The Nephron from lecture 2 Flashcards
(32 cards)
Countercurrent Exchange is one of the most important physiological phenomena in all of nature. (Among other things) It allows ________________ of substances.
hyperconcentration
__________________ is a pair of adjacent channels or tubes containing fluids flowing in opposite directions and having an energetic gradient directed between one channel and the other. (In other words, stuff can flow between the tubes.)
1) COUNTERCURRENT EXCHANGE 2) fluids flowing in opposite directions
this is what a nephron looks like
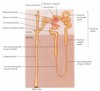
The arrangement of tubes in ____________________ means that even as the tube starts with lower concentration and picks up solutes, even when it get to the end it can still pickup a bit, as it is encountering the highest concentration of adjacent tube.

OPPOSITE FLOW DIRECTIONS
A COUNTERCURRENT EXCHANGE SYSTEM can only work if there is an __________ in the system.
In this case, there is ___________ in only one direction. In the case of the kidney, salts are being transported to concentrate salts in the ________.
1) asymmetry
2) active transport
3) urine
Helpful to know

Proximal Convoluted Tubule:
Initiate concentration of ___________ filtrate.
About ___ of _________ removed by active transport here, and chlorine follows passively.
Remaining fluid in _________ tube is about same concentration as that of surrounding interstitial fluid.
Remaining fluid reduce to about _____ original volume
1) glomerular
2) 75% of sodium
3) nephron
4) 25%

Loop of Henle:
Acts in manner of counter current exchanger. Note that each limb of loop has fluid moving in ________________ (even though connected at one end).
Further concentrates ________.
Also means that salt concentration will be highest near bend in the loop.
1) opposite directions
2) urine

No active transport of salt out of the____________________.
Chlorine ions actively transported out of loop into the interstitial space. Oppositely charged sodium ions follow. However, water does not move out of the ________.
A concentration gradient IN THE INTERSTITIAL SPACE has been set up by the chlorine ( plus sodium) transport.
1) descending loop of Henle
2) ascending loop
Distal Convoluted Tubule:
In addition to sodium-chloride, potassium, __________, and ____________ removed from filtrate here. These are retained as needed by the body.
At this point, nephron has used materials IN the glomerular filtrate to set up a concentration gradient in the _______________________
1) ammonia
2) carbonate
3) interstitial space of the kidney

Collecting Duct:
Receives many_______________________.
Collecting duct now passes through the concentration gradient set up by many _________________.
So, as glomerular filtrate passes down collecting tubule, it moves through ___________________ concentration of salts that were set up by loops of Henle.
1) proximal convoluted tubules
2) adjacent nephrons
3) higher and higher

By process of osmosis, water wants to move from region of_________________. This pulls water from filtrate, leaving behind a more concentrated “________”.
1) higher water concentration to lower
2) urine
REMEMBER
By setting up a countercurrent system, a salt concentration gradient is set up in the interstitial space (highest concentration near curve of loop of Henle).
——–>
As fluid in collecting tubules reacts to concentration gradient, water is pulled out, concentrating filtrate as urine.
CORTEX – part that contains the convoluted tubules and _____________, and _________________.
1) proximal part of Loop of Henle
2) proximal part of collecting tubules
MEDULLA – contains _______________, and ________________. Where most of the active transport takes place.
1) distal part of Loop of Henle
2) distal part of collecting tubules
In regards to urine production, the most important hormone is _______________
ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE, or ADH.
ADH makes the collecting duct MORE ___________ to water. Thus, secretion of ADH causes the retention of water in the body, and more _____________. (ADH is usually secreted in response to environmental situations that require the retention of water.)
1) permeable
2) concentrated urine
A diuretic will decreases permiability of ____________, so you lose lots of water (copious, dilute urine). Examples of diuretics: caffiene, alcohol (beer particularly due to the hops), capsasin (the active ingredient in hot peppers), others.
collecting tubule
The blood enters the nephron thru the ______________ and exits thru the __________________
1) afferent arteriole
2) efferent arteriole
_____________ is the major way of how things gets into the nephron from the blood
Filtration
Reabsorbtion is the movement of things back into the ____________________
blood from the nephron
the movement of stuff from the blood to the nephron is called _____________
secretion
The nephron is the tiny filtering structure in your kidneys. Each of your kidneys contain more than a __________ tiny filtering nephrons that help clean your blood.
million
Function of the Nephrons
Remove excess water,wastes and other substances from __________.
Return substances like sodium, ___________ or ___________ whenever any of these substances run low in your body.
1) your blood
2) potassium or phosphorus


