurement values for transudative pleural fluid :
pH
________________
Glucose
________________
pH = 7.4 - 7.55
________________
Glucose > 60

Causes of transudative pleural effusion -2
hypOalbumin (Cirrhosis / nephrOtic syndrome)
CHF

Causes of EXUDATIVE pleural effusion -3
[INFECTION (TB / FUNGAL)]
CA
PE

[Pleural Fluid LDH] that is > [2/3 Upper Limit of Normal Serum LDH] is
(⬜ transudate | EXUDATE)
EXUDATE

[Pleural Fluid LDH] that is ≤ [2/3 Upper Limit of Normal Serum LDH] is
(⬜ transudate | EXUDATE)
transudate

Explain MOD for CHF pts experiencing pulmonary edema after a MI
[precipitating factor(HTN* = “flash pulmonary edema”* , MI, arrhythmia, valve dysfxn) ] causes abrupt INC in [L atrial pressure (Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure)]
➜ INC transmitted back pressure to the pulmonary venous system = pulmonary edema
CHF Exacerbation
treatment? (3)
🆂🅿︎🅸
1.🆂table?([Respiratory❌→ NIPPV,O2] , [Cardiac shock → inotropes])
_________________
2.🅿︎[**P.O.N.D. PRELOAD REDUCTION][➜ DEC PCWP** (+/- DEC afterload)] = PPV&Position, O2, NTG, Diuretics]
_________________
3.🅸nvestigate cause(EKG, troponin, echo, CXR, BNP)

Pulm HTN = [≥25 Pulm Arterial Pressure ] (nl=20)
How is a female patient with new dx Pulmonary HTN related to pregnancy?
females with pulmonary HTN carry extremely high pregnancy mortality risk = [pulmonary HTN females] should AVOID PREGNANCY!

Pulm HTN = [≥25 Pulm Arterial Pressure ] (nl=20)
There are ⬜# causal groups for Pulmonary HTN
Briefly List general mgmt all Pulm HTN pts should receive? (6)
4
_________________
🎯REFER TO ACCREDITED PH CENTER
🎯Stabilize
🎯[Contraception⚠️Pulmonary HTN females on Pulm HTN meds should AVOID PREGNANCY!]
🎯Immunization
🎯 ❤️Rehab
🎯BL lung transplantif Refractrory PH✳

[hot potato muffled voice] is one of the features of PTA (and other dz) caused by ⬜
_________________
What are the other clinical features of Peritonsillar abscess? (5)
[(PTA/epiglottitis/RTA/mass)]DEC space in POST pharynx ➜
1.⭐{DEC voice resonance = [hot potato muffled voice]⭐

2.[PTATRISMUS⊕]
3.[CTL uvea deviation uvula deviates OPPOSITE the lesion]
4.Sore throat w/dysphagia
5.Fever
6.saliva pooling
_________________
[trismus(inflammatory spasm of nearby pterygoid m)] differentiates [PTA(TRISMUS⊕)] from [tonsillitis(trismus⊝)]
Tx of Peritonsillar Abscess (2)
[Drain AbscessNeedle aspiration > I&D ]
+
[AbxGASP + Respiratory AnAerobes]

✏️[trismus(inflammatory spasm of nearby pterygoid m)] differentiates [PTA(TRISMUS⊕)] from [tonsillitis(trismus⊝)]
Trismus is defined as ⬜
How is it related to Peritonsillar Abscess and Tonsillitis?
inflammatory spasm of pterygoid muscles ➜ inability to open mouth = SURGICAL INTERVENTION if PTA
_________________
[trismus differentiates [PTA(TRISMUS⊕/surgical intervention)] from [tonsillitis(trismus⊝)]

A pt with throat pain also begins having ear pain. why?
referred ear pain occurs with multiple throat pathologies 2/2 overlapping innervations from the afferent[glossopharyngeal CN9] and afferent[Vagus CN10] –both traveling into ear

Smoking Cessation tx = CBT + Rx
List and Briefly describe the 4 [Rx pharmacologic] options for smoking cessation?
_________________
Although ⬜ is the MOST effective, which of these treatments are better together than alone?
_________________
VARENICLINE ; [LANRT + SANRT (combined NRT is better!]

benign [Solitary Pulmonary coin nodules] have what type of radiographic Calcification? (4)
[Hamartoma POPCORN calcification]
concentric
central
[diffuse homogenous]

