U1-2-2 - Electronic Configuration Flashcards
(18 cards)
Aufbau principle
Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy.
E.g. 1s before 2s, 2s before 2p.
4s orbitals are an exception when filling orbitals because ___________.
they are filled before 3d.
Hund’s rule
Electrons first fill degenerate orbitals singly with parallel spins.

Pauli exclusion principle
No two e− in one atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
(So no orbital can hold more than two e<strong>−</strong> and these two e− must have opposite spins.)

Aluminium has the electronic configuration [Ne] 3s2 3p1.
What does [Ne] mean?
Shorthand for electronic configuration of neon: 2, 8.
Ground state
Lowest energy electronic configuration (default)
Name the principle described
Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy.
E.g. 1s before 2s, 2s before 2p.
Aufbau principle
Name the principle described
Electrons first fill degenerate orbitals singly with parallel spins.
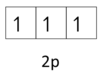
Hund’s rule
Lowest energy electronic configuration (default)
Ground state
Name the principle described
No two e− in one atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
(So no orbital can hold more than two e<strong>−</strong> and these two e− must have opposite spins.)

Pauli exclusion principle
What decides which block (s, p, d, f) in the periodic table an element is placed in?
Last occupied subshell
(e.g. 1s2 2s2 2p6 = p block)
The s block contains __________.
groups 1 and 2, and helium
The p block contains ___________.
groups 3 – 8, except helium
The d block contains __________.
the transition metals
The f block contains __________.
lanthanides and actinides
Subset of transition metals shown under the periodic table
The more stable the electronic configuration, the _____________ the ionisation energy.
higher
State three features that make an electronic configuration stable.
Ends in a full shell (e.g. 2nd shell)
or full subshell (e.g. 3p6)
or half-filled subshell (e.g. 2p3).
The more stable the electronic configuration, the ____ reactive the species.
less


