Nail Disease Flashcards
The nail unit consists of what 5 structures?

- Nail matrix
- Nail bed
- Hyponychium
- Proximal nail folds
- Lateral nail folds.
What is this and what does it represent?

The Lanula.
It is the white part of the nail matrix.
What is this and what does it represent?
Is it pathological?

Beau’s Lines
- It represeents a slow down in the growth of the nail matrix.
- In newborns they are not pathological
- In adults, they can come due to: allergic reaction, surgery, medical illness.
What is this?
What pathology should you consider?

Koilonychia
(Spoon shaped nails)
- In adults, consider:
- Iron deficiency
- Thyroid problems
- Connective tissue disease?
What is this?
Is it pathological?
What conditions is it associated with?

Onychorrhexis
- Normal in the elderly
- In adults consider:
- Lichen planus
- Darier’s disease
- Circulatory disorders
What is this?
Who gets it?

Melanonynia
(Naevus in the nail matrix)
Darker skin types.
What is this?

Onychoschizia
- Usually due to water exposure. (i.e. sucking thumb)
What are these?

Onychogryphosis
- Hyperkeratotic thickened nail plates.
- Elderly due to mobility issues and poor nail grooming.
What are the most causative pathogens in Onychomycosis?
- Trichophyton rubrum
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes
What conditions can mimic Onychomycosis?
- Psoriasis
- Lichen Planus
- Congenital Nail disease
What are the topical treatments for onychomycosis?
When would you consider them?
- <2 nails are affect or <50% of the nail plate.
-
Amorolfine 5% lacquer.
- Apply twice weekly for 6-12 months.
- File the nail before hand.
-
Alternative topicals include:
- Ciclopirox 8% OD for 48 weeks.
- Tioconazol
- Newer Triazol Eficonaconazol.
- Consider 40% urea to help penetration enhancement.
What are systemic therapies for onychomycosis?
- Terbinafine (First line)
- S/E - Nausea, Diarrhoea, hepatic dysfunction & permanent taste distrubances..
- Baseline LFTs and FBC are needed.
- Do not give if alcohol misuse or hepatitis
What are the most effective oral treatments for Candida infections?
Azoles (Itraconazole)
What is useful against yeasts, dermatophytes and non-dermatophyte moulds?
Itraconazole
What are the side effects of itraconazole?
- Headaches
- GI Upset.
If someone is on the COCP, why should you be careful about prescribing Itraconazole?
It is a potent p450 inhibitor
Who is itraconazole contraindicated in?
- Congestive heart failure
- Arrythmias
Describe the 2 treatment approaches with Itraconazole?
- Continuous: 200mg daily for 12 weeks
-
Pulsed: 400mg/d for 1 week per month
- 2 pulses for fingernails
- 3 for toenails.
What should you take with itraconazole?
food
What is the relapse rate for onychomycosis?
40-70%
What should patients do to avoid reinfection?
- Minimise trauma
- Keep the nails short
- Treat affect family members
- Wear protective footwear.
- Reduce fungal elements from shoes
- Antifungal powders
- Napthalene mothballs.
What is this?

Acute Paronychia
What causes acute paronychia?
- Staph. Aureus
- Beta-haemolytic Streptococcus
What is this?

HSV infection causing an herpetic whitlow
What is this?

Distal Blistering Dactylitis
What is this and what is the treatment?

- Periungual warts.
- DO not cryotherapy
- Salicylic acid with scraping - once or twice weekly for several months should be considered.
-
If more challenging:
- Imiquimod 5% cream
- Diphencyprone immunotherapy
What % of psoriasis sufferers have nail changes?
50%
Nail changes in psoriasis are strongly linked to what other psoriatic related problems?
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Enthesitis
What nail changes can psoriasis sufferers have?
- Main ones:
- Irregular pitting
- Salmon patches of the nail bed (óil drop’)
- Onycholysis + irregular border.
- Others
- Splinter haemorrhages
- Subungual hyperkeratosis
- Onychorrhexis
- Paronychia
What does nail psoriasis often resemble?
Onychomycosis
What is the name of the scoring system for assessing psoriasis severity?
NAPSI (Nail Psoriasis Severity Index)
NOTE:
PASI
(Psoriasis Severity Index)
What is this nail change and what condition is it seen in?

oil drops
Psoriasis
What is this nail change and what condition is it seen in?

