(11) Contractility and Cardiac Output (Ballam) Flashcards
What are the 4 factors that you need to consider with cardiac output?
Heart rate
Contractility
Preload
Afterload

What is contractility?
How foreceful the cardiac muscle contracts when stimulated
What is positive iontropy?
Increased force of contraction
What is negative iontropy?
Decreased force of contraction
Contractility is generally proportional to…
Amount of calciu that is available to troponin on actin filaments
Define Preload
Wall tension in RV or LV just before contraction is initiated
Define Afterload
Pressure in ventricle that is required to eject blood
Important concept with afterload:

Higher volume of blood to eject = lower velocity of ejection
Lower volume of blood to eject = higher velocity of ejection
Identify where preload and afterload are on the graph


What is the stroke volume equation?
Stroke volume (volume of blood ejected by ventricle with each beat)
SV = EDV -ESV
(usually about 70 mL)
What is the ejection fraction equation?
Ejection fraction - fraction of the EDV ejected in each stroke volume
EF% = SV /EDV
(Usually about 55%)
What is the equation for cardiac output?
CO (or Q) = SV x HR
*usually about 5L/min
What is the frank-starling relationship?
Volume of blood ejected by the ventricle depends on the volume present in the ventricle at the end of diastole
*relates length-tension to functionality
Graphically, show what a positive vs. negative iontropic effect would look like

Ventricular Pressure Volume Loops
Describe what is occuring in:
1 to 2
2 to 3
3 to 4
4 to 1
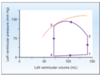
1 to 2 | Isovolumetric contraction
2 to 3 | Ventricular ejection
3 to 4 | Isovolumetric relaxation
4 to 1 | Ventricular filling

Draw what increased:
Preload
Afterload
Contractility
Would look like in the Left Ventricle in comparison to normal

Sympathetic stimulation causes a __________
Positive iontropic effect on CO
Parasympathetic influence on CO includes ….
Negative ionotropic effect in atria only
Increased heart rate (positive chronotropic effect) in turn…
Increases contractility (positive ionotropic effect)
What is the positive staircase effect (bowditch staircase)?
More Ca2+ enters cells and taken up into SR
What is postextrasystolic potentiation?
Arrhythmia, extra beat
What does the Fick principle measure?
Cardiac output
Draw the cardiac function curve

The cardiac function curve represents __________ relationship
Frank starling




