U3-2-1 - Geometric Isomers Flashcards
When can geometric isomers occur?
When there is a lack of free rotation around a C to C bond, e.g. C=C or ring structure.
Is this isomer cis or trans?

Cis
both CH3 groups on the same side of C=C
Is this isomer cis or trans?

Trans
both CH3 groups on opposite sides of C=C
Why is this isomer cis?

Both substituents (CH3) on the same side of the C=C bond.
Why is this isomer trans?
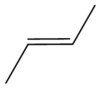
Both substituents (CH3) on opposite sides of the C=C bond.
Why does propene not have geometric isomers?

Propene has two hydrogens attached to the first carbon of C=C.
Will cis or trans isomers have the higher melting point?
Trans
Why do trans isomers have higher melting points?
Closer packing due to their shape allows for stronger IMFs.


