Topic 6 - NERVOUS SYSTEM IV - Motor "Output" - Autonomic Nervous System Flashcards
(22 cards)
efferent (motor) nervous system: Autonomic Nevous System
CNS ⇒ ?
smooth and cardiac muscle, glands
efferent (motor) nervous system: autonomic nervous system
- how many neurons to effector?
- neurons can be what?
- 2 neurons to effector (preganglionic and postglanglionic)
- neurons can be distinguished by the type of nt released:
- cholinergic = Ach
- adrenergic = norepinephrine (NE)
efferent (motor) nervous system: autonomic nervous system
what are the 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
- sympathetic nervous system
- parasympathetic nervous system
what are the 3 functions of the sympathetic nervous system?
- prepares body for activity
- fight or flight response
- activated during exercise
draw diagram for the sympathetic nervous system

what do you need to do to stop chemical stimulation in the sympathetic nervous system?
and what are the steps?
need to remove neurotransmitter
-
ACh broken down by acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
- on postsynaptic membrane (cell body/dendrites of postsynaptic cell)
-
Norepinephrine broken down by Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)
- in synaptic end bulb of neuron that is released
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
- rest and digest
- “housekeeping”
draw diagram for parasympathetic nervous system
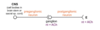
most organs innervated by ANS have what?
most organs innervated by ANS have both SNS + PSNS and side effects - usually opposite actions
what has both SNS + PSNS and effects? - usually have opposite actions
most organs innervated by ANS have both SNS + PSNS and effects? - usually have opposite actions
what does ANS regulate?
ANS regulates internal processes continuously and automatically
example: heart rate ⇒ SNS excites, PSNS inhibits
effects of ANS
organ: pupil of eyes (iris muscles)
SNS:
PSNS:
SNS: dilate
PSNS: constrict
effects of ANS
organ: heart
SNS:
PSNS:
SNS: increased heart rate and force of contraction
PSNS: decreased heart rate
effects of ANS
organ: gastrointestinal tract
SNS:
PSNS:
SNS: decreased motility
PSNS: increased motility
effects of ANS
organ: blood vessels (smooth muscle)
SNS:
PSNS:
SNS: vasoconstriction
PSNS: *no innervation of blood vessels (except penis and clitoris*
effects of ANS
organ: sweat glands
SNS:
PSNS:
SNS: increased secretion (cold sweat)
PSNS: *no innervation*
effects of ANS
organ: digestive glands
SNS:
PSNS:
SNS: decreased secretion (Except saliva)
PSNS: increased secretion
effects of ANS
organ: genitals
SNS:
PSNS:
SNS: ejaculation (male)
PSNS: erection, lubrication (male/female)
higher control of ANS
draw diagram

hypothalamus does not need ______ for its ___ functions, but ______ can cause _____ ______.
hypothalamus does not need cerebral input for its ANS functions, but emotions can cause autonomic effects
hypothalamus ____ ____ _____ celebral input for its ANS functions, but emotions ___ _____autonomic effects
hypothalamus does not need celebral input for its ANS functions, but emotions can cause autonomic effects
hypothalamus does not need celebral input for its ANS functions, but emotions can cause autonomic effects
examples: ???
- blushing
- fainting
- cold sweat
- increased heart rate