MALIGNANT [Solitary Pulmonary coin nodules] have what type of radiographic Calcification? (3)
RIP
RETICULAR
[IRREGULAR = ECCENtRIC, asymmetrical]
PUNCTATE
[Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency] __(MOD)_ is a potential cause of ⬜
[α1aT inhibits neutrophil elastase from breaking down lung tissue
. so
⬇︎α1aT → ⇪ neutrophil elastase lung tissue breakdown which → emphysema)]
_________________
; emphysema
What is Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
[inhaled antigen(poultry/mold/meth?)] overactivates Pulmonary immune system → Dyspnea & Cough
“Double Sickening” is a a common clinical sign of ⬜ by ⬜3.
Explain (2)
[ABRS (Acute Bacterial RhinoSinusitis)]; [SMH (Strep pneumo/Moraxella catarrhalis/HFlu)] ;
- Double Sickening Effect= { [viral URI] → [initial improvement]≥5d → [sudden clinical deterioration (SMHH sx)* * from ABRS] }
- Tx = {[Amox/clav PO]7d + [intranasal saline irrigation] + analgesics}
etx for [ABRS 2/2 viral URI]
_________________
ABRS: Acute Bacterial RhinoSinusitis
[Viruses (rhino/flu/adenovirus)] are most common to infect nasal/sinus mucosa = [(ARS) Acute rhinosinusitis] (resolves within 10d)
BUT…10% people develop secondary bacterial infection in which
[SMHbacteria→ SMHHsx = ABRS] ⼀this is Double Sickening effect
(Strep pneumo/Moraxella catarrhalis/HFlu)
[Snotty purulent nasal discharge/Maxillary facial pain/HA/Hot>39C] ≥3d = ABRS
Diagnostic criteria for [(ABRS) Acute Bacterial RhinoSinusitis] -3
any 1 of the following:
- mild[smhhsx ]≥10d ⼀(persistent)
- SEVERE[SMHHsx]≥3d
- Double Sickening effect

ABRS = [(Strep pneumo/Moraxella_catarrhalis/HFlu) → SMHHsx ]
_________________
SMHHsx = [Snotty purulent nasal discharge/Maxillary facial pain/HA/Hot>39C]
Tx for [(ABRS) Acute Bacterial RhinoSinusitis] -3
What are 2 alternative abx if [1st line abx] is unavailable?
{[Amox/clav PO]7d+ [intranasal irrigation] + analgesics}
- alt: Doxy or Fluoroquinolones*
- *
[Snotty purulent nasal discharge/Maxillary facial pain/HA/High Fever>39C]

▶ Pts with [mild rhinosinusitis sx] less than ___ days likely have viral ARS and should receive symptomatic treatment only
_________________
▶ when should you suspect Acute Bacterial RhinoSinusitis? (3)
ARS: Acute RhinoSinusitis
▶10 (viral ARS resolves by 10 days)
_________________
▶
any of below:
- mild[smhhsx ]≥10d ⼀(persistent)
- SEVERE[SMHHsx]≥3d
- Double Sickening effect
Varenicline MOA (2)
_________________
There are 4 stages for [smoking cessation (NRSQ)]
At what stage of smoking cessation is Varenicline indicated? and why?
- [Nicotine R BLOCKER]= ⬇︎ cigarette gratification
PLUS
- [Nicotine R agonist]= prevents nicotine withdrawal sx
* * *
1S[Not readyto quit]
( in [“future quitters” ⼀patients unable to give quit date now BUT interested in cutting down in undetermined future]…Varenicline DOUBLES probability of smoking cessation!
= prescribe [Varenicline12w trial] to “future quitters” as part of reduce-to-quit strategy)

The 4 [smoking cessation stages] are ⬜
Describe the 3 interventions employed for smoking cessation stage
1 _____?
1[Not readyto quit] → 2[Readyto quit] → 3[Strugglingto quit]→ 4QUIT
1[Not readyto quit]
1.MIV: Motivational Interviewing (reswo)
2.Repeat screening every visit
3.1º🚭Rx[Varenicline12w trial]

🚭= smoking cessation
The 4 [smoking cessation stages] are ⬜
Describe the 4 interventions employed for smoking cessation stage
2 _____?
NRSQ
1[Not readyto quit] → 2[Readyto quit] → 3[Strugglingto quit]→ 4QUIT
2[Readyto quit]
- 2º🚭Rx[Vareniclineprescribe stage 1-N /NRT/Bupropion]x 12w trial
- [SET FIRM QUIT DATE]
- [DISARD PARAPHERNALIA]
- Behavioral counseling
NRT=Nicotine Replacement Therapy

The 4 [smoking cessation stages] are ⬜
Describe the 3 interventions employed for smoking cessation stage
3 _____?
NRSQ
1[Not readyto quit] → 2[Readyto quit] → 3[Strugglingto quit]→ 4QUIT
3[Strugglingto quit]
- [Reinforce partial achievement]
- [Identify & link struggling triggers to other activities]
- Biofeedback loops(exhaled CO monitoring, mobile app gamification)

The 4 [smoking cessation stages] are ⬜
Describe the 4 interventions employed for smoking cessation stage
4 _____?
NRSQ
1[Not readyto quit] → 2[Readyto quit] → 3[Strugglingto quit]→ 4QUIT

