Unit 8 Posterior Triangle and Root of the Neck Flashcards
(57 cards)
What is it called where the left and right halves of the mandible join?
the mental symphisis
How far does the body of the mandible extend?
extends back to the angle
What muscle is found on the external portion of the angle of the mandible?
the masseter mucle

Where would one find the facial artery?
inferior border of the mandible near the anterior border of the masseter muscle

what is the mastoid process of the skull?

what is the difference between the medial and lateral end of the clavicle?
medial end in rounded, lateral end is flattened
Where is the inferior border of the clavicle?
spine of CV7
What is the hyoid bone?

What bone does the hyoid articulate with?
none
What is suspended from the hyoid bone and by what means?
The larynx is suspended by the thyrohyoid membrane
What is the thyroid cartilage?

What is located in the midline of the neck?
Adam’s Apple (laryngeal prominence)
What is inferior to the thyroid cartilage?
cricoid cartilage of the larynx
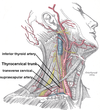
What separates the anterior and posterior triangles of the neck? What is found under the midpoint of this structure?
The sternocleidomastoid muscle, the spinal accessory nerve

What is found in the superficial cervical fascia?
fat, cutaneous nerves, muscles of facial expression, their nerves and veins

What nerves make up the cutaneous component of the cervical plexus?
lesser occipital (C2), Great auricular (C2,3), Transverse cervical (C2,3), supraclavicular nerves (C3,4)
What skin is innervated by the lesser occipital nerve?
skin of neck and scalp posteriosuperioly to the auricle of the ear

Where is the great auricular nerve? What skin does it innervate?
Innervates the skin of the parotid region and auricle, supplies skin of the mandible to the mastoid
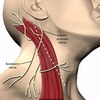
Where is the transverse cervical nerve? What skin does it supply? What does it join?
skin of anterior triangle of neck, joins cervical branch of the facial nerve inferior to the parotid gland

Where are the supraclavicular nerves? What do they supply?
supply skin of inferior half of the posterior traingle of the neck, supply skin of the upper thoracic region and deltoid regions

What is the platysma muscle? What innervates this muscle?
innervated by C7 (facial muscle) as it is considered a facial expression muscle

What two veins join to form the external jugular vein? What does it drain into?
Notice in the picture that the external jugular is posterior and superficial to the internal jugular….the two veins that join are the retromandibular and posterior auricular veins…it drains into the subclavian

What is the major facia of the neck?
deep cervical fascia

What is the anterior layer of deep cervical fascia? What is its function?
called the investing layer of fascia, not surprisingly it invests the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid (invests) as well as forms the roof of the anterior and posterior traingles of the neck