Unit Two Vertebral Column, Spinal Cord, Meninges Flashcards
(67 cards)
How many vertebrae are there?
33

What are the two primary curvatures of the vertebrae that are present at birth?
thoracic, sacral
What are the two secondary curvatures that develop after birth?
Cervical, lumbar
What is an exaggeration of the thoracic curvture called?
kyphosis

What is an exaggeration of the lumbar curvature called?
lordosis

What is an abnormal lateral curvature called?
scoliosis

What protects the spinal chord?
vertebral arch
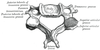
What connects the lamina to the body of vertebrae?
the pedicle

What are the lamina of the vertebrae?
two flattened processes that connect pedicles to spinal processes

What does the vertebral foramen contain?
spinal chord and meninges
What is the superior verebral notch?
Superior concavity above the pedicle
What is the inferior vertebrla notch?
concavity inferior to the pedicle
Where do intervertebral roots pass through in the spinal chord?
Intervertebral foramen
What do the first 7 cervical vertebrae have that the others do not, and what is contained in them?
transverse foramen, vertebral artery
What is an alternative name for the CV1?
atlas
What is an alternative name for cv2?
axis
What is supported by the articular processes of the atlas?
occipital condyles
What does the atlas have in place of a spinous process?
anterior and posterior arches
What is the projection off of the body of the axis? What is it’s purpose?
odontoid process; serves as rotation point for the skull
What holds the odontoid process/ dens in place?
(the transverse ligament of atlas)
What are the surfaces of the thoracic vertebrae where they meet ribs?
costal surfaces or facets
What is located on the superior articular process of the lumbar vertebrae?
mammillary process

What is on the transverse process of the lumbar vertebrae?
accessory process

What does the sacrum articulate with?
ilium of the hip








