UE Myology Flashcards
What are the thoracoappendicular (anterior axioappendicular) muscles?
- pectoralis major M.
- pectoralis minor M.
- subclavius M.
- serratus anterior M.

Pectoralis Major M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Pectoralis Major M.
(described as having a clavicular head and much larger sternocostal head)
- Origin: clavicular head (medial 1/2 clavicle), sternocostal head (anterior surface of sternum), costal cartilages 1-6, aponeurosis external abdominal oblique M.
- Insertion: lateral edge intertubercular groove of humerus
- Action: adduct and medially rotate humerus, protracts and depresses scapula, clavicular head flexes humerus, sternocostal head extends humerus from flexed state
- Innervation: lateral and medial pectoral N.

Pectoralis Minor M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Pectoralis Minor M.
(deep to pectoralis major M., usually pierced by medial pectoral N.)
- Origin: medial aspect of ribs 3-5
- Insertion: coracoid process of scapula
- Action: stabilizes scapula by protracting and depressing it against the thoracic wall
- Innervation: medial pectoral N.

Subclavius M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Subclavius M.
- Origin: upper border 1st rib and 1st costal cartilage
- Insertion: inferior aspect of the clavicle
- Action: positions and depresses the clavicle
- Innervation: nerve to the subclavius M. (C5-6)

Serratus Anterior M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Serratus Anterior M.
- Origin: lateral external surface of ribs 1-8
- Insertion: anterior surface of medial border of scapula
- Action: protracts the scapula, thereby stabilizing it against the thoracic wall, rotates the glenoid cavity superiorly
- Innervation: long thoracic N.

Paralysis of the _______ ______ muscle, usually as a result of injury to the _____ _______ nerve, results in “winging” of the scapula away from the thoracic wall, which makes abducting the upper limb beyond the horizontal position difficult.
- serratus anterior M.
- long thoracic N.

What are the posterior axioappendicular muscles?
- trapezius
- latissimus dorsi
- rhomboid major
- rhomboid minor
- levator scapulae
(we were tested over this in back myology)

What are the scapulohumeral muscles?
- deltoid M.
- subscapularis M.
- supraspinatus M.
- infraspinatus M.
- teres minor M.
- teres major M.

Deltoid M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Deltoid M.
- Origin: lateral 1/3 clavicle, scapular spine, acromion
- Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus
- Action: anterior part (flex and medially rotate the humerus), middle part (abduct the humerus), posterior part (extend and laterally rotate the humerus)
- Innervation: axillary N.

Subscapularis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Subscapularis M.
- Origin: medial aspect of subscapular fossa
- Insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus
- Action: medially rotate and adduct humerus, holds humeral head in glenoid cavity
- Innervation: upper and lower subscapular N.

Supraspinatus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Supraspinatus M.
(rotator cuff muscle)
- Origin: supraspinous fossa of scapula
- Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
- Action: w/ the deltoid M. abduct the humerus, holds the humeral head in glenoid cavity
- Innervation: suprascapular N.

Infraspinatus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Infraspinatus M.
(rotator cuff muscle)
- Origin: infraspinous fossa of scapula
- Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
- Action: laterall rotates the humerus, holds the humeral head in glenoid cavity
- Innervation: suprascapular N.

Teres Minor M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Teres Minor M.
(rotator cuff muscle)
- Origin: middle part of the lateral border of the scapula
- Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
- Action: laterally rotates the humerus, holds the humeral head in the glenoid cavity
- Innervation: axillary N.

Teres Major M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Teres Major M.
- Origin: posterior aspect of the inferior angle scapula
- Insertion: medial edge of the intertubercular groove of humerus
- Action: adduct and medially rotate the humerus
- Innervation: lower subscapular N.

- these 4 muscles are collectively referred to as the rotator cuff muscles:
- offer stability to the glenohumeral joint
- trauma can injure or tear any of these muscles, resulting in instability of the glenohumeral joint
- the ____________ muscle is the most commonly injured

- supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis Ms.
- supraspinatus M. most commonly injured

What is the surgical treatment for a rotator cuff tear?

