156 Move Exam Flashcards
(52 cards)
A.Identify this cell.
B.This cell acts against (bacteria, parasites, allergies).

A.eosinophil
B.parasites
A.Identify this cell.
B.T/F This is the largest among all leukocytes

A.monocytes
B.T
A.Identify this cell
B. T/F All subtypes of this cell are involved in innate immunity.

A.lymphocyte
B.F
A.identify the cell
B.this cell against (bacteria, fungi, alllergies)

A.basophil
B.allergies
[Neutrophils]
A) Which is the mature form?
B) Which is the immature form?

A) B
B) A
A.Which came first, A or B?
B.identify A & B, respectively

A. A
B. A: promyelocyte. B: myelocyte
A.identify this RBC abnormality
B. T/F This cell has increased resistance to osmotic lysis

codocyte
[Codocyte]
found in all except:
A.Hemoglobin C Disease
B.Sickle Cell Anemia
C.Thalassemia
D.Leukemia

D
This cell is called __ and it is found in the ff conditions, except:
A. Hypochromic anemia
B. Brain disease
C. Hemolytic anemias
D. Post-splenectomy
codocyte
; B (brain disease)
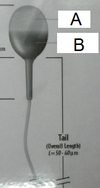
A. Identify the structure pointed using purple arrows.
B. T/F The presence of this in urine is pathologic in cause

A. fine granular casts
B. F
A. Identify the slide
B. Most important clinical indication
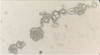
A. uric acid crystals
B. diagnosis of gout
A. identify the slide
B. T/F [insert your answer in A] - contaminants always

A. yeast cells
B. No. May also signify ppathologic condition
A. identify the slide
B. Presence of dysmorphic forms of this cell in urine: suggests ___

A. RBCs in urine
B. glomerular disease such as glomerulonephritis
A. identify the slide
B. two general, not necessary renal, conditions in which this may occur

A. WBCs in urine
B. fever, post-strenuous exercise
A. identify the slide
B. Is this only present in urine of sick people?

A. hyaline cast
B. no
A. identify the slide
B. significance

A. squamous epithelial cell
B. possible contamination of specimen w/ skin flora
A. identify the slide
B. increse of this in urine signifies ___

A. mucous threads
B. bacterial irritation/inflammation
A. identify the slide
B. Are these water-soluble?

A. sulfonamide crystals
B. yes
A. identify the slide
B. T/F This is present in urine of healthy people

A. RBC cast
B. F
A.identify slide
B.enumerate two ways on how this can be forme

A. hippuric acid crystals
B. 1. heating benzoic anhydride with glycine
2. heating benzamide with monochloroacetic acid
A. identify the slide
B. most likely with…. (proteinuria? glycosuria? pyuria?)

A. cholesterol crystals
B. proteinuria
A. identify the slide
B. occurs @ urine with (low, neutral, high) pH

A. cystine crystals
B. acid urine / low pH
A. identify slide
B. When seen, it’s of high clinical value because ___
A. yeast cells cast
B. indicative of pyelonephritis