Connective Tissue Disease Flashcards
In SLE, who are more commonly affected, men or women?
Women (8:1)
What is the peak age of onset in SLE?
Mid-thirties
What drugs can cause SLE?
Hydrazine and Isoniazid
What is the Mnemonic for remembering how SLE manifests?
SOAP BRAIN MD
- Arthritis
- ANA Positive
- DS DNA Positive
- Seizures
- Pleuritis Percarditis
- Malar Rash
- Discoid Rash

If a patient is photosensitive, what should you always do?
Test for ANA to exclude lupus
What are some cutaneous signs of lupus?
- Butterfly rash - photosensitivity over cheeks and nose.
- Urticarial lesions that are not itchy that last more than 24 hours.
- Vasculitis - if so, always screen for SLE.
- Nail fold telangectasia and splinter haemorrhages.
- Non-scarring hair loss - 50% of cases.
What investigations should be done if SLE is suspected?
- Urine - test for blood and protein
- FBC - thrombocytopenia
- ESR - raised in active disease
- U&Es - renal involvement
- LFTs - hepatitis
- Lupus serology - ANA, dsDNA & ENA
- Complement - low C3 or C4 suggests active disease.
With serological markers, what is quite indicative of Lupus?
Both Positive dsDNA and positive ANA.
What is the diagnostic criteria of SLE?
The presence of any 4 of the following:
- Malar rash
- Discoid rash
- Abnormal photosensitivity
- Oral ulceration
- Non-erosive arthritis
- Serositis (pleurisy or pericarditis)
- Renal disease (proteinuria or renal casts)
- Neurological disease (epilepsy or psychosis)
- Haematological disorder (anaemia, leucopenia, lymphopenia or thrombocytopenia)
- Abnormal serology; ANA, dsDNA
What is the treatment for SLE?
- Immunosupression is the main treatment - this depends on the overall degree of involvement.
- Oral steroids
These all usually are initiated and monitored by a specialist.
What are the 2 main types of lupus?
- Subacute Cutaneous Lupus
- Discoid Lupus
What % of patients with either form of cutaneous lupus go on to get systemic symptoms?
5%
How does subacute cutaneous lupus present?
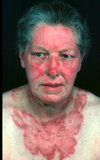
- Rash on sunexposed areas.
- Often annular
- Some scaling
- Lasts weeks or months.

What does the rash of discoid lupus look like?
What is the cardinal sign?
it is red and scaly.
The cardinal sign is atrophy and scarring.

Can lupus cause scarring?
yes

What are the investigations for cutaneous lupus?
-
Biopsy - remember to look for Immunofluorescence
- On IMF - they will see the LUPUS BAND, IgG and C3 in the dermoepidermal junction.
-
Autoantibodies
- Subacute cutaneous lupus - Usually ENA positive.
- Discoid lupus - negative for autoantibodies
- Screen with ANA, dsDNA & Complement. If positive, these patients are more likely to develop Systemic Lupus.
What are some complications of cutaneous lupus?
- Discoid lupus - can progress to SCC.
- SCLE - if Ro antibody positive - this antibody can cross the placenta causing neonatal heart block and SCLE in the neonate.
What is the treatment of cutaneous lupus?
- Avoid UV exposure
- Oral prednisolone (10-40mg OD) - short term
-
Hydroxycholorquine Oral - 200-400mg daily over summer months.
- This with sunblock helps to reduce lesions in 80% of patients.
What are the most common drugs to cause lupus?
- Hydralazine
- Procainamide
- Quinidine
- Isoniazid
- Diltiazem
- Sulphasalazine
- Minocycline
How long does drug induced lupus last when the drug is stopped?
The symptoms usually clear within weeks.
What are the symptoms of drug induced lupus?
- Muscle and joint pain
- Swelling
- Flu-like symptoms such as fatigue and fever
- Serositis
- Skin rash
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Positive ANA test results
What antibodies are present in drug induced lupus?
- Positive ANA
- Negative Anti-ds DNA
- Anti-histone antibodies. (In 75% but not specific)
What is this?

