W25 - Haem interactive cases Flashcards
Myeloblasts may have ________
Myeloblasts may have Auer rods
Myeloblasts in BM:
<5% =
5-20% =
>20% =
Myeloblasts in BM:
<5% = normal
5-20% = myelodysplasia
>20% = AML
Lymphoblasts in BM:
<5%
>20%
Lymphoblasts in BM:
<5% = normal
>20% = ALL
Lymphoblasts are ____ positive
Lymphoblasts are TdT positive
TdT is a marker of mature/immature T and B lymphoblasts
TdT is a marker of immature T and B lymphoblasts
36 year old woman. History of fatigue, joint pains and with a butterfly/malar rash on face. Also experienced menorrhagia. ESR is 80mm/hr (<15) Bilirubin 32 umol/l (<21)
Write down a likely Haematological diagnosis?

Haemolytic anaemia
Spherocytes - autoimmune or inherited. One test to confirm which:
- Hb electrophoresis
- DAT (direct antiglobulin)
- Sickle solubility
- Unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia
- DAT (direct antiglobulin)
Spherocytes - when do we see them?
hereditary spherocytosis, or
autoimmune haemolytic anaemia which has sphercoytes but is also DAAT +
Inherited haemolytic anaemias - name 4 conditions
Membrane: 1) hereditary spherocytosis
Enzymes: 2) G6PD deficiency
Haemoglobin: 3) Sickle cell, 4) Thalassaemia major
A 40-year-old woman of Indian origin, she eats a vegan diet and has five children . She takes regular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication for arthritis. She was anaemic on FBCs performed during her pregnancies. Aside from Hb and MCV the remainder of FBC is normal Hb (women)
What is the diagnosis?
A) Iron deficiency anaemia
B) Anaemia of chronic disease
C) Beta thalassemia trait
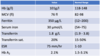
B) Anaemia of chronic disease
= essentially anaemia of (inflammation) chronic disease. ESR raised. but the key to distinguish IDA from ACD is TRANSFERRIN
- in IDA => transferrin is HIGH
- in ACD => transferrin is normal/reduced
Acquired haemolytic anaemias - name immune and non-immune conditions
Immune: 1) Immune haemolytic anaemia
Non-immune: 2) Malaria, 3) MAHA, 4) drug-induced, 5) HUS, 6) snake bites
59 year-old woman. fatigue. PMH Hypothyroidism and vitiligo
Chose the most likely diagnosis?
A) Folate deficiency
B) Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia
C) B12 deficiency
D) Acute leukaemia

Hb low, MCV very high, WCC low, neutrophils low, platelets low
C) B12 deficiency = she likely has pernicious anaemia (hence not folate)
59 year old man. Pharyngitis not responded to antibiotics, Recurrent nose bleeds. fatigue, difficulty passing urine and haematuria
Interpret bloods and blood film. What is the most likely haematological diagnosis?

Hb low, MCV normal, WCC low, neurophil low, platelets low = pancytopaenia
Peripheral blood film: nucleated RBcs, myelocytes (immature cell which should be in BM, not in peripheral blood), tear drop cell
= leuko-erythroblastic picture due to BM infiltration either by 1) blood cncer, 2) metastatic cancer
this is likely prostate cancer metastasized to BM
How to distinguish ACD from IDA on blood test?
Transferrin (which is essentially TIBC)
IDA => transferrin is HIGH
ACD => transferrin is LOW/NORMAL
Interpret bloods, peripheral blood film, and come up with signle most useful test.
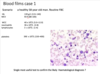
bloods: WCC VERY HIGH, neutrophil count VERY HIGH, rest is normal
blood film: lots of neutrophils, some basophils, some myelocytes
likely CML = check for Ph chromosome = BCR-ABL ASSAY
Why is iron low in ACD?
ACD = anaemia of inflammation => hepcidin levels are high in inflammation => high hepcidin inhibits GP asborption of iron + sequesters Fe in macrophages and Kupffer cells (as a means to remove available iron for invading bacteria)
Interpret results. What treatment would you give?

CML that has now entered blast phase => TKI that works directly to inhibit ABL =>
imatinib
What is the likely haematological diagnosis at month 60?

Blast crisis => disease has gone from CML to AML (blast cell 25% in peripheral blood)
Single most useful test to confirm the likely haematological diagnosis?
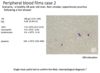
JAK2-V617F mutation
Peripheral blood leucocyte immunophenotyping is performed.
What is the likely diagnosis? What test is most useful?
A) DAT
B) Immunophenotyping for CD19/CD5/CD3 expression
C) HTLV1 serology
D) BCR-ABL assay
E) JAK2-V617F mutation analysis
F) Factor V leiden screen

high WCC, high lymphocytes = likely CLL
B) Immunophenotyping for CD19/CD5/CD3 expression
Pancytopaenia
name non-malignant (2) and malignant (2) causes
Pancytopaenia
non-malignant (2):
- DNA synthesis failure (B12 or folate)
- Aplastic anaemia
malignant (2):
- metastatic non-haem cancer (i.e. breast)
- haem cancer infiltrating BM (i.e. leukaemia, myeloma, lymphoma)
Write down the likely underlying diagnosis ?

Hb low, calcium high, IgA very high with suppression of IgM and IgG
Multiple myeloma
NB: A mid-femur fracture in a 59 year old man is either due to 1) trauma, or 2) cancer spread to bone or 3) MM.
CML - common symptoms and signs
CML history: lethargy/hypermetabolism/thrombotic event (monocular blindness CVA) bruising, bleeding
CML exam: massive splenomegaly +/- hepatomegaly
Most likely cause of renal failure?

Cast nephropthy
Cast nephropathy are depositions of free light chains depositing and blocking off nephrons
This patient has sky high levels of free light chains – these pass through BM of kidney and may precipitate renal failure
CML - common FBC and blood film findings
- Hb and platelets well preserved or raised
- Massive leucocytosis 50-200x109/L
- Blood film: Neutrophils and myelocytes (not blasts if chronic phase), Basophilia
The \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ translocation produces the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome which expresses...
The **t(9;22)** translocation produces the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome which expresses **a fusion oncoprotein with TK acitvity driving myeloid proliferation**
CLL - name 3 cell based prognostic factors.
- IgHV mutation status
- CLL FISH cytogenetic panel
- TP53 mutation status (Chromosome 17p del and/or TP53 point mutation) *most imp
Which 2 drug are used in treatment of CLL?
- Ibrutinib (Briton tyrosine kinase inhibitor)
- Venetoclax (BCL2 inhibitor)
MM - Define CRAB
Calcium
Renal failure
Anaemia
Bone disease


