Viral and Fungal Infections Flashcards
Incubation and shedding duration of influenza
Incubation: 1-4 days
Shedding: 0-10 days
3 antivirals for influenza
Oseltamivir
Zanamivir (inhaled)
Peramivir (IV)
Antiviral in influenza not recommended in asthma/COPD
Zanamivir
Difference between CMV infection and CMV disease
Infection: lab confirmed virus, regardless of signs/symptoms
Disease: signs and symptoms of disease
Most common forms of aspergillus in humans
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus flavus
Clinical spectrum after aspergillus spore inhalation

Fungal tests affected by antibiotics
Beta Glucan and Galactomannan (also by pasta and rice)
First line treatment of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
Voriconazole
Drug for IPA prophylaxis in AML, MDS, and GVHD
Posaconazole
Medications to treat chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis
Voriconazole
Itraconazole
Ampho B
Caspofungin
Treatment options for aspergilloma
Observation if asymptomatic
Itraconazole (only 60% effective)
Surgical resection
Bronchial artery embolization
Criteria for ABPA
Must have either asthma or CF
Aspergillus skin test or IgE against A. fumigatus
TOTAL IgE > 1000
Treatment for severe blastomycosis
Ampho B 1-2 weeks, then itraconazole
Treatment for mild to moderate blastomycosis
Itraconazole 6-12 months
Treatment for blasto with CNS disease
Ampho B
Treatment for blasto in pregnancy
Ampho B (No Azoles)
Treatment for invasive candidemia
Echinocandins over azoles initially, can switch later
If candidemia alone, 2 weeks from negative culture
If endopthalmitis, 4-6 weeks
Percentage of coccidioidomycosis that are asymptomatic
60%
Clues for coccidioidomycosis over CAP
Hilar adenopathy
Eosinophilia
Erythema nodosum
Diagnosis of coccidioidomycosis
Antibody testing or isolation of spherules from culture
Treatment for coccidioidomycosis
- Immunocompetent: observation (90% self limited)
- If sxs > 6 weeks, consider treatment
- Immunosuppressed
- Fluconazole
- Amphotericin
Treatment of cryptococcus
Lung: Fluconazole
CNS: Ampho + flucytosine
Treatment for histoplasmosis
- Mild or chronic: Observation
- Moderate: Itraconazole
- Severe: Ampho
2 complications of histoplasmosis infection
Broncholithiasis and fibrosing mediastinitis

Aspergillus

Mucormycosis
3 species of mucormycosis causing disease in humans
rhizopus
lichtheimia (absidia)
Mucor
Classic presentation of pulmonary mucor
Sputum can be bloody
Will have multiple nodules WITH effusion (as opposed to IPA without)
Histology of mucor
Pauci-septated (ribbon) hyphae
Branch at right angles
Fungus NOT detected by beta glucan or galactomannan test
Mucor
Drug that must be stopped in mucor infection
deferoxamine
First line treatment of mucor
Ampho B with surgical resection
Treatment for PCP pneumonia
Bactrim for 21 days if HIV +
Add steroids if A-a gradient is > 35
Alternative regimens for PCP if not HIV
- Severe disease
- Clindamycin + primaquine
- IV pentamidine
- Mild disease
- Trimethoprim + dapsone
- Atovaquone
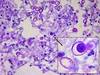
Blastomycosis