Neonatal Lupus
What is this?

Lupus Profundus
- (Lupus that affects the deep paniniculus)
- Usually affects the face.
What is this?

Lupus Tumidus
- Cherry pink dermal inflammatory plaques and patches.
- Stimulated by sunshine.
- Disappears in the winter.
In dermatomyositis, there are two peak ages. What are they?
- Childhood type - before the age of 10 years - benign.
- Adult (age 40-60 years) - associated with paraneoplasms.
If someone developed dermatomyositis in adulthood,
what else should you do?
Seek an underlying malignancy
What rash is seen around the eyes/on the face in dermatomyositis?
Heliotropic rash
Purplish rash around the eyes, forehead, temples and cheeks.
Oedema can also occur around the eyes and chest.

What is this in dermatomyositis?

Gottron’s Papules
A purplish-red rash on the dorsum of the hands.
What is dermatomyositis sensitive to?
The Sun
The rash gets worse with the sun.
What is another feature of dermatomyositis apart from the cutaneous symptoms?
Musle Weakness
- Usually proximal muscles
- If severe, patient can be laryngeal weakness and difficulty breathing.
What investigations should be done in Dermatomyositis?
- Blood tests
-
Autoantibodies
- Do DsDNA and Lupus Anticoagulant (To Exclude Lupus
- ANA - Positive in 80%
- Anti-Ro & Anti-Jo
- FBC, U&Es and LFTs
- CRP & CK should be raised.
-
Autoantibodies
- Biopsy with H&E - is usually unremarkable.
- EMG - to confirm myopathy.
- Muscle Biopsy
- MRI - may show proximal muscle oedema.
What are 2 important associated conditions in dermatomyositis?
-
Malignancy in 50% of adult patients with dermatomyositis
- Breast and Ovarian in women.
- Prostatic, Lung and Colon Cancer in Men.
- Systemic Lupus or Mixed Connective Tissue Disease
What is the treatment for dermatomyositis?
- Oral Prednisolone and then switch to:
- Methotrexate, Azathioprine or cyclosporin for maintenance.
Once you treat an underlying malignancy in deramtomyositis, what happens?
The symptoms of dermatomyositis settle
What is the treatment for cutaneous disease in Dermatomyositis?
200-400mg of hydroxychloroquine daily.
Scleroderma can be a spectrum of conditions. How do you break it down?
Scleroderma
- Vasculopathy - Raynaud’s phenomenon
-
Systemic
- Limited systemic sclerosis
- Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis
-
Localised
- Morphoea - localised and generalised
- Scleroderma
What is this?
Tell me a bit about it?

Morphoea
- Localised plaques of collagen
- It is due to a build up of collagen by fibroblasts underneath the skin.
- Females > Males
- Any age
- Woody and atrophic feeling to the skin.
What is this?

Linear Morphoea
- More common in childhood
- Usually as indurated lesions in the extremeties.
- Treat aggresively otherwise it spreads to bones, muscle and soft tissue.
What is this?

En Coup De Sabre Morphoea
What is the treatment for Morphoea?
- Initially: Superpotent topical steroids
- Narrow band UVB if extensive
-
Linear Moprhoea - refer to consultant dermatologist.
- They may beed immunosuppresive therapy - methotrexate etc.
- Consider Borrelia Burgdorferi serology (Lyme’s disease) as Morphoea can occur after this.
What is CREST Syndrome?
It is a limited form of systemic sclerosis involving:
- Calcinosis
- Raynaudsd
- Eosophageal Dysmotility
- Sclerodactyly
- Telangiectasia
In CREST Syndrome, what is often the first sign to appear?
Raynauds Syndrome
(Often by Years)
What autoantibody is positive in CREST?
Anticentromere antibody
Is linear morphoea symmetrical or unliateral?
Unilateral
What can happen in linear morphoea if untreated?
It can lead to limb contractures.


