16 Dermatologic Diseases Flashcards
(118 cards)
What is the best known form of ectodermal dyslpasia?
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
What are distinguishing traits of people with Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia?
- fine, sparse hair
- brittle nails
- hypoplastic/absent salivary glands
- abnormal dental crowns
Patient also has fine hair and high heat intolerance. What do they likely have?

Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
Hypohidrotic E.D. has a predeominance for which sex, and is linked with which sex chromosome?
Male predominance, X-linked
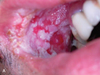
What defect in keratins presents as white, corrugated plaques bilaterally on buccal mucosa?
White sponge nevus
what is a genetically determined skin disorder?
Genodermatosis
White sponge nevus is recessive or dominant?
Autosomal dominant
What does this suggest? (hint: bilateral presentation)

white sponge nevus
When did these lesions most likely first appear? (hint: presents bilaterally and autosomal dominant)

birth or early childhood
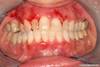
What presents intraorally as a white lesion with a warty or roughened surface?
Warty Dyskeratoma
Warty dyskeratomas histopathologically identical to what disease?
Darier disease
Pt is over 40 and presents with this asymptomatic, rough-surfaced lesion on keratinized mucosa. What is it?
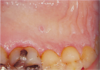
Warty Dyskeratoma
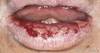
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome is characterized by what?
- freckle-like lesions on skin around hands, mouth, and intraorally
- intestinal polyposis
- predisposition to develop cancer
What is Peutz-Jegher’s inherited as?
Autosomal dominant
What is unique about the freckles seen with Peutz-Jegher’s Syndrome?
They don’t change darkness with sun exposure like regular freckles
Peutz-Jegher’s patients are __ times more likely to develop cancer in their lifetime.
18 times more likely
Why do Peutz-Jegher’s patients commonly experience intestinal obstruction?
Intussusception, which is telescoping of the proximal bowel into the distal portion
If Peutz-Jegher’s Syndrome, what else might they present with?

Perioral and intraoral freckling
Also has intestinal polyps. What do they have?

Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
What are some characteristics of tuberous sclerosis?
- mental retardation
- potato-like growths (tubers)
- epilepsy
- shagreen patches
- ash-leaf spots
- angiofibromas of skin
- ungual fibromas
A patient with tuberous sclerosis might show facial angiofibromas where on the face?
nasolabial fold area
What is a shagreen spot?
A connective tissue hamartoma (benign neoplasm that grows at same rate as tissue around it)
What is an ash-leaf spot?
an ovoid area of hypopigmentation
What heart condition is associated with tuberous sclerosis?
Rhabdomyoma