2 ⼀NEUROLOGY II Flashcards
(289 cards)
53
In regards to Carpal Tunnel, the ⬜ n. courses between the ⬜ and ⬜ muscles before crossing under the ⬜ inside the carpal tunnel
In regards to Carpal Tunnel, the Median n. courses between the [Flexor Digitorum superficialis] and [Flexor Digitorum Profundus] before crossing under the [Flexor Retinaculum transverse carpal ligament] inside the carpal tunnel

Although [minor head trauma] does NOT usually indicate [nHCT]
these 3 “special” groups do…
[HIGH RISK: subjects | symptoms | signs]
_________________
Name the [HIGH RISK subjects]? (6)
subjects AKA “patients”
1. age ≥65
2. Coagulopathic
3. IntoxicationDrug/EtOH
4. [PHM([ped vs auto])]
5. [PHM( [vehicular ejection])]
6. [PHM([Fall from height])]
| PHM = Patients with High-Risk Mechanism

[minor head trauma] does NOT usually indicate [noncontrast Head CT].
Although [minor head trauma] does NOT usually indicate [noncontrast Head CT], there are 3 “special” groups that do…
[HIGH RISK: subjects | symptoms | signs]
_________________
Name the [HIGH RISK symptoms]? (7)
- Retrograde amnesia ≥30min before injury
- [Vomiting ≥ 2]
- Seizure
- Severe HA
- AMSincluding LOC
- Neuro deficit
- GCS ≤14

Minor head trauma does NOT usually indicate [noncontrast Head CT].
There are 3 groups that require [noncontrast Head CT] after Minor head trauma..
[HIGH RISK: subjects | symptoms | signs]
_________________
Name the [HIGH RISK signs]? (2)
- depressed skull fx
- Basilar skull fx (CSF drainage, hemotympanum, [battle’s postauricular ecchymosis], periorbital hematoma)

Injury to the ⬜ causes ⬇︎ ability to Dorsiflex
[PF(common or deep) nerve]
________________
foot dropPED

✏️PF = [Peroneal⼀Fibular] - L4 (S1-S2)
Lennox Gastaut Dx?
Slow Spike-Wave EEG
________________
Lennox Gastaut
Lennox Gastaut CP-2
Lennox Gastaut
- Lala Land Retarded before 5 yo
- Generalized Tonic Clonic Seizures SEVERE
Levodopa is used to treat Parkinson’s Disease
Early SE?-3
_________________
Late SE?
Early SE (HAD) = Hallucinations/Agitation/Dizziness
_________________
Late SE (5-10 yrs post tx) = Involuntary mvmnts
[Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB)] Tx- 2
footnote
1. Rivastigmine AChinesterase inhibitor
- [2nd Gen Antipsychotic] for visual hallucination
* REMEMBER THAT DLB PTS ARE SENSITIVE TO ANTIPSYCHOTICS*
“DLB at the DMV “
List the difference between Primary and Secondary Generalized Tonic Clonic Seizures
________________
Seizure ATTaCK
Primary GTC occur when electrical discharge simultaneously comes from diffuse bilateral cortical areas (i.e. Absence)
vs
Secondary GTC comes from the spread of a [simple partial seizure]
List the sequence of events for a [GTC Seizure] - 5
Seizure ATTaCK
1st: Aura (nausea/dizziness) vs Simple Partial
2nd: Tonic: Sudden Stiffness–>Falling and cry out
3rd: [Time Out: aPNEA] –> Cyanotic, dusky face
4th: Clonic convulsions + oral involvement
5th: [Krazed: Postictal Amnesia (pt only recalls aura) + Lethargy + incontinence]
Pt just fell and started GTC seizing right in front of you!
How should you manage them? - 4
Seizure ATTaCK

1st: Roll pt onto side
2nd: Stabilize Head BUT NOT THEIR MVMNTS
3rd: KEEP THINGS OUT OF MOUTH OR AROUND PT
4th: ER if > 5 min
Main Features of TIA - 3
TIA(Transient Ischemic Attack) is
1. {Transient = [usually < 20m but ≤60m REQD]}
- {Ischemia (without infarction) is FOCAL(→ FOCAL neuro sx)}
- {Attack is [REVERSIBLE⼀NO residual sx⼀NO residual radio]}
🔎radio = radiomanifestations (⊝MRI)

Management for Epidural Spinal Cord Compression? -3
- [High Dose Dexamethasone IV]
- MRI
- Neurosurg consult
[Medial Midbrain Syndrome of Weber] etx
________________
CP-2
PCA infarct ➜ damage to –>
- [Oculomotor CN3] → [iPL DOPe]
- [Crus CerebriCST & CorticoBulbar)] → [CTL Hemiparesis→ Face, UE, LE]
_________________
DOPe = [(Down & Out eye) + Ptosis + (eye dilated)]

Memantine
MOA
_________________
Indication
Blocks Glutamate from binding to NMDA Receptor
_________________
Moderate to Severe Alzheimer’s
Memory depends on a BL 4-way circuit
What is this circuit?-4
“Having Fun Memories Around”
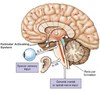
[Hippocampus temporal lobe] –> Fornix –> [Mamillary Bodies] —> [ANT Thalamus]

Meniere’s Disease etx
⬆︎endolymphatic fluid in inner ear–> Membranous labyrinth swelling and rupture –> [KRE- K+ Rich Endolymph] leak into [Na+ rich perilymph] –> abnormal hair cell function –> VTNH sx
**Very Terrible Nystagmus & Hearing **
_________________
same sx as Acute Labyrinthitis

Acute Labyrinthitis CP - 4?
**Very Terrible Nystagmus & Hearing **
- Vertigo
- Tinnitus
- Nystagmus
- Hearing loss which –> Permanent eventually
same sx as Meniere’s Disease

MeningoVascular syphilis infects ⬜ , which can present as stroke (2/2 to ⬜) , and is confirmed via ⬜
What is the tx?
[subarachnoid space vessels] ; intracranial arteritis ; [CSF VDRL]
_________________
PCN

Meniere’s Disease tx - 5
1st: Diet(restrict Na+, caffeine, Nicotine, EtOH)
2nd: [antihistamines ⼀Benzo ⼀antiemetics]
3rd: DiureticsLong Term
_________________
Sx = VTNH (Vertigo, Tinnitus, Nystagmus, Hearing loss)

Mgmt of Epidural hematoma -3
- [Reduce ICP“Stop My Head Swelling!”]
a) SBP > 100
b) Mannitol IV
c) [Hyperventilate to pCO2 25-30]
d) Stress px(H2🟥, PPI)
_________________
2. Remove hematoma
_________________
3. Cauterize Dura (Electrocoagulate & Ligate middle meningeal a. of the dura arteries)

Name the 5 components of reducing Intracranial Pressure?
“Stop My Head Swelling (Cancer) !”
a) SBP > 100
b) Mannitol IV
c) [Hyperventilate to pCO2 25-30]
d) Stress px(H2🟥, PPI)
➜ e)+/- {CTS (for [CA|Trauma|Sickness_infxn] etx}
Most common side effects of INH isoniazid (2)
Injuries to
Nerves= Neuropathy (Pyridoxine B6 = tx/px)
and
Hepatocytes= Hepatitis - THIS IS SELF LIMITED AND RESOLVE WITHOUT INTERVENTION