4QUIT
1.Congratulate
2.Continue support
3.Continue 🚭Rx x 12w
4.[encourage reflection“how has your life changed?”]
[Motivational interviewing (MIV)] guides “quitting addictions or habit”.
Describe the 4 rungs of MIV
{stage 1N[re s w o]MIV}
_________________
roadblocksto quitting the a/h
⬆
rewardsto quitting the a/h
⬆
risksto quitting the a/h
⬆
relevant⼀Based on how an addiction/habit is affecting pt’s life rn⼀does pt consider quitting that a/h a relevant interest at this time? [Y → next rung | N → inquire why not]
_________________
“climb 4 rungs of MIV up and out of of addiction”

The 4 [smoking cessation stages] are ⬜
In which [smoking cessation stage] is___X___ employed?
a. [MIV (Motivational Interview)]
* * *
b. [Biofeedback loops (i.e. ⬜2)]
* * *
c. [Nicotine Replacement Therapy or bupropion]
NRSQto quit
a. 1[Not readytq]
* * *
b. (i.e. exhaled CO monitoring, mobile app gamification) = 3[Strugglingtq]
* * *
c. 2[Readytq]

The 4 [smoking cessation stages] are ⬜
In which [smoking cessation stage] is___X___ employed?
[Setting a firm Quit Date & Discarding Smoking Paraphernalia]
2[Readytq]

NRSQto quit
clinical features of [Cough Variant Asthma] (6)
- [chronic nonproductive cough]
- triggered by forced expiration, nighttime, exercise, allergens
- NO classic asthma [sx(wheeezing/SOB)]
- NO classic asthma [pex(rhonchi)]
- Dx: ⊕methacholine challenge (inducible airway obstruction)
- Tx: same as Asthma

Sudden SensoriNeural Hearing Loss
a. SSNHL presents as ⬜, and once diagnosed requires what course of management? (2)
b. How would you expect Rinne and Weber to result for Sensorineural Hearing loss?
a. Sudden Hearing loss with [normal H & P]:
-[URGENT ENT CONSULT( [+/- MidEar CTS_high dose] within 24H) ] (for audiogram, MRI)

- nml hx (no recent trauma, no recent pain)
- nml ear exam
- nml neuro exam (aside from SSNHL)
a. [normal Rinne = ⬜] and [normal Weber = ⬜]
_________________
b. How would you expect Rinne and Weber to result for Conductive Hearing loss?
normalRaaWM
_________________
cdlrbwa

a. [normal Rinne = ⬜] and [normal Weber = ⬜]
_________________
b. How would you expect Rinne and Weber to result for Sensorineural Hearing loss?
normalRaaWM
_________________
SSLRaaWU

a. [normal Rinne = ⬜] and [normal Weber = ⬜]
_________________
b. How would you expect Rinne and Weber to result for mixed hearing loss?
normalRaaWM
_________________
mXLRbWu

name the 4 groups (with examples) of asthma triggers

[Viral URI] > [House dust mites] > {[Animal dander] = [Aspergillus mold]}
Inhaled allergens are the most common group of asthma triggers
Of the Inhaled allergens group, ⬜ is the overall most common asthma trigger; with ⬜ and ⬜ following after.
[House dust mites]60-90% of cases > [Animal dander] = [Aspergillus mold]

⚠️note: [Viral URI] is the most common trigger of asthma exacerbation
Inhaled allergens are the most common group of asthma triggers
Explain why [House Dust Mite] control is an important adjunctive tx for persistent asthma
60-90% asthma exacerbation are related to HDM (microscopic translucent critters that infest woven material like bedsheets/carpets) leave immunogenic fecal particles→ allergic inflammation = Mite control DEC exacerbations & improves lung fxn
_________________
[House dust mites]60-90% of cases > pet dander = [Aspergillus mold]

[Viral URI] > [House dust mites] > {[Animal dander] = [Aspergillus mold]}
[SVC syndrome] must be suspected in any high risk CA pt who presents with what 4 things?
The best diagnostic test for [SVC syndrome] is ⬜
- [⭐BILATERAL⭐ facial/neck edema(uL = brachiocephalic vein obstruction)]
- subQ venous dilationcervical, UE
- dyspnea
- coughpersistent
_________________
[contrast CTNeck / Chest]
_________________
Superior Vena Cava syndrome is likely 2/2 bronchogenic carcinoma

✏️Both SVC and brachiocephalic vein obstruction → facial/neck edema but [SVC is BL] and [brachiocephalic = uL]
⬜ should be considered in the ddx for HD patients with sudden dyspnea and flushing shortly after starting HD and receiving iron infusions (or other meds) during HD
Anaphylaxis1A
GIVE [EPIC ➜ chag]!

