12.1 Soft Tissue Tumors Flashcards
(63 cards)
What is a malignant tumor of the connective tissue called?
Sarcoma
What is a malignant neoplasm of the epithelium called?
Carcinoma
What is the most common tumor in the oral cavity?
Fibroma
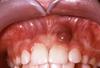
What could this be?

Fibroma
Where is the most common place to find the most common tumor of the oral cavity?

Buccal mucosa along the occlusal line (pathology = fibroma)
What is this? What causes it?

Fibroma, caused by irritation or trauma
What is a fibroma?

Reactive hyperplasia of the connective tissue due to local irritation or trauma
What are these called?

Retrocuspid papilla
How do these normally present?

Typically bilateral, and in 99% of children (regress with age)
These typically have a papillary surface and occur at a younger age than other types of fibromas. What is this?
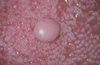
Giant cell fibroma
Giant cell fibromas don’t typically get larger than ______mm wide.
5-6mm
What is this?

Epulis fissuratum
What causes this?

Epulis fissuratum is IFH associated with the flange of an ill-fitting denture
What is this leaf-like projection?

Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia (IFH)
What is this called?

Epulis fissuratum
What is this?

Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
What causes this?

Wearing a denture too long or it irritates the underlying tissue
What other pathosis should you think to look for with this patient?

Candidiasis (patient has IPH)
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia is related to what three things?
- Ill-fitting denture
- Poor denture hygiene
- Wearing the denture for 24 hrs a day
What is the oral counterpart of a dermatofibroma?
Fibrous histiocytoma
Do older or younger patients usually present with fibrous histiocytoma?
Older (younger usually present with dermatofibroma)
Pt is older and histologically this lesion appears with a “whirly” pattern. What could this be?

Fibrous histiocytoma
What results from overproduction of hyaluronic acid by fibroblasts?
Oral focal mucinosis
Pt is a young female and test reveals a high concentration of hyaluronic acid. What is this?
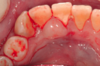
oral focal mucinosis