Understanding the Peritoneal Cavity Flashcards
What is the peritoneum?
- layer of serous membrane
- comprising connective tissue and squamous epithelium which lines the abdominal cavity
- has 2 parts parietal and visceral peritoneum

What does the peritoneum adhere to and is it the parietal of visceral peritoneum?
- anterior and posterior abdominal walls
- undersurface of the diaphragm
- cavity of the pelvis
- this is the parietal peritoneum (red in image)

What type of tissue lines the outside of the parietal peritoneum?
- loose areola tissue
- dense fibrous tissue
- fat
- all closely related to deep layer of abdominal muscles

What is the name of the cells, and the cell type of the peritoneum?
- mesothelial cells
- composed of simple squamous epithelial

Where does the visceral peritoneum line, and what type of cells is this composed of?
- surrounds organs of the GIT
- it is an extension of the parietal pleura
- simple sqaumous epithelial cells called mesothelium

Where does the visceral peritoneum line, and does it surround all organs in the GIT?
- no, does not surround more mobile organs
- moves around the SI and LI, fusing at back of them
- fusing begind the SI and LI forms the mesentary
What nervse innervate the parietal peritoneum and what are they able to sense?
- L2-L4
- somatic so are sensitive to everything
- pain is well localised
What nervse innervate the visceral peritoneum and what are they able to sense?
- visceral nerves
- stretch receptors only
Do the parietal and visceral peritoneum originate from the ecoderm, mesoderm or the endoderm in embryological development?

- formed of connective tissue
- all connective tissue comes from the mesoderm
- derive from the somatic mesoderm in the embryo

Does the GIT originate from the ecoderm, mesoderm or the endoderm in embryological development?

- endoderm

What does mesentrary mean?
- a double fold of the peritoneum
- attaches the stomach, small intestine, pancreas, spleen, and other organs to the posterior wall of the abdomen

In addition to providing support and attaching organs to the posterior wall of the abdomen, what else does the mesentary create?
- support ligaments for the stomach (gastrosplenic ligament)
- support ligaments for the spleen (lienorenal ligament)
Ventrally what else does the mesentary create?
- ligaments around the liver
- falciform ligament
- lesser omentum

What is Intraperitoneal?
- intra = inside the peritoneum
- completely wrapped in peritoneum
- peritoneal folds form mesenterys
What is retroperitoneal?
- retro means outside of peritoneum
- the anterior aspect of retroperitoneal organs attach to peritoneum
Are retroperitoneal or intraperitoneal organs more mobile?
- intraperitoneal are generally more mobile
- like the small intestines they can be moved easily in surgery
SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the S stand for?
- Suprarenal (adrenal) glands
SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the A stand for?
- Aorta and Inferior Vena Cava
SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the D stand for?
- duodenum (except for the first part)

SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the P stand for?
- pancreas
- except for the tail

SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the U stand for?
- ureters
- tube carrying urine from kidneys

SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the C stand for?
Colon
- ascending and descending parts

SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the K stand for?
- kidneys
SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the E stand for?
- Esophagus
SAD PUCKER can be used to remeber organs that are classed as retroperitoneal. What does the R stand for?
- rectum

The peritoneal cavity has two areas called sacs, what are their names?
- lesser sac (behind stomach)
- greater sac

What is the omenta in the GIT?
- fused peritoneal folds
- they attach the abdominal organs with one another
How many omentum are present in the GIT, and what are their names?
- lesser omentum
- greater omentum
What do the lesser and greater omentum both attach to in the GIT?
- stomach
- lesser is superior
- greater is inferior

What does the lesser omentum attach together in the GIT?
- stomach
- liver
- can be divided into hepatogastric and hepatoduodenal ligaments

What does the greater omentum attach together in the GIT?
- greater curvature of the stomach and the transverse colon
- lies over the infracolic compartment
- descrinbed as the policeman or an apron of the abdomen
- freely moveable and protect other organs from inflamed or diseased organs