[ironIV] is a known allergen, and is commonly used for treating anemia in HD pts.
⬜ is the most common trigger of asthma exacerbation. What is the clinical definition of asthma exacerbation? (2)
viral URI
_________________
INC asthma sx (cough, SOB, wheezing)
+
DEC peak expiratory flow rate >20%
a. treatment for [mild resistant(unresponsive to initial bronchoDilator) asthma exacerbation] in an outpatient setting
b. Why this treatment? (2)
a. [Prednisone40-60mg PO QD x 7d] (CTS short course)
b. [INC long term control] / [DEC future hospitalization]
Pts with smoker hx p/w non-resolving PNA should make you s/f ⬜. If so, obtaining ⬜-2 is 1st step for this diagnosis. Why?
[endobronchial malignancy (since obstructive endobronchial malignancy would prevent complete PNA drainage/resolution → nonresolving PNA)];
[CT chest → bronchoscopy]
→ will help diagnose & workup malignancy as well as diagnose other causes of nonresolving PNA (abscess/empyema)
bronchiectasis is characterized by ⬜ and ⬜
b. MOD for [focal bronchiectasis]
c. how do you diagnose and treat [focal bronchiectasis]?
[permanent airway dilation] and [daily copious mucus production]
b. Focal bronchiectasis (involvement of single lobe/segment only) indicates airway blockage (malignancy/foreign body) ⼀mucus becomes trapped behind obstruction → [bacterial overgrowth (i.e.post-obstructive PNA)] → inflammatory bronchial wall damage → focal permanent airway dilation.
c. bronchoscopy (allows for diagnostic and therapeutic removal of obstructing lesion {since note: initial CT may not reveal obstructing lesion})
general bronchiectasis dx = [airway dilation on High Res CT]
Clinical features of Bronchiectasis (3)
1.{impaired airway clearance → [chronic copious (+/- blood tinged)mucus production]}
2. → {[acute recurrent lung infections +/- frank hemoptysis2/2 airway destruction]}
3. → {[permanent airway dilationon HRCT = dx]2/2 continued airway destruction}

Major causes of Bronchiectasis (5)
- airway obstruction (focal)
- Mucostasis (CF, ABPA, Kartagener)
- Immune (Sjogren syndrome, immunodeficiency)
- Infection (TB, ABPA)
- Toxic inhalation

Bronchiectasis dx (3)
-[HRCT chest(airway Dilation)] = needed for dx

-[PFT(Obstructive pattern)]
-[Investigate etx(cx, Ig levels)]
Bronchiectasis
tx (3)
- [Airway clearancechest physiotherapy , mucolytics]
- [Abxtreats overgrowth & exacerbations]
- [Address underlying etx]

(⬜ dx?) is typically caused by ⬜
Pts with risk factors should undergo ⬜ and make Modifications to their ⬜-2 to prevent recurrence

Lung Abscess; [aspiration of anaerobic bacteria]
________________
[speech/swallow evaluation] ;
Diet (thickened liquids) and/or Positioning (chin tuck)

Describe the Chest CT
What’s the dx?

Lung [AIR FLUID LEVEL] amid pulmonary consolidation = LUNG ABSCESS
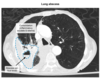
these pts also have sour tasting sputum
Anaphylaxis is difficult to diagnose in peds
describe the criteria
________________
Tx for peds Anaphylaxis -8
after allergen exposure, pt has acute allergic sx in ≥2 systems
[≥2 🅂 🅲 🆁 🅶{🄽**} Likely antigen]
________________
EPIC ➜ chag but
[Epinephrine 0.1 mg/kg IM]
** peds only

- [Skin/Neurologic/Respiratory/CV/GI]*
tx for [Necrotizing Malignant Otitis Externa] -4
NMOE
mild = topical acetic acid
moderate = topical cipro
[SEVERE (canal 100% occluded) = wick placement adjunct]
________________
INVASIVE! = CIPRO IV
7 day treatment
[NMOE = ⊕FEVER] vs [BOE= ⊝fever]
management of Acute Mastoiditis -2
[middle ear drainage (via mastoidectomy or {tympanostomy +/- ear tube placement})]
+
IV Abx

BPPV
CP-3
(Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo)
“BPPV gave me…Nauseating DixHallpike Nystagmus”*

Ca+ otoliths accumulated within semicircular canals –>
[brief < 1 min] episodes ([triggered by head position ∆ie Dixhall-Pike] ) of:
-Nauseating
-Dixpike-dizzy(Vertigo)
-Nystagmus
After receiving anesthesia, pt develops hypOtension, elevated peak pressures and DEC end tidal CO2. This is concerning for ⬜
how should you work this up? Tx?

ddx: Anaphylaxis (to rocuronium/abx/skin antisepsis products/blood);
dx: PHYSICAL EXAM (look for cutaneous rash/flushing!)
tx: Epinephrine

[PSPST (Pancoast SUP Pulmonary Sulcus Tumor)]
has 4 main clinical symptoms
________________
⬜ is the most common PSPST sx
> ⬜ and ⬜
which are > [⬜ (only present in 25% PSPST pts)]
-
R SHOULDER PAIN
_________________

