THRC.7 Flashcards
The tracts of the CNS can be divided into…
- Ascending pathways
- Descending pathways
What are the divisions of the ascending pathways?
- Medial lemniscus
- Extra-lemniscal system
List the ascending pathways
- Visual
- Vestibular + auditory
- Somatic afferent pathways
The medial lemniscus can be divided into…
- Spinal lemniscus (trunk + limbs)
- Trigeminal lemniscus (sensory nerves of the head)
The sensory neurons of the spinal lemniscus run along…
The dorsal funiculus of the spinal cord

Decussation of lemniscus

Medial lemniscus

Cuneate nucleus

Gracile nucleus

Fasciculus gracilis
Tracts from the caudal trunk + lumbosacral plexus are located…
- Medially:
- Fasciculus gracilis
Tracts from the cranial trunk + brachial plexus are located…
- Laterally:
- Cuneate fascicle

Fasciculus cuneatus

Optic nerve (CN-II)

Thalamus

Sensory area of neopallium
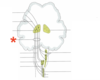
Medial lemniscus

Bulbothalmic tract

Spinothalmic tract

Pontine sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve

Gracile + cuneate nucleus
Where does the lateral-most tract terminate?
Nucleus cuneatus of dorsal medulla oblongata
Where does the medial-most tract terminate?
Nucleus gracilis of dorsal medulla oblongata
Where does the medial lemniscus join with sensory fibres of the trigeminal nerve?
The brain stem
Which tract is formed by the extra-lemniscal system?
Spinothalamic tract
Give the termination pathway of the spinothalamic tract
- Neurons of the dorsal horns (close to spinal root) →
- White matter → Ventrolateral funiculi
- Thalamus
- Some tertiary neurons project more rostrally
Pathway of proprioceptive information to the brain
- Receptors in tendons + muscles
- Dorsal horn → Cerebellum (via spinocerebellar tracts)

Optic chiasm

Optic tract

Optic thalamus

Visual cortex

Rostral colliculus

Pituitary gland
Give the pathway of the optic tract
- Eyes → Optic chiasm
- Optic tract:
- → Optic thalamus
- → Rostral colliculus
- Visual cortex → Rostral colliculus
Where is the visual cortex located?
Occipital lobe
Which system is shown?

Medial lemniscal system
What is shown?

Vestibular + auditory pathway

Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN-VIII)

Vestibulocochlear nuclei

Caudal colliculus

Rostral colliculus

Acoustic area

Medial geniculate nucleus

Lateral lemniscus nucleus
Location of primary neurones concerned with the vestibular + auditory pathways
- Spiral ganglion
- Vestibular ganglion
- Cochlea
The vestibulocochlear nerve enters the…
Trapezoid body
Fibres leading to the temporal lobe are associated with which sense?
Conscious perception
List the descending pathways
- Somatic motor pathways
- Lower motor neurons
- Upper motor neurons
- Pyramidal system
- Extrapyramidal system
Location of lower motor neurons
- Ventral column of the grey matter (Spinal cord)
- Motor nuclei of the cranial nerves
Function of lower motor neurons
- Simple reflexes
- Controlled by upper motor neurons
Location of upper motor neurons
- Neopallium
- Red nucleus
The connection of the upper and lower motor neurons are grouped into which descending pathways?
- Pyramidal system
- Extrapyramidal system
Function of:
- Pyramidal system
- Extrapyramidal system
- Pyramidal system: Finely adjusted movement
- Extrapyramidal system: Coarse movement
What is shown?

The pyramidal system

Motor area of neopallium

Corticostriate tract

Corticorubral tract

Striate body

Red nucleus

Oculomotor nuclei

Motor nuclei of the spinal cord
Structure of the extrampyramidal system
- Multisynaptic pathways
- Originate from:
- Corpus striatum
- Subthalamic nuclei
- Substantia nigra
- Red nucleus
Central autonomic nervous system is concerned with…
- Function of inner organs (viscera)
- Inspiration, digestion, metabolism, temperature
- Regulated by hypothalamus
Pathway of the autonomic nervous system
- Hypothalamus
- Autonomic nuclei of the brain/spinal cord
Hypothalamus receives information from almost all parts of the body via…
Mesencephalic nuclei
Pathways of the central autonomic nervous system
- Visceral pathway
- Afferent pathway
- Efferent pathway
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic


