Genital Dermatology Flashcards
When someone complains of itchy genitals what should we do?
Break it down into
- Infectious
- Inflammatory
- Neoplastic
What are some causes of infection/infestation in the genitals?
-
Candidiasis - Treat partners aswell.
- For ladies use cream and nightly pessaries for 1-3 nights.
- If recalcitrant, give or fluconazole 150mg stat
- If very resistant then for 1 week.
- Scabies
- Herpes Simplex - HSV-2. Treat with oral aciclovir.
- HPV - condylomata accuminata - can be solitary or coalescent. Treat with CO2 laser, cryotherapy, podophyllin or imiquimod.
- Erythrasma - symmetrical brown red scaling. Wood’s light flouresces coral red. Treat with azoles or erythromycin.
- Tinea Cruris - usually never infects the labia minora or the scrotum or penis.
What are some inflammatory disorders in the genitals?
- Eczema/Contact Dermatitis - if not responding to steroids consider patch testing.
- Lichen Simplex Chronicus - check serum ferritin if generalised itch.
- Psoriasis - genitals affected in 20% of cases.
- Seborrhoeic Dermatitis
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Lichen Planus - tx with steroids, tacrolimus, antimalarials, dapsone or systemic immunosuppressants.
What is this?

Lichen sclerosus
Who usually gets lichen sclerosus?
Post-menopausal women
But can also occur in childhood.
What are some features of Lichen Sclerosus?
- Whitish pallid atrophic
- Sclerotic plaques affect the labia, clitoris or introitus, and the perianal area in women may also be involved - the so-called ‘figure of 8’ sign.
- Longstanding
- Fusion of the labia
- Loss of the clitoral hood
- Narrowing of the introitus.
What is this?

Lichen Planus
What are the clinical features of lichen planus on the genitals?
- Keratinised skin lesions appear identical to those elsewhere - i.e. violaceous papules with Wickham’s striae.
What is this?

Genital Psoriasis.
What is this?
What are the penile and anal versions called?

VIN (Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia)
PIN (Penile Intraepithelial Neoplasia)
AIN (Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia)
What is neoplasia of the genitals associated with?
HPV
What can VIN or PIN be confused with?
Lichen sclerosus, Lichen Planus or HPV infection.
If you suspect VIN or PIN what should you do?
Biopsy.
When someone complains of painful genitals, how should we subclassify it?
Genital pain with visible vulval lesions
Genital Pain WITHOUT visible vulval lesions.
What are some causes of genital pain with visible vulval lesions?
-
Infections -
- Herpes simplex (acute or recurrent),
- candidiasis (remember syphilitic primary chancre is painless)
-
Inflammatory
- Lichen sclerosus,
- lichen planus,
- Behcet’s disease,
- Pemphigus vulgaris,
- Cicatricial Pemphigoid ,
- Stevens Johnson syndrome,
- Crohn’s disease
- Neoplastic -VIN, SCC
- Drugs - bullous drug eruption, TEN
- Atrophic vulvovaginitis also relevant in an older patient.
What is the main cause of vulval pain WITHOUT visible vulval lesions?
Vulval Pain syndrome
This is subdivided into:
- Vulvar Vestibulitis Syndrome
- Dysaesthetic Vulvodynia
Tell me about Vulvar vestibulitis Syndrome?
- Premenopausal women.
- Dyspareunia on penetration
- O/E: normal vulva. Gently pressing the vestibule produces severe pain.
-
Treatment
- Vulval care - avoid soaps and bubble baths, tight underwear and tight trousers.
- Treat with TCA (Amitryptiline 25-50mg Nocte and titrate up.
- Consider Gabapentine as an alternative.

Tell me about Dysaesthetic Vulvodynia?
- Persistent burning pain over the entire vulva.
- Worsened by movement or wearing underwear.
- Associated with IBS.
- Treatment
- TCA, acupuncture, self help groups.
What is the male equivalent of dysaesthetic vulvodynia called?
Scrotodynia
What is this?

Genital Psoriasis
What is this?

Scabies
What is this?
What is it associated with?

Lichen Sclerosus
Autoimmune diseases - in particular thyroid disease
What is this and what is the treatment?

Lichen Planus
Topical steroids
if you have genital warts, what are you at increased risk of getting?
Genital neoplasia
What is this?

Genital Herpes
Treat with aciclovir.
What is this?

Bowenoid Papulosis
- Seborrhoeic keratosis-like lesions on genitalia
- Sometimes over the thighs.
- Pre-malignant and needs observing.
- May respond to cryotherapy.
Describe the 2 types of condylomata?
- Condylomata lata - Syphilis
- conylomata accuminata - HPV

What are the infectious causes of penile lesions?
-
Syphilis - chancre on genitals or oral mucoa appears 2-3 weeks after sexual contact.
- Painless and associated lymphadenopathy.
- Condylomata lata - secondary syphilis - very infectious.
- Human Papilloma Virus - the conylomata accuminata
- Herpes Simplex
- 3-4 weeks to heal.
- 304 days of prodromal neuralgic pain.
- Molluscum Contagiosum
What are the inflammatory causes of penile lesions?
- Lichen Sclerosus (Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans)
- Lichen Planus - affects shaft or glans.
- Zoon’s Balinitis
- Psoriasis
- Behcet’s Disease
What is this?

Zoon’s Balanitis
- A result of poor genital hygeine
- Only happens in uncircumcised men
- Cure is circumcision.
What is this?

Penile Lichen planus
What is this?
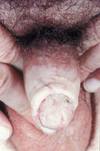
Penile Lichen sclerosus
aka BXO
(Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans)
What is the treatment for BXO?
Super-potent topical steroids.
(It can predispose to SCC formation)


