Cardiac Histopathology Flashcards
What are the 4 constituents of the heart and what are the functions?
•Cardiac muscle
For contraction to propel the blood
•Fibrous skeleton
Provides attachment for the atrial/ventricular myocardium
•Conducting system
For initiation and propagation of rhythmic depolarisations, which results in rhythmic cardiac muscle contractions
•Coronary vasculature
Coronary arteries for blood supply to the heart; cardiac veins for venous drainage of the heart
What are the 3 heart wall layers? And where are they?
•Endocardium (inner)
Lines the ventricles/atria and covers the cardiac valves;
Monolayer of endothelium; inner subendothelial layer with dense collagen; outer subendothelial layer with collagen, elastin, and blood and lymph vessels
•Myocardium (middle)
Cardiac muscle cells (myocytes), embedded in a well-vascularized connective tissue framework (cardiac interstitium)
Epicardium (outer)
= visceral serous pericardium
Layer of mesothelium resting on elastic fibre-rich connective tissue, which is often rich in adipocytes
What is the pericardium? Where is it?
Fibroelastic sac that surrounds the heart;
Visceral and parietal serous pericardium, pericardial cavity, fibrous pericardium
Label this heart wall

A) Coronary artery
B) Atrial wall
C) Endocardium
D) Epicardium
E) Myocardium
F) Ventricular wall
G) AV valve
Label this heart wall

- Epicardium
- Myocardium
- Endothelium
- Endocardium
- Mesothelial
What is this?

Longitudinal section of myocardium
What is this?

Transverse section of myocardium
What are the 6 types of cardiac disease?
•Congenital abnormality
Malformations causing systemic-pulmonary shunting
Malformation of heart valves
Others
•Pericardial disease
Non-inflammatory
Inflammatory
•Endocardial disease
Degeneration
Inflammation
•Myocardial disease
Haemorrhage
Degeneration
Necrosis
Inflammation
Cardiomyopathy
- Diseases of the conduction system
- Neoplasia
Label (bovine)


What is this?
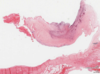
Valvular endocarditis

What is this?

Inflammatory cells and fibrin in the thrombus
What is this ? (dog)


What is this?

Haemangiosarcoma

What can be seen here?

Descending aorta thrombus
What can be seen?


How do we classify canine CDVD?
Whitney criteria

What are the 2 types of Canine dilated cardiomyopathy and where are they seen?
Attenuated wavy-fibre type (most common in giant breeds) and a fatty infiltrative type (more common in boxers and Dobermans)
What is this?

Left ventricular myocardium of a dog with attenuated wavy fibre type of DCM. The myofibres are thinner than normal and have a wavy appearance.
What is this?

Left ventricular myocardium of a dog with fatty infiltration–degenerative type of DCM. Vacuolar degeneration of myofibers (small arrows), atrophic myofibers, lipid deposits (large arrows), and cords of collagen (blue staining) are evident. Masson’s trichrome. Bar = 20 µm
What can be seen?

Coronary vessels appear whitish and thickened
What is shown?


What can be seen?

Neutrophils