2.[PAM Horner Syndrome(2/2 sympathetic chain/stellate ganglion invasion)]
3.[Hand atrophy/weakness(2/2 C8-T2 spinal cord invasion)]
_________________
4.[asymmetric LE HYPERreflexia(2/2 spinal cord compression)]= only 25% of PSPST pts
In Smokers, ⬜ may be first sign of Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Why is this?
[persistent Recurrent PNA]
________________
{[Bronchogenic Carcinomaolder|smokers] or [Carcinoid tumoryoung | NONsmoker</sup]}[FOCAL Endobronchial Obstruction]
= [FOCAL endobronchial obstruction] ➜ ⬇︎clearance and eventually causes stasis of airway secretions
➜ [persistent Recurrent PNA (despite previous tx success)]
🔬Gold Standard dx = FLEX BRONCHOSCOPY
how do you diagnose Bronchogenic Carcinoma (or any endobronchial obstructing lesion) ?
_________________
Name an alternative
[CONFIRMATORY FLEXIBLE BRONCHOSCOPY]
________or_________
[alternative nonConfirmatory HRCT]
_______________
HRCT: High Res CT
Although RARE, Recurrent Pulmonary Embolism can (rarely) present as nonresolving [PE-related⬜] ;
but this condition will have what distinguishing symptom from its sister condition [NONPE-related⬜] ?
PE-related[persistent Recurrent PNA]
; *PE-PNA → *[pleuritic cp with hypoxia]
PE causes Pleurisy

*PE-PNA → *[pleuritic cp with hypoxia]
NON*PE (or regular) PNA *has no [pleuritic cp with hypoxia]
[Bacterial otitis externa] and [Necrotizing malignant otitis externa] both present with ⬜ and ⬜ from ⬜
________________
how do you differentiate the two?
[pain with ear manipulation] and [purulent ear drainage] ; pseudomonas
________________
NMOE = FEVER+[involves neighboring skull bone] + [only in elderly|DM|immunocompro]
vs
BOE = NO fever
cp for [Suppurative Bacterial Otitis Media] (4)
[fever + cranky]
➜ [purulent ear drainage w resolution of cranky]
and [NO pinna manipulation pain]

[Suppurative Bacterial Otitis Media] etx
GASP (from nasopharynx) infects middle ear ➜ TM pressure/bulging –(if untreated)–> TM perforation ➜ nonpainful otorrhea purulent ear drainage with [NO pinna manipulation pain] = SBOM
________________
*[fever + cranky(from GASP nasopharyngeal infxn)] ➜ [ nonpainful suppurative (purulent) ear drainage with resolution of cranky]
⭐nonpainful = [NO pinna manipulation pain]*

[Serous Otitis Media with effusion] etx
sOME = asymptomatic middle ear effusion in the absence of infection /inflammation
________________
SBOM (➜sOME)
postop
CXR shows [linear opacifications in the b/l lung bases]
dx?
Atelectasis

Postoperative atelectasis is common ⬜ days after operation
________________
how is this managed? -2
2-5
________________
+respiratory secretions = [Chest Physiotherapy + suctioning]
NO respiratory secretions = CPAP

Name the 6 major causes of Postoperative Hypoxemia

Name 5 distinguishing features for differentiating [NonAllergic rhinitis] from [Allergic Rhinitis]
________________
Tx for NAR? -3
_N_AR :
1. [No Kids (= cp> 20 yo)]
2. [No ocular sx (= Nasal sx with NO ocular sx - blockage/rhinorrhea/postnasal drip)]
3. [No identifiable allergen]
4. [No identifiable season / perennial (year long) sx]
5. [No blue Nasal mucosa (= NAR = erythematous Nasal mucosa)]
________________
[Intranasal Fluticasone] or [Intranasal Azelastine (antihistamine)] –(prn) –> BOTH

Pediatric patient comes in with c/f PNA
What are the 4 classic symptoms of PNA?
________________
How do you work up pediatric PNA ?
PNA? FACT
Fever / Adventitious lung sounds / Cough / Tachypnea
________________

Which 2 abx are used for pediatric [Community Acquired PNA]?
{amoxicillin([LOE4 yo] or [focal lung sounds])}
vs
{AZithromycin([ GOE5 yo] or [BL lung sounds i\well appearing])}

________________
PNA? FACTsx
Postoperative pulmonary complications occur most in pts undergoing ⬜ or ⬜ surgery.
What 4 factors make this Risk Greatest? How do you mitigate these?
thoracic; upper abd
_________________
COPD / smoker / CHF / OSA
SURGERY IS DELAYED until these pulm/cardiac conditions are treated and optimized
BPPV p/w ⬜ and is treated with ⬜
_________________
How do you diagnose BPPV?
BPPV= Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
[brief < 1 min] episodes ([triggered by head position ∆ie Dixhall-Pike] ) of:
-Nauseous
-Dizzy(Vertigo)
-Nystagmus
; [Epleycanalith repositioning procedure]
_________________
dx: [Dix-Hallpikecanalith diagnositc procedure]
“BPPV gave me…Nauseous Dizzy Nystagmus”
Both Meniere disease and [Middle ear effusion 2/2 nasopharyngeal mass] have aural fullness and hearing loss
How do you differentiate them?
{Meniere disease (24VATH]<sub sx</sub>)}
= effusion is in the labrinyth and not observed on physical exam
________vs_________
MEE = effusion(persistent, uL, middle ear) IS observed on physical exam,
etx possibly 2/2 nasopharyngeal carcinoma mass obstructing eustachian tube orifice. requires fiberoptic nasal endoscopy

