Develompment and Structure of the Exretory System 2 Flashcards
the word __________ means kidney’s, or a part of it.
Nephron
Kidneys are derived from __________________.
INTERMEDIATE MESODERM
Kidney starts out as a __________ STRUCTURE.
SEGMENTAL
Bladder, as part of the embryonic ___________ derived from __________.
1 ) gut tube lining 2) endoderm
kidney’s are for _________ NOT __________.
1 ) EXCRETION (urine removal from the body) 2) ELIMINATION (Defecation, removal of solid waste)
There is a segment of intermediate mesoderm for every _____________.
body segment
The Earliest kidney appears in the cervical region of the body! (About week 3.) is called the ____________.
PRONEPHROS
we have Kidney segments from our cervical to _________ region that we use all the time.
sacral
Pronephros Develop very close to the_______. (They battle it out for the nearby ducts)
gonads
Pronephros Has NO_________________.
EXCRETORY FUNCTION
THE PRONEPHROS Functions to INDUCE DEVELOPMENT of middle segments of intermediate meosderm called ____________
MESONEPHROS
the duct that attaches to the mesonephros is called the ______________ is very important in INDUCING DEVELOPMENT OF THE CAUDAL KIDNEY SEGMENTS called ____________
1) MESONEPHRIC DUCT 2)METANEPHROS
The Mesonephric Duct is derived from ____________, it also heads towards the _________.
1) Mesoderm 2)bladder
METANEPHROS becomes the
Kidney that functions in us after birth
Pronephros is the kidney that starts in our neck, it induces (cause it to rise) the middle region known as ______________ which induces the back region known as ___________.
1) Mesonephros 2)Metanephros
Induction is very important in _____________ process.
developmental
__________________ reaches all the way to end of gut tube (cloaca).
Mesonephric Duct
The mesonephric Duct connects to the ___________ and it is needed to induce the __________.
1 )Bladder 2)Ureter (but it does not become the ureter)
A new tube grows from the ___________ to the ___________ ureter.
1) Bladder 2)Metanephros
The mesonephric Duct becomes the sperm duct in men known as _______________
Ductus or vas deferens
the __________ is the exit from the bladder
Urethra
After the ________________ attaches to cloaca, the embryonic URETER grows from ______________ to attach to mass of metanephric kidney.
1) mesonephric duct 2)caudal to cranial
Allantois is a big sac that leads to the belly button out of the ______________
umbilical tube
“The fetus starts metabolizing right away” what does that mean?
fetus starts making cellular waste that gets passed down to the mother thru the placenta.
the ____________ connects the bladder to the allantois
Urachus
Kidney’s are ___________ so they are sliding up the back body wall. while the bladder is ____________.
1) Retroperitoneal 2)intraperitoneal
the sperm tube is ________ to the ureter
ventral
the _____________, grows between the more dorsal part of the gut tube and the more ventral part that will become the bladder.
URORECTAL SEPTUM
like the heart, and the lungs, __________ is ventral to your gut tube.
the bladder
Kidneys don’t stay at caudal end of body. They “_________” to a position just caudal to diaphragm and liver.
ascend
the action of the kidney’s rising is called
ASCENT OF THE KIDNEYS
________ kidney is a bit lower due to mass of liver.
Right
kidney’s work their way up by attaching to successive segmental arteries. what is the last artery they attach to called?
the renal artery
while our kidney’s __________, gonad’s (testicles) _________.
1) Ascend 2)Decend
where are the adrenal glands (also known as the supernal glands) located?
ventral to the Kidney’s (above them)
In the kidney’s Large vessels are usually ventral to ____________
ureter exit.
(They do move a reasonable amount when you breathe. – This is why they can REALLY hurt when they have problems. Retroperitoneal pain can be extreme.) “NOT A QUESTION”
(They do move a reasonable amount when you breathe. – This is why they can REALLY hurt when they have problems. Retroperitoneal pain can be extreme.)
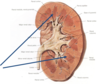
where are the arrows pointing to?

1) top Outer CORTEX
2) bottom Inner MEDULLA
URETER runs from kidneys to ___________.

urinary bladder
Ureter ends in a dilated _______________.

RENAL PELVIS
Renal pelvis branches into structures called the ___________

MAJOR CALYCES
Major calyces divided into ______________.

MINOR CALYCES
Minor calyces receive __________ from many microscopic collecting tubules.
fluid outflow (urine)
NEUROVASCULAR SUMMARY
Kidneys (and superior ureter)
Arterial Supply: _____________
Venous Drainage: ______________
1) Renal artery
2) Renal vein
NEUROVASCULAR SUMMARY
Kidneys (and superior ureter)
Sympathetic Innervation/Levels: ______________________________________
Sympathetic Preganglionic and Postganglionic Synapse: _____________________
Parasympathetic Innervation: __________________
1) T5-T9 & T10-T11. carried mainly by the greater splanchnic nerve, although some of it may be carried by the lesser splanchnic nerve.
2) This is preganglionic sympathetic innervation and synapse occurs in the celiac ganglion.
3) There is no significant parasympathetic innervation.
THE BLADDER is ___________ in shape.
tetrahedron
the bladder has
•_____ ATTACHMENTS - one at each corner.
•One corner lies at top edge of pubic symphysis (here, vestigal ________ holds it down)
•Right and left _________ dump in cranio-dorsally.
•URETHRA exits caudally (inferiorly).
1) 4
2) URACHUS
3) URETERS
4) URETHRA
The triangle defined by the connection of the two ureters and the exit of the urethra is NOT ELASTIC. It is known as the _________________.
TRIGONE OF THE BLADDER
The __________ closes at birth
Urachus
The bladder is lined by a special type of epithelium called _________________
TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM (it’s stretchy).
URETER ATTACHMENT
- Traverse the bladder obliquely.
- So, when bladder is full, they get ___________.
- There is no valve, but this passive closing prevents ________________
1) squeezed flat
2) urine from backing up into the kidneys.
NEUROVASCULAR SUMMARY
Bladder (and inferior ureter)
Arterial Supply: _____________________________________________
Venous Drainage: _____________________________________________
1) Superior and inferior vesicle arteries (branches of internal iliac artery).
2) Superior and inferior vesicle veins (tributaries of internal iliac vein).
NEUROVASCULAR SUMMARY
Bladder (and inferior ureter)
Sympathetic Innervation/Levels: ___________________________
Sympathetic Preganglionic and Postganglionic Synapse: __________________
Parasympathetic Innervation: ________________________________
1) T12 via least splanchnic nerve.
2) in inferior mesenteric ganglion and plexus.
3) Sacral outflow (S2-4) via pelvic nerves.
embryos produce 4 extraembryonic membranes which are:
1) amnion
2) yolk sac
3) chorion
4) allantois


