22: Subjunctive Mood Verbs Flashcards
(28 cards)
ἀμήν
truly (amen)
ἄν
(not usually translated; indefinite particle) “ever”
ἐάν
if, if ever (combination of εἰ and ἄν)
ἐὰν μή
unless; if not
ἕως
until; while (adverb); as prep. + gen. to, until
ἵνα
in order that; that
ὅπου
where
ὅπου ἄν or ὅπου ἐάν
wherever, whenever
ὅπως
in order that; that
ὅταν
when, whenever (from ὅτε + ἅν)
ὅτε
when
οὕτως
so, thus, in this way (adverb from οὗτος + ὡς)
ὡς
as; like (with numbers: “about”, “approximately”)
πῶς
how?
τέρας, τέρατος, τό
wonder, miracle
Recite Present Active Subjunctive
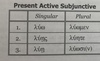
Recite Present Middle/Passive and Deponent Subjunctive

Recite Aorist Active Subjunctive

Recite First Aorist Middle/Deponent Subjunctive

Recite First Aorist Passive/Deponent Subjunctive

What are the irregular verb patterns we have seen until now?
- Contract Verbs
- Second Aorists
- Liquid Verbs
Recite Subjunctive forms of ἐιμί

What does the subjunctive mood express?
An indefinite event whose agent, object, time, condition being met, etc. is not expressed or left open.
What are the 4 most important uses of the subjunctive mood and their helping clauses?
- Purpose or Result Clauses (ἵνα, ὅπως)
- Future Condition (ἐάν, έάν μή)
- Indefinite Temporal Clause (ὅταν)
- Emphatic Negation (οὐ μή)