“Meniere must”DABtx on **24*VATHsx *”
🔎24VATH = [24m-24H] Vertigo, Aural fullness, Tinnitus, Hearing loss uL
Biostatistically, what are the major benefits of smoking cessation? (2)
{AT ANY AGE ⼀ [within 5 years of Smoking cessation]}
pt will have ⬇︎ risk of:
1. [all-cause mortality]
2. [CV events]
Although tx for OSA in adults is ⬜ , what’s the first line tx for OSA in children?
_________________
OSA = Obstructive Sleep Apnea
CPAP ;
[Tonsillectomy with Adenoidectomy] = 1st line for peds
Anaphylaxis is a Type __ reaction
Describe the reaction
1A
[IgE-mediated immediate hypersensitivity] rxn

Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia is a Type __ reaction
Describe the reaction
2C
Autoantibodies directed against the host cells

Contact Dermatitis is a Type __ reaction
Describe the reaction
4D
[Delayed hypersensitive T-cell mediated] rxn

Serum Sickness is a Type __ reaction
Describe the reaction
3i

(Free antigen binds to IgG → binds Complement = [FIC Immune Complex] ➜ embeds in membranes where it cont activating more Complement → tissue damage(fever, polyarthritis, dermatitis)
pts with [persistent Recurrent single lobe PNA(despite previous tx successes) ] raises suspicion for ⬜ as the cause
[FOCAL Endobronchial Obstruction]
✏️2/2 {[Bronchogenic Carcinoma*older|smokers*(+/- focal bronchiectasis)]
or
[Carcinoid tumor*young | NONsmoker*](+/- focal bronchiectasis)}
✏️GOLD STANDARD DX = FLEX BRONCHOSCOPY
In PostOp Hypoxemia, how do you tell the difference between Atelectasis and Residual Anesthetic Effect?
Atelectasis = POD 2-5
[Residual Anesthetic Effect] (DEC central resp drive)can occur immediately

Allergic Rhinitis Sx -4
- 👃[Rhinitis with pale/blue nasal mucosa]
- 👁️ [ Itchy / watery/periorbital edema ]
- Young onset < 20 year old
- Associated with other allergy DO (asthma, eczema, allergy season)
Rhinitis = Cough 2/2 postnasal drip , watery rhinorrhea, congestion, sneezing, [🤧allergic pale/blue nasal mucosa] vs [NAR🐽erythematous nasal mucosa])
[🤧= Allergic Rhinitis only] / [🐽= NONAllergic Rhinitis only]

ALLERGIC RHINITIS
________________
TREATMENT -3
1st: ALLERGEN AVOIDANCE
–(prn)-➜
{[Intranasal fluticasone] + [PO antihistamine]}

What are the ONLY contraindications for the MMR vaccine? -4
”(❌-M-M-R) to (P-A-I-d)”
1. Pregnancy
2. [AGPN(Anaphyalxis to Prior MMR|Neomycin|Gelatin)]
3. [ImmunodeficiencySEVERE]
⛔ 4.[do NOT give APAP px for pts with pre-existing fever. They don’t need it.]
MOD Type 1 Hypersensitivity Reaction? (2)
ACID
1A. [(AAAA)⼀free Ag] rapidly crosslinks [preformed IgE bound to hypersensitive basophil & mast cells ]➜ [hyperacute histamine-mediated vasodilation/bronchoconstriction/edema]
+
1B. [Arachidonic Acid] conversion ➜ Leukotrienes = +/- 6H delayed response also

AAAA= Allergy/Asthma/Atopy/Anaphylaxis
MOD for Type 2 Hypersensitivity Reaction?
ACID
[{Cytotoxic IgG or IgM} bind to [fixed antigen on enemy Cell] ➜ [enemy Cell undergoes destructive “D.I.P.” (Dysfunction|Inflammation|Phagocytosis) ✏️]

✏️
Cytotoxic = ➜ [enemy Cell undergoes destructive “D.I.P.”] via:
3. [enemy Cell (D)ysfunction ⬅︎ {ec⼀AbFc}]
4. [enemy Cell (I)nflammation ⬅︎ {ec⼀AbFc⼀Complement}]
5. [enemy Cell (P)hagocytosis from opsonization ⬅︎ {ec⼀AbFc⼀Complement}]
MOD for Type 3 Hypersensitivity Reaction?
ACID
[Immune complex fiC] = {(Free Ag +IgG) together binds/activates Complement}] all 3 = [Immune complex fiC] ➜ neutrophils release lysosomal enzymes