The peritoneal cavity includes the greater lesser sacs. The greater sac can be subdivided into the Supra and Inferior colic compartments. What is the dividing line for these compartments?
- mesentary attaching transverse colon to posterior abdominal wall
- this mesentary is called the mesocolon
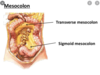
What is contained within the Supra colic compartment of the greater sac of the peritoneal cavity?
- most of the foregut
- stomach
- liver and biliary tree
- pancreas
- spleen

What is superior border of the Supra colic compartment of the greater sac of the peritoneal cavity?
- diaphragm
- costal margin
The greater momentum contains a number of things to supply and insulate the organs in that area. What are these contents?
- blood vessels
- fat
- lymphatics
Where is the lesser sac within the Supra colic compartment of the peritoneal cavity?
- posterior to the stomach and lesser omentum
- functions by allowing the stomach to move freely against the structures posterior and inferior to it
The greater and lesser sacs of the supra colic compartment are able to communicate via what?
- epiploic foramen
- ep-ee-plow-ic

The epiploic foramen is the communication between the greater and lesser sacs of the supra colic compartment. Why can this be surgically important?
- if liver bleeds a clamp can be placed here
- stops blood leaking into both sacs
Is the supracolic and infracolic compartments larger?
- infracolic

The infra-colic compartment has 2 gutters running either side of it, what are these called?
- left and right para colic gutters
- either side of the ascending (right) and descending (left) colon

Where does the right para colic gutter run?
- crosses betwee the supra and Infra-colic compartment
- up to right kidney
- undersurface right lobe of liver – (recess called the hepato-renal pouch)
- lateral to ascending colon and caecum to pelvic cavity

Where does the left para colic gutter run?
- left side of transverse mesocolon
- lateral to descending colon and base of sigmoid mesocolon
- runs to pelvic cavity

The infra-colic compartment of the greater sac can be further subdivided into the left and right intracolic compartments. What divides left from right intracolic compartments?
- root of small intestines mesentery attached to posterior abdominal wall

The infra-colic compartment of the greater sac can be further subdivided into the left and right intracolic compartments. What is included within the right intracolic compartment?
- small intestines
- ascending colon

The infra-colic compartment of the greater sac can be further subdivided into the left and right intracolic compartments. What is included within the left intracolic compartment?
- larger than the right
- descedning colon
- transverse colon
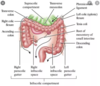
What is the vesico-uterine pouch that is formed by reflections of the peritoneum?
- bladder and uterus in females
- fluid can collect here causing abscess formartoon
- abscess (pus formation) can form bulges that can be palpated

What is the recto-uterine pouch that is formed by reflections of the peritoneum?
- pouch between uterus and rectum
- abscess (pus formation) can form bulges that can be palpated

What is the recto-vesical pouch that is formed by reflections of the peritoneum?
- pounch between bladder and rectum
- abscess (pus formation) can form bulges that can be palpated

How does the peritoneum contribute to immune function?
- contains phagocytes to protect viscera
- mesothelial cells transform to fibroblasts for healing
- greater omentum physically protects (like an apron)
What is peritonitis?
- inflammation of the peritoneum
- common
How does appendicites cause peritonitis?
- appendix bursts
- contents infect peritoneum
- greater omentum tries to encompass this
What is Peritoneal Malignancy?
- cancer that has spread to the peritoneum
There are some therapeutic approaches that can be used to treat the peritoneum. What is intraperitoneal chemotherapy?
- chemotherapy delivered directly into the peritoneum
There are some therapeutic approaches that can be used to treat the peritoneum. What is peritoneal dialysis?
- dialysis uses peritoneum as a membrane
- fluid and substances can dissolve through peritoneum into blood
- can remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure

There are some therapeutic approaches that can be used to treat the peritoneum. What is peritoneal-venous shunts?
- peritoneal fluid is drained into veins using a 1 way valve
- can be used in patients with refractory ascites