- arthroscopic surgery: either repair the tendon if it has not atrophied back into the shoulder joint, OR shave part of the tendon down (if partial tear) to prevent catching of the tendon and pain

What are the brachial arm muscles of the anterior and posterior compartments?
- anterior: biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, and brachialis Ms.
- posterior: triceps brachii and anconeus Ms.

Biceps Brachii M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Biceps Brachii M.
- Origin: long head (supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula), short head (coracoid process of the scapula)
- Insertion: radial tuberosity and anterbrachial fascia as the bicipital aponeurosis
- Action: flex the humerus, flex the supine forearm and supinate the forearm, short head resists dislocation of the shoulder
- Innervation: musculocutaneous N.

Coracobrachialis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Coracobrachialis M.
- Origin: coracoid process of scapula
- Insertion: medial aspect of humeral body
- Action: flex and adduct the humerus
- Innervation: musculocutaneous N.

Brachialis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Brachialis M.
- Origin: distal half of the anterior aspect of the humeral body
- Insertion: ulnar tuberosity and coronoid process
- Action: flex the forearm
- Innervation: musculocutaneous N.

- reflex elicited by striking the thumb (physician’s) placed over the bicipital tendon w/ a reflex hammer
- failure of the tendon to tighten up and forearm to flex slightly could suggest injury to the ______________ nerve or ___ and ___ anterior rami
- bicipital myotactic reflex
- injury: musculocutaneous N. or C5/C6 anterior rami

- inflammation of the biceps tendon
- caused by repetitive movement of the long head of the biceps T. through the intertubercular groove
- can also cause crepitus (crackling noise)
- if the tendon dislocates out of the intertubercular groove, or even separates entirely from the supraglenoid tubercle, this can result in the muscle balling up in the mid arm and creating a: ________ ________
- biceps tendinitis
- popeye deformity

Triceps Brachii M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Triceps Brachii M.
- Origin: long head (infraglenoid tubercle of scapula), lateral head (posterior aspect of humeral body, superior to radial groove), medial head (posterior aspect of humeral body, inferior to radial groove)
- Insertion: olecranon of ulna and antebrachial fascia
- Action: extend the forearm, long head resists dislocation of shoulder
- Innervation: radial N.

Anconeus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Anconeus M.
- Origin: lateral humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: lateral aspect of olecranon
- Action: w/ triceps brachii M. extend the forearm, stabilizes the elbow joint
- Innervation: radial N.

Triangular Space on posterior shoulder
- borders:
- contents:
Triangular Space on posterior shoulder
- borders: teres minor M., teres major M., and long head of triceps brachii M.
- contents: circumflex scapular A. and V.

Quadrangular Space on posterior shoulder
- borders:
- contents:
Quadrangular Space on posterior shoulder
- borders: teres minor M., teres major M., long and lateral heads of triceps brachii M.
- contents: posterior humeral circumflex A. and V. and axillary N.

Triangular Interval on posterior shoulder
- borders:
- contents:
Triangular Interval on posterior shoulder
- borders: teres major M., long and lateral heads of triceps brachii M.
- contents: deep brachial A. and radial N.
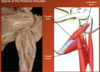
What are the superficial flexors of the antebrachium?
- pronator teres M.
- flexor carpi radialis M.
- palmaris longus M.
- flexor carpi ulnaris M.

Pronator Teres M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Pronator Teres M.
- Origin: humeral head (medial humeral epicondyle), ulnar head (coronoid process of ulna)
- Insertion: lateral aspect of radius
- Action: pronate and flex forearm
- Innervation: median N.

Flexor Carpi Radialis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Flexor Carpi Radialis M.
- Origin: medial humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: ventral aspect of the base of the 2nd metacarpal
- Action: flex forearm, flex and abduct hand at the wrist
- Innervation: median N.

