W23 - Neurodegeneration Flashcards
A patient with a clinical history consistent with dementia and movement disorder, who dies within 1 year = what should you think of?
CJD/Prion disease
Prion disease - what is involved?
proteinaceous infectious only = prion
Kuru - what is it and what causes it?
One of the first forms of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE), also known as prion diseases, arising from cannabalism
kuru = to shake
Name 4 types of Prion diseases that affect humans
•Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sporadic or genetic)
•Gerstmann-Straüssler-Sheinker syndrome
- Kuru (cannibalism)
- Fatal familial insomnia (found in some families in Italy and North America)
What does this H&E stain on brain tissue show?

Spongiform changes
Prion protein:
- What protein form is it normally in?
- What protein form can it turn into?
- What is the abnormal protein?
Prion protein:
- What protein form is it normally in = typically alpha helical format
- What protein form can it turn into = unfolded form, beta-sheet form
- What is the abnormal protein = aggregates of beta sheet form

Which form of prion protein does it appear we could spread?
beta sheet
Left = normal elderly brain
What do you see in right scan and specimen? Diagnosis?

Right = massive ventricles, cerebral atrophy (large spaces, large lateral fissure), severe atrophy of the hippocampus bilaterally
specimen = frontal atrophy, widening of sulci, thinning of gyri
DIAGNOSIS = AD!
What are these in a brain tissue staining?

Senile plaques, aka Amyloid plaques /Aβ plaques -
extracellular deposits of the amyloid beta (Aβ) protein mainly in the grey matter of the brain.
*look like lump of protein, halo, more diffuse protein around it*
This is a staining of vessels in brain tissue. What does it show?
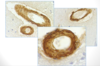
build up of amyloid in blood vessels = cerebral amyloid angiopathy (seen in AD)
New variant CJD (vCJD):
- typical presentation?
- Linked to…?
- # of cases in last 5 years?
New variant CJD (vCJD):
- typical presentation = young patient (<45), cerebellar ataxia, dementia, longer duration than CJD
- Linked to BSE
- # of cases in last 5 years = 0!!
What 5 effects could buildup of intracellular AB oligomers cause?
- Calcium dysfunction
- Synaptic dysfunction
- Proteosome blockage
- Mitochondrial block => buildup of ROS
- Hyperphosphorylated tau => tau tangles

Describe 4 pathologies seen in brain of those with AD
- Extracellular plaques
- Neurofibrillary tangles (intraneuronal)
- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (due to extracellular plaques)
- Cerebral loss/neuronal loss (due to protein buildup)
Amyloid protein precursor - explain the 2 processing pathways
1. Non amyloidogenic pathway (does not produce AB peptide)
2. Amyloidogenic pathway = produces AB peptide = when this increases, it can accumulate + aggregate
Tau is an intra/extra cellular pathology
Tau is a _____________ protein
Tau is an intracellular pathology
Tau is a cytoskeletal protein
What is the phosphorylation status of tau in AD?
hyperphosphorylated
Staging of Tau in AD - What is Braak stage I?
changes in medial temporal lobe (MTL), transentorhinal regions
Staging of Tau in AD - What is Braak stage II?
spread to posterior parts of temporal lobe + hippocampus, entorhinal region
These are post-mortem dissections of midbrain. Explain the 2 samples

Left = normal brain, , you see the substansia nigra
Right = Parkinson’s Disease brain, lack of substantia nigra
Staging of Tau in AD - What is Braak stage III?
temporo-occipital gyrus involvement
Staging of Tau in AD - What is Braak stage IV?
temporal cortex involvement
What do these stains of the midbrain show?

Pigmented neurons in substantia nigra being disrupted by the lewy bodies
lewy bodies are the circular clumps of protein
Staging of Tau in AD - What is Braak stage V?
Peristriatal cortex involvement
Staging of Tau in AD - What is Braak stage VI?
Striatal cortex involvement






