Week 3 - Bacterial Skin Infections Flashcards
What are the 3 key reasons why bacteria infect skin?
- Skin Integrity break down
- Poor host immunity
- Skin’s normal flora is compromised
What is the most common skin infection in the UK?
Impetigo/cellulitis/boils
(Staph infections)
What is the most common cause for skin infections in developing countries?
- TB
- Leprosy
- Impetigo
90% of cases of Impetigo are due to Staph A.
What is the second most common organism?
Group A Streptococci
What is the topical treatment for localised impetigo?
Fucidin TDS
+
Antispetic povidine Iodine for 1 week
What are the antibiotics used for extensive Impetigo due to Staph and the Abx for Strep please?
Flucloxacillin 500mg QDS for 7-10 days for Staph.
Penicillin V 500mg QDS for 7-10 days for Strep
What are the school exclusion criteria for impetigo?
Avoid school whilst lesions are weepy and crusty
If someone gets recurrent impetigo, cellulitis or boilds…
What should you do?
- Skin swabs (To exclude MRSA or PVL Staph)
- Nasal swabs
- Consider immunosuppression/diabetes
If nasal swabs show staph or MRSA, how do you treat this?
Mupirocin (TDS for 1 week)
Don’t forget to Ix and treat the whole family - Abx, Chlorhexidine, Mupirocin etc)
What is cellulitis of the face called?
Where on the face does it usually star?
Erysepilas
It usually starts under the eye or bridge of the nose.
How can you confirm if cellulitis is due to streptococci infection?
ASOT (Streptococcal titres)
What is the treatment for cellulitis?
Oral penicillin or Erythromycin 500mg BD
What condition is this?
What is it’s treatment
Who is more likely to get it?

Dissecting cellulitis of the scalp
Oral tetracyclines, Intralesional steroids or surgery
Fitzpatrick skin type 6
What is this?
What skin type is more likely to get it?

Sycosis Barbae (Folliculitis due to shaving)
Fitzpatrick skin type 6
What are the different types of folliculitis
- Hot-tub folliculitis
- Pityrosporum folliculitis - fungal folliculitis
- Steroid acne
- Itchy folliculitis - can be a sign of HIV infection
- Folliculitis Keloidalis - more common in black males. Avoid shaving and treat with long term antibiotics (6 months)
32y/o IV drug user has this on his skin.
What is this?
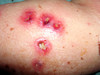
Echtyma
(Impetigo that invades the dermis)
If someone gets it…consider immunosuppresion - diabetes, HIV etc.
What 2 genes are responsible for hydradenitis suppurativa and how is it inherited in some people?
Autosomal dominant
PSENEN gene & NCSTN gene
What are some other causes of hydradenitis suppurativa?
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Drugs e.g. lithium
- Hormones
- Infection
- Apocrine gland structure
What are some treatments for HS?
- Weight loss
- Chlorhexidine soap
- Oral antibiotics (Erythromycin, Tetracyclines)
- Oral antiandrogens
- Isotretinoin/acitretinin
- Oral zinc sulphate 10mg/kg (max 400-600mg daily)
- Axillary botox.
What is this?
How can you tell the difference from Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis?

Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome
It doesn’t involve the mucosa (mouth etc) because it only attacks the outer epidermis.
What is the cause of Scarlet Fever?
Strep Pyogenes
(Group A Strep)
What are some complications of scarlet fever?
- Arthritis
- Meningitis
- Osteomyelitis
What is this and what causes it?

Erythrasma
Caused by Cornebacterium Minutissimum
It flouresceces coral pink under a Wood’s light.
How do you treat Erythrasma?
Oral Erythromycin 500mgQDS for 10 days
What is this?
What Causes it?
How do you treat it?

- Pitted Keratolysis
- Corynebacterium
- Topical antibiotics - Erythromycin, Fusidic Acid orclindamycin-twice daily for 2-4 weeks) + Anti-sweating treatment.
What two infectious skin conditions does Corynebacterium cause?
Pitted Keratolyis
and
Erythrasma


