wk 2 - Gluconeogenesis & General Regulatory Mechanisms COPY Flashcards
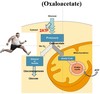
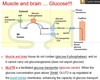
In Cori Cycle, lactate is produced in the ———– (organ) and it is converted to ———- (carbohydrate).
In Cori Cycle, lactate is produced in the liver and it is converted to glucose.
10?
(pathway)

lipolysis
(triacylglycerols/fatty acids are broken down via beta oxidation to produce acetyl coa molecules & glycerol)
Glycerol is mostly found in the adipose tissue (subcutaneous), it goes to the —-where it gets converted to —-, which can be used as a fuel in other tissues.
a) Adipose tissue
b) Muscle
c) Liver
d) Glucose
e) Glycogen
Glycerol is mostly found in the adipose tissue (subcutaneous), it goes to the liver where it gets converted to glucose, which can be used as a fuel in other tissues.

Which 3 reactions during glycolysis are irreversible during gluconeogenesis?
a) Step 1, 8 & 10
b) Step 1, 3 & 10
c) Step 1-3
d) Step 8-10
b) Steps 1, 3 & 10
(3 kinases)
S1 - hexokinase requires 2 ATP
S3 - PFK-1 requires 2 ATP
S10 - pyruvate kinase requires 4 ATP

The liver itself can’t use the ketone bodies as a source of energy as it lacks the enzyme ____ ________ ___ ________, also called _________, that is responsible for producing acetyl CoA from the ketone bodies.
The liver itself can’t use the ketone bodies as a source of energy as it lacks the enzyme β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase, also called thiophorase, that is responsible for producing acetyl CoA from the ketone bodies.

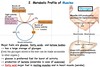
during starvation, in what order are the following molecules utilised as fuel?
- proteins (muscle)
- ketones
- glucose
- fatty acids + minimal proteins
- glycogen
- Glucose
- Glycogen
- Fatty acids + minimal protein
- Ketones
- Proteins (muscle)
…then death

during starvation, the human body’s first priority is to:
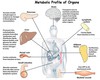
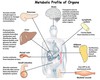
provide sufficient glucose to brain and other tissues that are dependent on it (Figure A)

8?
(pathway)

glycolysis - TCA cycle
pyruvate is sent from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria via pyruvate translocase, and is then converted to acetyl CoA via pyruvate deydrogenase complex (PDH) to enter the TCA cycle
________ is an important product for the synthesis of ATP and citrate via the Krebs Cycle. It is produced from:
- fatty acids (during beta oxidation - lipolysis)
- glucose (end product of glycolysis)
- amino acids (during Cahill cycle)
- ketone bodies (precursor for ketogenesis)
- oxaloacetate (during Gluconeogenesis)
- and ethanol (via ADH)
Acetyl CoA

If acetyl CoA is the precursor for production of energy via TCA cycle, what is the purpose of converting acetyl CoA by the liver mitochondria to ketone bodies, then re-converting ketone bodies to acetyl CoA in the tissues?
ketone bodies are water soluble and can be transported from the liver to other tissues easily without the need of albumin or lipoproteins as carriers.

In the human body, which fuel store can last for the longest time?
adipose fat
Lymphatic cells absorb and transport fatty acids and lipids as _____ from the digestive system
Lymphatic cells absorb and transport fatty acids and lipids as lymph from the digestive system
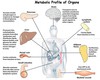
When _________ stores are depleted, the liver is able to synthesize glucose from lactate, via ___________

When Glycogen stores are depleted, the liver is able to synthesize glucose from lactate, via gluconeogenesis
13?
(pathway)

ketogenesis
acetyl CoA is used to make ketone bodies - betahydroxybutyrate & acetoacetate
A ketogenic amino acid can be degraded directly into ________, which is the precursor of ketone bodies
A ketogenic amino acid can be degraded directly into acetyl-CoA, which is the precursor of ketone bodies

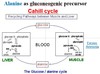
When do muscle cells use the Cahill cycle and not the Cori-cycle?
When the muscles need to get rid of ——-
a) Ammonia
b) Oxaloacetate
c) Water
d) Lactic acid
a) Ammonia

In the Cahill cycle, pyruvate is converted to alanine in muscle cells, then to glucose in the liver when there is a need to transfer ammonia to the liver.
Compartmentation is the seperation of ________ and _________ pathways
Compartmentation is the seperation of synthesis and degradation pathways

What is the main hormone secreted to reduce the blood glucose level?
a) Glucagon
b) Growth hormone
c) Insulin
d) Oestrogen
c) Insulin
Glycolysis produces —– ATP, whereas, gluconeogenesis consumes —- ATP.
Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, whereas, gluconeogenesis consumes 6 ATP.
Glycogen is formed from ——, which is glycolysed to —-, then to —–, then getting stored in ——— as glycogen.
a) Adipose tissues and liver
b) Glucose
c) Glucose-1-phosphate
d) Glucose-6-phosphate
e) Muscle and liver
Glycogen is formed from Glucose, which is glycolysed to Glucose-6-phosphate then to Glucose-1-phosphate, then getting stored in Muscle and liver as glycogen.

The glycogen stored in muscle is made accessible to be used by other organs.
a) True
b) False
b) False

- Only the glycogen stored in the liver can be made accessible
to other organs.
The Cori cycle (lactate to glucose) normally accounts for 20% of glucose turnover, but it was shown to be increased to 50% in ————— patients.
a) Arthritis
b) Cachectic cancer
c) Cirrhosis
d) Diabetic
e) Glucoma
The Cori cycle (lactate to glucose) normally accounts for 20% of glucose turnover, but it was shown to be increased to 50% in Cachectic cancer patients.
(Cachexia is characterized by loss of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle mass - wasting syndrome)

ethanol is primarily metabolised by the liver, converted to ___________ by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) which takes place in the cytoplasm. This toxic product is then converted to ______ by aldehyde dehydrogenase
(some is metabolised in the stomach - the stomach lining contains ADH)
ethanol is primarily metabolised by the liver, converted to acetaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) which takes place in the cytoplasm. This toxic product is then converted to the relatively inert acetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase
(some is metabolised in the stomach - the stomach lining contains ADH)

GLUT2 is a facilitated glucose transporter (glucose carrier). When the glucose concentration goes above 30mM, GLUT2 is up-regulated at the _____ _______ ________, enhancing the capacity of glucose transport
GLUT2 is a facilitated glucose transporter (glucose carrier). When the glucose concentration goes above 30mM, GLUT2 is up-regulated at the brush border membrane, enhancing the capacity of glucose transport.