Subungual Hyperkeratosis
Psoriasis
What is this nail change and what condition is it seen in?

Irregular Pitting
Psoriasis
What condition is this?

Acrodermatitis Continua of Halopeau
(Pustular eruption of the nail bed)
What condition is Acrodermatitis Continue of Hallopeau seen in?
What is the treatment?

Variant of pustular psoriasis
- Topical VitaminD3 analogues
- +/- betamethasone
- If severe consider systemic retinoids (acitretin)
What is the treatment for psoriatic nail changes?
-
Topical
- Vitamin D3 analogues
- Betamethasone
- Tazarotene
- Injections - Trimacinolone injections.
-
Systemic
- MTX
- Acitretin
- Cyclopsorine
- Conseal with coloured nail varnish
What % of patients with lichen planus have nail changes?
10%
What condition is this?

Lichen Planus
(Longitudinal fissuring)
What is the treatment of lichen planus?
- Topical or intralesional steroids.
- Systemic corticosteroids can be considered if multiple nail involvement.
In what condition is this sort of pattern seen?

Alopecia Areata
(REGULAR Geometric pitting as opposed to the irregular pitting of psoriasis)
What condition is this seen in?

Eczema
(Transverse ridges)
What condition is this seen in?

Eczema
(Irregular pitting)
What are the treatments for eczematous nails?
- Emollients
- Moderate to high potency topical steroids
- Avoid triggers
What conditions is this seen in?

- Congenital
- Acquired
- Lung cancer
- Bronchiectasis
- IBD
- Thyroid disease
Does COPD cause clubbing?
NO
In what condition, is this seen?

Scleroderma
(Loss/ulceration of the pulp of the finger)
This is a form of Leukonychia called “Terry’s nails’ (Almost full withening of the nails.)
What condition is this seen in?

80% of patients with liver cirrhosis
This is a form of Leukonychia called ‘Muehrcke’s nails’.
(Multiple transverse whitae bands)
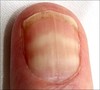
Hypoalbuminemia
This is a form of Leukonychia called ‘half and halfnails’.
What condition is it seen in?

Chronic Renal failure
What is this?

Subungual haematoma
How can you differentiate a subungual haematoma at the nail bed from a melanoma?

Place a nick at the base of the nail.
As the haematoma grows out the nick will stay at the distal end of the haematoma.
What is this?
What conditions is it seen in?

Splinter Haemorrhage
- Common: trauma, psoriasis & onychomycosis
- Rare(usually located proximally):
- Endocarditis
- Vasculitis
- SLE
What is this?
What condition is this seen in?

Onychotillomania
- Self inflicted nail abnormality.
What is this?

Subungual exostosis
- (A localized outgrowth of bone that manifests as a flesh-coloured papule or nodule)
- Painful
- Young people
- Occurs due to trauma
- Surgical Excision required.
What is this?

Digital mucous cyst (aka Myxoid pseudocysts)
- End of the finger
- Painless
- Accumulation of mucin in the dermis.
- Women.
-
Tx: Squeezing, Cryotherapy, intralesional steroids, surgical removal.
- All have a high relpase rate.
What is this?

Pyogenic granuloma
- Due to trauma (or infection, systemic drugs) or pregnancy.
- Occursi n the nail apparatus
- Treat with curettage, cautery or surgical excision.
What is this?

Glomus Tumour
- Very painful
- Lesion of the nail bed dermis
- Pink or Blue Macule.
- Due to trauma
- Treatment: Surgical excision.
What is the most prevalent malignancy of the nail apparatus?
SCC
(HPV can be a cause)
What is this?

Nail Melanoma
In 25% of cases of nail melanoma, what does it look like?
Pyogenic granuloma
What is the difference in nail melanoma rates between caucasians and Asians/African-Americans?
1-2% in Caucasians
25% in African-Americans
What is Hutchinson’s sign of the nail?
it is where the melanoma of the nail grows into the nail periungual skin.
This is part of the radial phase of the melanoma.

What is this most common cause of ingrown toenails?
Congenital Malignment of the great toenails

What is this?

Racquet Thumbs (Brachyonychia)
- Inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion.
What inherited condition does this represent?

Darrier’s Disease
(Follicular dyskeratosis) - autosomal dominant.
White and red longitudinal lines with notching in the nail.


