URT Disease Flashcards
What is you diagnosis, action and treatment?
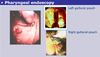
Diagnosis: Gutteral pouch mycosis
Action: REFER.
Treatment: Ligation and balloon affect artery.
What is your diagnosis?
What are the management options?
What is the prognosis?

Diagnosis
Cleft palate
Manage
- Hard
- Poor success rate of surgery
- PTS?
Prognosis
- POOR
- Recurrent infections
- Poor athletic function
EHV1,4 Serology = 1:256
EHV1,4 Serology 2 weeks later : 1:1024
Diagnosis and treatment?

Diagnosis: Equine herpes virus
Treatment: Anti-inflammatories and nursing care
· The case presented to you on Monday (Dominic Adams) was shown to culture positive for Strep equi var equi
· The horse recovers initially very well without treatment (as most do), however one month later becomes depressed and anorexic
– Fibrinogen 8g/l (normal 1-5)
– Inflammatory marker
– SeM Serology 1:5600
– Abdominocentesis contains large number of neutrophils and occasional gram-positive cocci
Clinical Assessment: It is presumed that the horse has developed abdominal abscessation (a very rare complication). You elect to treat this complication with oral doxycycline for 14 days
what drug shall we give?
– In the end – used 6-week course of this
– Problem with this is that it is acidic, and horse has got to eat it, times where we will justify using an unlicensed formulation
– Reason for is this metastatic spread
– Can use canine tablets under a poultry formulation
– Poultry formulation: contains doxycycline hyclate – Soludox® 500 mg/g Powder for Use in Drinking Water for Pigs and Chickens
Underr the cascade what do we need to get owners to do when using off license products?
Sign a conset form
What advice can we give owners about the use of doxycycline in horses?
· Some horses will go off their food. This can often be managed by syringing the product directly into the horse’s mouth, rather than mixing in feed. Refrigerating the medicine may improve palatability. If you horse stops eating completely or becomes depressed, you should contact vet immediately and stop administering the product. Occasionally horses will develop diarrhoea. This can occur with ANY antibiotic and is not unique to doxycycline. If this occurs, you should contact your vet immediately and stop administering the product.
· Rarely horses may develop mouth ulcers that can extend into their food pipe (oesophagus). If you observe these, please contact your vet immediately and stop administering the product.
What advice do we give owners on prescriptions?
A high street pharmacy: High street pharmacies rarely carry stock of equine specific medicines,but may be able to supply human medicines. They are not permitted to substitute a human medicine for a prescription of a veterinary medicine or provide a different product from that stated on the prescription.
A different veterinary practice: Some veterinary practices may be able to dispense medicines against a veterinary prescription.
An online pharmacy: There are an increasing number of veterinary pharmacies, many of whom are properly regulated and reputable. To protect consumers, the VMD have established the Accredited Internet Retailer Scheme. Accredited retailers will display the VMD logo with their registration number. When you click on this logo you will be redirected to the VMD’s website where you can check the details of the online seller. Further details can be found here
You should avoid unregulated suppliers since you cannot be sure of the safety of the product being supplied. You may become the victim of fraud and may be sold a product that is not what is claimed. Many oral medications look similar to each other and it is very easy for fraudsters to refill used packages, especially syringes, with fake compounds to make money. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is. In particular avoid
Overseas websites: It is illegal and unwise to import medicines since you and your horse lack the protection you would have when these are purchased in the UK
Social Media: It is illegal to sell unused product direct to another horse owner. If they are willing to break one law, they are probably willing to break others
What are alar fold abnormalities?
• Alar folds are mucocutaneous structures in the dorsal aspect of the nasal cavity. These form the ventral and medial aspects of the false nostril. Flaccid or redundant alar folds are an infrequent cause of respiratory tract noise or exercise intolerance in performance horses. Pathogenesis unknown. Standardbreds and American Saddlebreds may be at increased risk. Signs: Loud vibrating noise during exercise in severe cases may be heard at rest. Exercise intolerance dynamic collapse of the unsupported tissues of the upper airway. Resection of the alar folds is an infrequently performed technique. In young male horses whose canine teeth are not yet erupted, the alar folds may produce a relative obstruction that decreases when these teeth finally erupt
What is nasal amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal protein, known as amyloid fibrils, builds up in tissue.
What is Mycotic rhinitis?
