11-13 - The Renal System Flashcards
(85 cards)
The majority of blood flow to the kidneys goes to the…
Renal cortex
(93%)
Which type of nephron is responsible for the production of concentrated urine?
Juxtamedullary nephrons
Name the 6 main parts of the nephron…
- Bowman’s capsule
- Proximal tubule
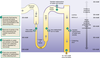
- Loop of Henle
- Distal tubule
- Collecting tubules
- Collecting duct
The vasa recta surround the…
Nephron
Describe the vasculation of the nephrons…
- Afferent arterioles
- Capillaries (at glomeruli)
- efferent arterioles
- peritubular capillaries (vasa recta)
- renal veins
- inferior vena cava
Outline the 3 functions of the kidneys…
- Homeostatic regulation of water/ion content of blood
- Excretion of metabolic waste (urea, creatinine, urobilinogen etc)
- Production of hormones
Name 4 hormones produced or activated in the kidneys…

- erythropoietin
- renin
- prostaglandins and kinins
- vitamin D (activated)
Which 3 processes occur at the nephron?
- Glomerular filtration
- Tubular reabsorption
- Tubular secretion
All plasma constituents are filtered through the glomerulus, except…
Larger proteins
(>67kDa)
GFR stands for…
Glomerular filtration rate
The average GFR is…
180L/day
__% of cardiac output is recieved by the kidneys and __% of plasma filters into the nephron (this is known as the _______ ___________)
25% of cardiac output is recieved by the kidneys and 20% of plasma filters into the nephron (this is known as the filtration fraction)
Podocytes are cells in the Bowman’s capsule in the kidneys that wrap around the capillaries of the…
Glomerulus
The renal corpuscle is the bundle of ___________ ___________ within _____________ ___________
The renal corpuscle is the bundle of glomerular capillaries within Bowman’s capsule

Glomerular capillaries are ___________, allowing blood to be filtered out
Glomerular capillaries are fenestrated, allowing blood to be filtered out

The basement membrane between the fenestrated capillary and the podocyte feet forms the main…
Filtration barrier

99% of filtrate is…
a) Excreted
b) Reabsorbed
c) Secreted
d) Filtered
99% of filtrate is…
a) Excreted
b) Reabsorbed
c) Secreted
d) Filtered
1% of filtrate is…
a) Excreted
b) Reabsorbed
c) Secreted
d) Filtered
1% of filtrate is…
a) Excreted
b) Reabsorbed
c) Secreted
d) Filtered
A small amount of secretion contributes to the excreted urine, which mainly occurs at the…
Proximal convoluted tubule
Reabsorption involves the movement of solutes out of the __________ and back into capillaries via _________ ___________ mechanisms.
Reabsorption involves the movement of solutes out of the filtrate and back into capillaries via epitheleal transport mechanisms.
What is the difference between epithelial transcellular transport and paracellular transport…
Epipethelial transcellular transport = through cells/ across cell membranes
Paracellular transport = via cell-cell junctions (doesn’t cross cell membranes)
Summarise the cellular mechanisms by which solutes move from the filtrate across the epithelial cells to the peritubular capillary…
- Co-transporters
- Transporters
- Membrane pumps
- Membrane carriers
- Membrane channels
Summarise the passive mechanisms by which solutes move from the filtrate across the epithelial cells to enter the peritubular capillaries…
- Leak channels
- Diffusion (if membrane permeable solute)
- Paracellular transport (via cell-cell junctions)
The route taken by solutes to cross the epithelial cells depends on ____________ gradient and the ___________ of epitheleal junctions.
The route taken by solutes to cross the epithelial cells depends on electrochemical gradient and the permeability of epitheleal junctions.