MOD for Type 4 Hypersensitivity Reaction?
ACID
[Delayed T cell rxn] involving [(hyper)sensitized T-cells that (WITH NO ANTIBODY INVOLVEMENT)] secrete [macrophage-activating cytokines] when encountering certain antigens ➜ macrophage phagocytosis

Define Presbycusis
gradual [high frequency sensorineural hearing loss]
ex.⬇︎ ability to discriminate (make out) speech in a noisy environment

What kind of hearing loss does Presbycusis cause?
gradual [high frequency sensorineural hearing loss]
ex.⬇︎ ability to discriminate (make out) speech in a noisy environment

How does [High Frequency Loss from Presbycusis] affect hearing?
DECREASES ability to discriminate (make out) speech in a noisy environment
Which pharmacologic agents cause asthma exacerbation? (4)
- ASA
- NSAIDs
- [generalBeta Blockers]
- [tartrazine(coloring agents)]

How do ASA and NSAIDs exacerbate asthma?
inhibition of COX1 and COX2 shunts Arachidonic Acid down the [(LipOxygenase → Leukotriene) pathway] –<sup></sup>>🔥Leukotrienes{[🔥LT: C4/D4/E4]→ bronchoconstriction} = [🔥LTB4 → chemotaxis of neutrophils] = asthma exacerbation
🔥=PROinflammatory

fill-in-Blank (19)


NSAIDs and ASA inhibition of COX1 and COX2 shunts Arachidonic Acid down Leukotriene pathway –> INC Bronchial tone ➜ worsens asthma
acute asthma exacerbation ABG shows (⬜ low/high) paCO2
low

status asthmaticus ABG shows (⬜ low/high) paCO2
HIgh

the [5 step Asthma plan] is based on both {[SABA] and [⬜]}
Recite the [5 step Asthma plan]
⼀based on [SABA]
[SABA] use
[NightAwakenings]

“Treating Asthma is SILIO!”
Tx for Asthma Step__:
① [SABA prn]
② [ICSLd]
③ [LABA vs LAA vs Leukotriene🟥]
④ [ICSHIGH DOSE]
5⃣[Oral CTSLd +/- Anti-IgE]
the [5 step Asthma plan] is based on both {[⬜] and [N.A.]}
Recite the [5 step Asthma plan]
⼀based on [NightAwakenings]
🔎N.A. = NightAwakenings
[SABA]use

“Treating Asthma is SILIO!”
Tx for Asthma Step__:
① [SABA prn]
② [ICSLd]
③ [LABA vs LAA vs Leukotriene🟥]
④ [ICSHIGH DOSE]
5⃣[Oral CTSLd +/- Anti-IgE]
Name the 5 ways you can diagnose Asthma?
“Either…
[BD ➜ ⇪ GOE 12E| 12V| 200C]
OR
[Methacholine ➜ ⬇︎GOE 20E| 20V] “
_________________
1. BD ➜⇪ GOE [12% FEV1]
2. BD ➜⇪ GOE [12% FVC]
3. BD ➜⇪ GOE [200 CC FVC]
4. Methacholine ➜⬇︎GOE [20% FEV1]= bH
5. Methacholine ➜⬇︎GOE [20% FVC]= bH

🔎
[🔎BD = BronchoDilator]
[🔎E = FEV1]
[🔎V = FVC]
[🔎C = CC of FVC]
[🔎bH = bronchial Hyperresponsiveness]
asthma exacerbation MOA
Excess TH2 cells (recruited by hypersensitive APC to inhaled allergens) secrete IL4
–>IL4 activates [B-lymphocyte class switching for IgE Ab]
–> IgE binds to Mast cells which will then secrete IL5
–>IL5 Recruits Eosinophils–>which release mediators like [Leukotrienes & Histamine]
→[bronchoconstriction + inflammation]

radiographic finding associated with Asbestos? -2
- calcified pleural plaques
- honeycomb lung (eventually)

