Unit One Muscles of the Back Flashcards
(61 cards)
Superior Nuchal Line
Posterior Superior Ichiac Spine

Scapula

Which layer of fascia has contains fatty deposits?
Superficial Fascia
What factors can affect the thickness of the superficial fascia?
Gender, Age, Nutrition, Sex Hormones
Transverse Process

For the superficial muscles of the back, where do the majority insert? Originate?
Majority insert on the pectoral girdle or the humerus, and they originate from the axial skeleton.
Give the origin, insertion, action, and innervation of the trapezius.
origin: superior nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, ligamentum nuchae, and the spinous processes of CV7-CV12
Insertion: upper fibersinsert on Lateral third of the clavicle, acromion process, and spine of scapula; lower and medial fibers insert on the medial end of the spine of scapula
Action: Upper fibers elevate the shoulder, the middle fibers retract the shoulders, the upper and lower fibers together rotate the shoulder
Innervation: Accessory Nerve and C3 and C4 nerves
Trapezius

Does the trapezius work on the shoulder joint?
No, it does not cross the shoulder joint
What is the principle blood supply of the trapezius?
superficial cervical arteries
Give the origin, insertion, action, and innervation of the latissimus dorsi.
Origin: from the spinous processes of TV7 down to the back of the sacrum, from the crest of the ilium and from the lower ribs
Insertion: lesser tubercular ridge and interubercular sulcus of the humerus
Action: extends, adducts, and medially rotates the humerus
inner vation: thoracodorsal nerve
imagine the latissimus dorsi
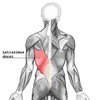
In the lumbar region, from where does the latissimus dorsi originate?
posterior lamella of the thoracolumbar fascia
What provides the blood supply for the latissimus dorsi?
thoracodorsal vessels



