Palmaris Longus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Palmaris Longus M.
- Origin: medial humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: palmar aponeurosis, flexor retinaculum
- Action: flex forearm, flex hand and tense the palmar aponeurosis
- Innervation: median N.

Flexor Carpi Ulnaris M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris M.
- Origin: humeral head (medial humeral epicondyle), ulnar head (olecranon and posterior ulna)
- Insertion: pisiform, hook of the hamate and base of 5th metatarsal
- Action: flex forearm, flex and adduct hand at the wrist
- Innervation: ulnar N.

Flexor Digitorum Superficialis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis M.
(only intermediate antebrachial flexor)
- Origin: humeroulnar head (medial humeral epicondyle and coronoid process of the ulna), radial head (superior half of anterior aspect of radius)
- Insertion: bifed insertion on the intermediate phalanges of digits 2-5
- Action: flex forearm, flex hand at wrist, flex proximal and intermediate phalanges of digits 2-5 at the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints respectively
- Innervation: median N.

What are the deep flexors of the antebrachium?
- flexor digitorum profundus
- flexor pollicis longus
- pronator quadratus

Flexor Digitorum Profundus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Flexor Digitorum Profundus M.
- Origin: proximal ulna and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: ventral aspect of bases of distal phalanges 2-5 (tendon passes through bifed tendon for the flexor digitorum superficialis M. to its insertion)
- Action: flex hand at wrist, flex all phalanges 2-5 at metacarpophalangeal, proximal, and distal interphalangeal joints 2-5
- Innervation: medial part = ulnar N.

Flexor Pollicis Longus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Flexor Pollicis Longus M.
- Origin: anterior aspect of radius and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: ventral aspect of base of distal phalanx of pollux
- Action: flex hand, flex and abduct 1st metacarpal at 1st carpometacarpal joint, flex both phalanges of pollux at intercarpal joint
- Innervation: anterior interosseous N. (of the median N.)

Pronator Quadratus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Pronator Quadratus M.
- Origin: anterior aspect of distal ulna
- Insertion: anterior aspect of distal radius
- Action: pronate forearm, deep fibers hold ulna and radius together
- Innervation: anterior interosseous N. (of median N.)

What are the superficial extensors of the antebrachium?
- brachioradialis
- extensor carpi radialis longus
- extensor carpi radialis brevis
- extensor digitorum
- extensor digiti minimi
- extensor carpi ulnaris

Brachioradialis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Brachioradialis M.
- Origin: lateral humeral supracondylar ridge
- Insertion: lateral aspect of distal radius
- Action: flex forearm (most force when forearm is midpronated)
- Innervation: radial N.

Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus M.
- Origin: lateral humeral supracondylar ridge
- Insertion: dorsal aspect of base of 2nd metacarpal
- Action: extend and abduct hand at wrist (active during fist clenching)
- Innervation: radial N.

Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis M.
- Origin: lateral humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: dorsal aspect of base of 3rd metacarpal
- Action: extend and abduct hand at wrist
- Innervation: deep radial N.

Extensor Digitorum M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Digitorum M.
- Origin: lateral humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: extensor expansions of digits 2-5
- Action: extend hand at wrist, extend all phalanges of digits 2-5 at metacarpophalangeal, proximal, and distal interphalangeal joints
- Innervation: posterior interosseous N.

Extensor Digiti Minimi M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Digiti Minimi M.
- Origin: lateral humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: extensor expansion of digit 5
- Action: extend all phalanges of digit 5 at the metacarpophalangeal, proximal, and distal interphalangeal joints
- Innervation: posterior interosseous N.

Extensor Carpi Ulnaris M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris M.
- Origin: lateral humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: dorsal aspect of base of 5th metacarpal
- Action: extend and adduct hand at wrist (active during first clenching)
- Innervation: posterior interosseous N.