MOA: lung macrophages phagocytose [mineral silicate fibers] ➜ release lysosomal enzymes ➜ [ILD fibrosis] ➜ progressive dyspnea/cough ➜ {[+/- bronchogenic carcinoma] > mesothelioma}
Asbestos MOA (6)
lung macrophages phagocytose
[mineral silicate fibers] ➜ release lysosomal enzymes ➜ [ILD fibrosis] ➜ progressive dyspnea/cough ➜ {[+/- bronchogenic carcinoma] \> mesothelioma}
Asbestos Tx
NONE
complications of Asbestos exposure? -3
- [ILD fibrosis]
- Bronchogenic Carcinoma (INC risk with smoking)
- Mesothelioma
MOA: lung macrophages phagocytose [mineral silicate fibers] ➜ release lysosomal enzymes ➜ [ILD fibrosis] ➜ progressive dyspnea/cough ➜ {[+/- bronchogenic carcinoma] > mesothelioma}
Which additional vaccines do COPD patients need? -2
MUST ADD…
1. Pneumococcal Q5 year
2. influenza Q1 year
How does cigarette smoking cause Emphysema -5
ACAMP→ emphysema
- ciliary mvmt abnormalities
- [mucus-secreting gland] hyperplasia
- alveolar macrophage inhibition
- Proteolytic enzyme release from neutrophils
- AntiProteolytic enzyme inhibition
emphysrema MOD = alveolar septae destruction ➜ irreversible dilatation of distal air space + loss of airway elastic recoil (AKA radial traction) ➜ airway collapse during forced expiration) ➜ prolonged expiratory phase + [INC residual volume/air trapping] + [INC WOB] ➜ [dead space physiology(more air ventilated than can be perfused)]
MOD emphysema
alveolar septae destruction ➜ irreversible dilatation of distal air space + loss of airway elastic recoil (AKA radial traction) ➜ airway collapse during forced expiration) ➜ {prolonged expiratory phase + [INC residual volume/air trapping] + [INC WOB]} ➜ [dead space physiology(more air ventilated than can be perfused)]
Antitrypsin is an enzyme that inhibits ______ and _______ in the lung
Patients with Antitrypsin deficiency develop ___________
= trypsinase and elastinase
= Panacinar emphysema
Describe the 2 types of emphysema
- centroacinar = respiratory bronchioles alone
- panacinar =[respiratory bronchioles] + [distal airways (consider Antitrypsin deficiency)]
T or F: Obstructive sleep apnea increases Risk for Cardiovascular Mortality
TRUE
Obstructive Sleep Apnea dx -3
- Polysomnography ⼀ OSA dx confirmation
- [AHI(Apnea-Hyponea Index) ] ⼀ measures OSA severity
- [STOPBang ≤2 = no OSA] ⼀OSA screening

Describe how severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea is measured?
AHI (Apnea-Hypopnea Index) = sum of apnea and hypOpnea events in 1 hour of sleep
5-15/hr = mild
16-30 = moderate
> 30 = SEVERE
T or F: Supplemental Oxygen alone prevents OSA complications
FALSE
(supp O2 + correct upper airway obstruction)
Describe radiographic findings for Granuloma -3
- dense
- centrally calcified
- smoothly bordered

radiographic central calcification in pulmonary nodules indicate ________ [malignant/benign] neoplasia
BENIGN
(“popcorn”, “onion skin”, “bull’s eye”)
radiographic eccentric calcification in pulmonary nodules indicate ________ [malignant/benign] neoplasia
[MALIGNANT or BENIGN]
Bronchial carcinoid tumors are ______-grade malignant neoplasm made of ___ cells , and about _____% of all lung tumors
low ; neuroendocrine ; 2
Why do Carcinoid tumors cause
_________ in lungs?
[lobar atelectasis] ; [Carcinoid tumors are located in the bronchus(which → lobar atelectasis)]
patients GOE _____ years old with significant smoking hx, should receive _____ for pulmonary nodules
45 ; biopsy
what are the 3 most critical parameters to stabilize in Anaphylaxis
ABC
- (A) airway (obstructed)?
- (B) Breathing/bronchioles bronchoconstricted?
- (C) hypOtension

what type hypersensitivity is Anaphylaxis?
1A

examples of [type 1 “A” hypersensitivity reaction] -5
- [type 1 AAAA hypersensitivity reaction]*
1. [Allergy (PCN)]
2. Anaphylaxis
2. Atopic (Asthma, rhinitis, eczema, hay fever)
3. IgA deficient patients ➜if receive blood products ➜ possible anaphylaxis (px = use WASHED RBC)



note: PGE1 also keeps PDA patent during cyanotic heart defects = “kEEps ur Penis and PDA Open”


note: PGE1 also keeps PDA patent during cyanotic heart defects = “kEEps ur Penis and PDA Open”


Which Leukotriene(s) responsible for
Bronchoconstriction?
LTC4 / LTD4 / LTE4

C/D/E
Which Leukotriene(s) responsible for
Neutrophil Chemotaxis?
LTB4

B
[PGE1 Prostaglandin]
Function (2)
_________________
Rx
- *PENIS*vasoDILATOR
- “kEEps PDA… patent”
_________________
[AlprostadilPGE1 Prostaglandin]
“PGE1 kEEPS Penis and PDA open!”

[PGE2 Prostaglandin]
Function (2)
_________________
Rx
1.ANTIinflammatory
2.[⇪ Uterine tone]
_________________
[DinoprostonePGE2 Prostaglandin]

B
[PGF2 Prostaglandin]
Function
_________________
Rx
[⇪ Uterine tone]
_________________
[CarboprostPGF2 Prostaglandin]

B
[pGi2 prostaCyclin]
Function (3)
_________________
Rx
- ANTIinflammatory❄
- [⬇︎ platelet aggregation](⬇︎clotting)
- vasoDILATOR
_________________
[EpoProstenolpGi2 prostaCyclin]

B
[TXA2 Thromboxane]
Function (3)
- 🔥PROinflammatory
- [⇪ platelet aggregation]
- vasoconstrictor

B


