wk 7 - Water and Electrolyte Balance Flashcards
A patient with Conn’s syndrome is expected to have _____ ADH, high-normal sodium, _____ potassium, and _______
a) Low
b) High
c) Acidosis
d) Alkalosis
A patient with Conn’s syndrome is expected to have high ADH, high-normal sodium, low potassium, and alkalosis

Water deprivation test could stimulate _____ secretion.
Water deprivation test could stimulate ADH secretion.

The two main signs of diabetes insipidus are:
a) High plasma osmolality, low urine osmolality and polyuria
b) High urine osmolality, high urine osmolality and polyuria
a) High plasma osmolality, low urine osmolality and polyuria
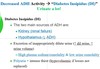
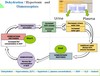
in increase in plasma osmolarity triggers thirst and release of ___________
in increase in plasma osmolarity triggers thirst and release of ADH
The effect of angiotensin II to stimulate aldosterone is amplified in ____________ states
The effect of angiotensin II to stimulate aldosterone is amplified in hyperkalaemic states

The two main organs for lack of ADH are:
a) Hypothalamus & liver
b) Kidney & brain
c) Kidney & hypothalamus
d) Liver & spleen
c) Kidney & hypothalamus

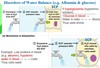
extracellular fluid is comprised of ____% interstitial fluid and ____% plasma
extracellular fluid is comprised of 80% interstitial fluid and 20% plasma
rapid and servere hyponatremia that causes entry of water into brain cells, which swell and manifest seizures, coma, respiratory arrest and death is termed _______________
rapid and servere hyponatremia that causes entry of water into brain cells, which swell and manifest seizures, coma, respiratory arrest and death is termed water intoxication
What factors are used to directly monitor the body fluid or electrolytes balance?
Volume and osmolarity
What is the effect of dehydration on:
Body water uptake?
increased body water uptake

a person feels thirsty when there is an increase in concentraion of what electrolyte in his/her plasma?
sodium
Cells move water molecules by __________
Cells move water molecules by osmosis

ANP and BNP are released by _______ _______ tissue
ANP and BNP are released by cardiac muscle tissue

Osmotic concentration, formerly known as osmolarity, is the measure of solute concentration, defined as the number of osmoles (Osm) of solute per _______.
a) Litre
b) Kg
Osmotic concentration, formerly known as osmolarity, is the measure of solute concentration, defined as the number of osmoles (Osm) of solute per Litre

Water deprivation test is used to differentiate between a patient with diabetes insipidus and other causes of :
a) Polyphagia
b) Polydipsia
c) Polyuria
b) Polydipsia

_____tonic = Concentrated
_____tonic = diluted
Hypertonic = Concentrated
Hypotonic = diluted

The extracellular fluid comprises of ____________
a) Interstitial fluid
b) Plasma
c) Plasma and interstitial fluid
d) Tissue cells
c) Plasma and interstitial fluid

high blood pressure is the result of a _________ ECF.
high blood pressure is the result of a hypotonic ECF.

The body’s homeostatic mechanisms that monitor and adjust body fluid composition respond to changes in the ____, not in the _____.
The body’s homeostatic mechanisms that monitor and adjust body fluid composition respond to changes in the ECF, not in the ICF.

Antidiuretic hormone _________ water reabsorption, thus _________ urinary water loss, _________ urine concentration and __________ plasma concentration.
a) Increases
b) Decreases
Antidiuretic hormone:
- increases water reabsorption
- decreases urinary water loss
- increases urine concentration
- decreases plasma concentration

_____________ refers to water created inside a living organism through their metabolism
Metabolic water refers to water created inside a living organism through their metabolism

To restore overhydration, secretion of ADH should __________
To restore overhydration, secretion of ADH should Decrease

If the extracellular fluid osmotic concentration increased, water will move from
a) ECF to ICF
b) ICF to ECF
b) ICF to ECF

After giving a patient a vasopressin analogue, if the patient is still failing to concentrate urine, then the patient has a ________ disease.
After giving a patient a vasopressin analogue, if the patient is still failing to concentrate urine, then the patient has a kidney disease.