- inflammation of the tendons of lateral epicondyle
- caused by repetitive use of superficial extensor muscles of forearm by repeated flexion/extension of wrist, straining periostium of lateral humeral epicondyle
- causes pain over lateral epicondyle and down posterior forearm
- elbow tendinitis, specifically lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)
(golfer’s elbow is medial epicondylitis)

What are the deep extensors of the antebrachium?
- supinator
- extensor indicis

Supinator M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Supinator M.
- Origin: lateral humeral epicondyle, radial collateral L. of the elbow, annular L. of the proximal radioulnar joint, supinator crest and supinator fossa of the ulna
- Insertion: proximal aspect of the radial body
- Action: supinate forearm
- Innervation: deep radial N.

Extensor Indicis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Indicis M.
- Origin: posterior aspect of the distal ulna and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: extensor expansion of digit 2
- Action: extend hand at wrist, extend 2nd digit
- Innervation: posterior interosseous N.

What are the outcropping muscles of the deep extensors of antebrachium?
- abductor pollicis longus
- extensor pollicis longus
- extensor pollicis brevis

Abductor Pollicis Longus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Abductor Pollicis Longus M.
- Origin: posterior aspect of proximal ulna, radius and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: base of 1st metacarpal
- Action: abduct hand at wrist, abduct pollux at carpometacarpal joint
- Innervation: posterior interosseous N.

Extensor Pollicis Longus M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Pollicis Longus M.
- Origin: posterior aspect of ulna and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: dorsal aspect of base of distal phalanx of pollux
- Action: abduct hand at wrist; extend 1st metacarpal, proximal, and distal phalanges of pollux at the carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints
- Innervation: posterior interosseous N.
Extensor Pollicis Brevis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Extensor Pollicis Brevis M.
- Origin: posterior aspect of radius and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: dorsal aspect of base of proximal phalanx of pollux
- Action: abduct hand, extend 1st metacarpal and proximal phalanges of pollux at carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints
- Innervation: posterior interosseous N.
Anatomical Snuff Box
- lateral (anterior) border:
- medial (posterior) border:
- contents:
Anatomical Snuff Box
- lateral (anterior) border: abductor pollicus longus M. and extensor pollicis brevis M.
- medial (posterior) border: extensor pollicis longus M.
- contents: radial A. (deep to tendons) and superficial radial N. (superficial to tendons)

What are the muscles of the thenar eminence?
- abductor pollicis brevis
- opponens pollicis
- flexor pollicis brevis
- adductor pollicis

Abductor Pollicis Brevis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Abductor Pollicis Brevis M.
- Origin: tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium bones and flexor retinaculum
- Insertion: lateral aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of the pollux
- Action: abduct pollux, aids in opposition
- Innervation: recurrent branch of the median N.

Opponens Pollicis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Opponens Pollicis M.
- Origin: tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium bones and flexor retinaculum
- Insertion: lateral aspect of 1st metacarpal
- Action: oppose pollux
- Innervation: reccurent branch of median N.

What are the 6 movements of the pollux (thumb)?
- abduction
- adduction
- extension
- flexion
- opposition
- reposition

Flexor Pollicis Brevis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Flexor Pollicis Brevis M.
(described as having a superficial and deep head)
- Origin: tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium bones and flexor retinaculum
- Insertion: lateral aspect of the base of proximal phalanx of pollux
- Action: flex 1st metacarpal and proximal phalanges of the pollux at the carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints
- Innervation: superficial head (recurrent branch of median N.), deep head (deep ulnar N.)

Adductor Pollicis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Adductor Pollicis M.
(described as having an oblique and transverse head)
- Origin: oblique head (capitate and bases of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bones), transverse head (anterior aspect of body of the 3rd metacarpal bone)
- Insertion: medial aspect of the proximal phalanx of pollux
- Action: adduct pollux
- Innervation: deep ulnar N.