• Mycotic rhinitis is a rare disease in horses. Clinical signs include dyspnoea, increased nasal breathing sounds, unilateral or bilateral mucopurulent (occasionally malodorous) nasal discharge, epistaxis, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, and head shaking/head shyness.1-6 Organisms isolated from fungal infections of the nasal cavity in horses include Pseudallescheria boydii,5Conidiobolus coronatus,1, 3Cryptococcus neoformans,7Penicillum sp.,6 and Aspergillus spp.1, 2, 6 Successful treatment of nasal mycosis in horses has been described in a limited number of cases. Amphotericin B,3, 4 nystatin, and natamycin2, 6 have been used topically. Oral treatment with itraconazole, griseofulvin,1 and potassium iodide as well as IV administration of sodium iodide3 and debridement or surgical removal of affected tissue1, 2, 4, 6 have also been reported as having various degrees of success
What is False Nostril Cyst?
- This is a soft to firm, non-painful swelling localized in the false nostril, a blind pouch in the outer wall of the nostril. It ranges in size from 1-3 centimetres in diameter. It is filled with sebaceous (oily) material. It is actually a congenital problem and is present at birth but only becomes noticeable in adulthood.
- Treatment is not necessary for health reasons. It is usually only a cosmetic problem and is removed for this reason.
- Treatment involves surgical removal of the cyst in its entirety. Other treatments include drainage and treatment with chemicals that destroy the lining of the cyst. I have used formalin in several and had acceptable cosmetic results.
What is nasal paralysis?
- Asymmetry of facial expression is common with unilateral lesions of the facial nucleus or nerve in most species. Bilateral facial paralysis may be more difficult to recognise but affected animals drool and have a dull facial expression. Complete facial paralysis is an inability to move the eyelids, ears, lips, or nostrils. Facial paresis is reduced movement of the muscles of facial expression and indicates milder nucleus or nerve involvement.
- In horses, the affected nostril is unable to dilate on inspiration. In chronic lesions, muscle fibrosis and contracture cause the nose to deviate toward the lesion, and the muscles feel firm and inflexible. Because the facial nerve provides sensory innervation to the distal tongue, a bitter substance such as atropine will not be recognized when placed on the distal tongue.
- In horses, halter injuries and prolonged lateral recumbency may injure the buccal branches of the facial nerve on the side of the jaw and cause unilateral or bilateral paresis or paralysis of the lips and nostrils
- Horses with collapsing nostrils may require corrective surgery
Wry nose:
Cause?
Signs?
Diagnosis?
Treatment?
Prognosis?
- Cause: congenital shortening and deviation of the maxillae, premaxillae, nasal and vomer bones, and nasal septum.
- Signs: complicates feeding, causes respiratory obstruction.
- Diagnosis: clinical examination, radiography.
- Treatment: bilateral osteotomy of premaxillae/maxillae and rib graft; unilateral osteotomy of premaxilla/maxilla and distraction osteogenesis; bilateral osteotomy of premaxillae/maxillae and external fixation.
- Prognosis: good for athletic endeavors after surgical correction. But a lot are PTS. Controversial
– Dentigerous cysts:
Cause?
Signs?
Diagnosis?
Treatment?
Prognosis?
- Cysts containing tooth fragments that are situated away from the normal location.
- Cause: develop from misplaced enamel organs (embryologic origin of teeth from first branchial arch).
- Signs: depend on location. Discrete swelling with a discharging sinus.
- Diagnosis: signs, radiography.
- Treatment: excision of cyst.
- Prognosis: good
What is Suture periostitis?
- Inflammation of the facial bone sutures
- A craniofacial suture is a specialised fibrous joint only present in the skull where flat bones are bound together by collagen fibres and overlying periosteum (Williams and Warwick 1980). These sutures are the primary site of craniofacial bone growth and unless they become closed, a small amount of movement can occur at them, which contributes to the compliance and elasticity of the skull, especially during birth and later as mechanical stress absorbers
What is Guttural pouch tympany?
• Guttural pouch tympany is an uncommon ailment in which excessive amounts of air become trapped in the pouch, resulting in abnormal expansion. Tympany is usually unilateral, but in some cases can affect both pouches. It is seen most often in young foals and is more common in females than in males. Tympany results in non-painful, soft swelling beneath the ear and behind the jaw. Additional symptoms may include roaring, difficulty breathing, and difficulty swallowing and/or aspiration pneumonia. Diagnosis is achieved through radiography and endoscopic evaluation. The specific cause of guttural pouch tympany is not known, but it is suspected that it is more common when there are defects of the plica salpingopharyngeus, and/or the pharyngeal orifice where they act as a one-way valve that does not allow air to escape. Because of the risk of secondary infection, it is crucial that tympany be treated as soon as possible. Treatment protocols may include, but are not limited to, surgical intervention and in cases where surgery is not an option, insertion of a transnasal Foley balloon catheter in an attempt to remodel the pharyngeal orifice


