Posterior Thigh and Popliteal Fossa Flashcards
When you move the hip into flexion, which of the small lateral rotators in the gluteal region lose most of their function?
quadratus femoris

Posterior Thigh Muscles
- Common name:
- Common proximal attachment:
- Common innvervation:
- Functions:
Posterior Thigh Muscles
- Common name: hamstrings (tendons posterior to knee area used to hang hams of pigs, hamstringing enemy and their horse during ancient times)
- Common proximal attachment: ischial tuberosity (except short head of biceps femoris)
- Common innvervation: tibial division of sciatic N. (except short head of biceps femoris which is by common fibular N.)
- Functions: thigh extension (except short head of biceps femoris) and leg flexion (all 4)

Semitendinosus
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Semitendinosus
(long, cordlike tendon that begins 2/3 of the way down thigh)
- Origin: ischial tuberosity
- Insertion: medial surface of superior aspect of tibia
- Action: extend thigh, flex leg (medially rotate)
- Innervation: tibial N.

What muscles comprise the pes anserinus?
- sartorius (femoral N.)
- semitendinosus (tibial N.)
- gracilis (obturator N.)

Semimembranosus
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Semimembranosus
- Origin: ischial tuberosity (flattened membranous proximal attachment)
- Insertion: posterior part of medial condyle of tibia
- Action: extend thigh, flex leg
- Innervation: tibial N.

The attachment of semimembranosus to posterior medial condyle of tibia blends w/ what tendon and provides what function?
- blends w/ popliteal fascia and becomes oblique popliteal ligament
- this reinforces the intercondylar part of joint capsule of knee

Biceps Femoris Long Head
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Biceps Femoris Long Head
- Origin: ischial tuberosity
- Insertion: head of the fibula
- Action: flex leg, extend thigh
- Innervation: tibial N.

Biceps Femoris Short Head
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Biceps Femoris Short Head
- Origin: distal lateral lip of linea aspera of femur
- Insertion: head of the fibula
- Action: only flexed leg
- Innervation: common fibular N.

Adductor Magnus (Hamstring Portion)
- Origin:
- Insertion:
- Action:
- Innervation:
Adductor Magnus (Hamstring Portion)
- Origin: ischial tuberosity
- Insertion: adductor tubercle on the medial epicondyle of femur
- Action: extend thigh
- Innervation: tibial N.

What are the boundaries of the popliteal fossa:
- superomedially:
- superolaterally:
- inferolaterally:
- inferomedially:
What are the boundaries of the popliteal fossa:
- superomedially: semitendinosus and semimembranosus
- superolaterally: biceps femoris
- inferolaterally: lateral head gastrocnemius
- inferomedially: medial head gastrocnemius

What is the order of popliteal contents? (superficial to deep)
- nerves
- popliteal vein, lymph nodes and branches
- popliteal artery and branches
- deepest structure in popliteal fossa
- continuation of femoral artery, becomes _______ artery after passing through adductor hiatus
- runs close to knee joint capsule, gives rise to genicular branches
popliteal artery
How does the body bypass the need for blood flow from popliteal or femoral As. if they are damaged?
- genicular branches of popliteal A. form genicular anastomosis
- important collateral circulation if knee is fully flexed too long or narrowed/occluded popliteal vessels
- supplies articular capsule and ligaments of knee joint
- descending branch of lateral femoral circumflex A. is especially important in supplying leg if femoral A. is severed or ligated

What 2 arteries does the popliteal A. divide into?
- anterior tibial A.
- posterior tibial A.
(and they said med school is hard :))
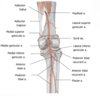
- small saphenous vein terminates into the _______ vein
- lies superficial to and in same fibrous sheath as popliteal artery
- becomes femoral vein after tranversing adductor hiatus
popliteal V.

Sciatic nerve usually ends at superior angel of popliteal fossa where it divides into the: (2)
- tibial N.
- common fibular (peroneal) N.

- most superficial structure relative to popliteal A. and V.
- innervation: superficial and deep posterior leg muscles, knee joint
tibial N.
- leaves popliteal fossa by passing superficial to lateral head of gastrocnemius
- winds around head and neck of fibula (susceptible to injury)
- deep to fibularis longus it terminates into: deep fibular N. and superficial fibular N.
common fibular (peroneal) N.

- composed of: medial sural cutaneous nerve (from tibial nerve); AND sural (or fibular) communicating branch (from common fibular nerve) OR lateral sural cutaneous nerve (from common fibular nerve)
- runs inferiorly w/ small saphenous vein
- innervates: distal posterior aspect of leg and lateral aspect of ankle and foot
cutaneous nerves: sural nerve