The complicated action of opposition of the thumb can be lost w/ injury to the _______ nerve. Even a superficial injury of the palm can damage the ________ _______ of the _______ nerve, which innervates the muscles involved in opposition.
- median N.
- recurrent branch of the median N.

What are the hands muscles of the hypothenar eminence?
- abductor digiti minimi
- flexor digiti minimi brevis
- opponens digiti minimi

Abductor Digiti Minimi M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Abductor Digiti Minimi M.
- Origin: pisiform bone
- Insertion: medial aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of 5th digit
- Action: abduct 5th digit
- Innervation: deep ulnar N.

Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis M.
- Origin: hook of the hamate bone and flexor retinaculum
- Insertion: medial aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of 5th digit
- Action: flex proximal phalanx of 5th digit
- Innervation: deep ulnar N.

Opponens Digit Minimi M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Opponens Digit Minimi M.
- Origin: hook of the hamate bone and flexor retinaculum
- Insertion: medial aspect of the 5th metacarpal
- Action: oppose 5th digit
- Innervation: deep ulnar N.
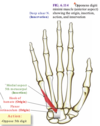
What are the intermediate muscles of the hand?
- 1st and 2nd lumbrical
- 3rd and 4th lumbrical
- dorsal interossei: (1-4) DAB
- palmar interossei: (1-3) PAD

1st and 2nd lumbrical M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
1st and 2nd lumbrical M.
- Origin: lateral side of lateral two flexor digitorum profundus tendons as unipennate muscles
- Insertion: radial aspect of extensor expansions of 2nd and 3rd digits
- Action: flex proximal phalanges of 2nd and 3rd digits at metacarpophalangeal joint, extend intermediate and distal phalanges of 2nd and 3rd digits by tightening extensor expansion
- Innervation: median N.

3rd and 4th lumbrical M.
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
3rd and 4th lumbrical M.
- Origin: between the medial three flexor digitorum profundus tendons as bipennate muscles
- Insertion: radial aspect of extensor expansions of 4th and 5th digits
- Action: flex proximal phanages of 4th and 5th digits at metacarpophalangeal joint, extend intermediate and distal phalanges of 4th and 5th digits by tightening extensor expansion
- Innervation: deep ulnar N.

Dorsal Interossei M. (1-4 DAB)
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Dorsal Interossei M. (1-4 DAB)
- Origin: adjacent sides of two metacarpals as a bipennate muscle
- Insertion: bases of proximal phalanges and extensor expansion of digits 2-4
- Action: abduct digits 2-4, flex proximal phalanges at the metacarpophalangeal joint, extend intermediate and distal phalanges by tightening extensor expansion
- Innervation: deep ulnar N.

Palmar Interossei M. (1-4 PAD)
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Palmar Interossei M. (1-4 PAD)
- Origin: palmar aspect of the 2nd, 4th, and 5th metacarpal bones
- Insertion: bases of proximal phalanges and extensor expansions of 2nd, 4th, and 5th digits
- Action: adduct 2nd, 4th, and 5th digits, flex proximal phalanges of 2nd, 4th, and 5th digits at the metacarpophalangeal joint, extend intermediate and distal phalanges of the 2nd, 4th, and 5th digits by tightening extensor expansion
- Innervation: deep ulnar N.

What are the 5 hand positions?
- power grip (palm grasp): digits acting against the palm while wrapped around an object w/ counterpressure from the pollux, includes involvement from the long flexors of the digits acting at the interphalangeal joint w/ intrinsic hand muscles acting at the metacarpophalangeal joint
- hook grip: as when carrying a suitcase, consumes less energy than power grip, involves mainly long flexors of the digits acting at the interphalangeal joint
- precision handling grip: as when writing, involves long flexor and extensor muscles in addition to the intrinsic hand muscles performing fine movements
- pinching: compressing an object between distal aspect of 1st and 2nd digits
- position of rest: inactive position



