Overview of the structures of the endocrine system lecture 4 Flashcards
We usually contrast nervous system structures with endocrine structures. But certain nervous system cells act as endocrine cells and certain endocrine tissues are derived from ______________.
neural ectoderm
Nerve cells that produce hormones and secrete them into the bloodstream are called _______________
NEUROSECRETORY CELLS
In humans, neurosecretory cells are found in the ________________.
HYPOTHALAMUS
PITUITARY GLAND prospers name is ______________
Hypophysis
Location of the pituitary gland Small but complex appendage that sits at ______________ – in the ___________– most median depression in the medial cranial fossa of the ______________.
1) the base of the brain 2) Sella Turcica 3) sphenoid bone
Pituitary lies just inferior to _____________.
hypothalamus
Hypothalamus and Pituitary connected by stalk containing ____________ and ______________.
1) nerve fibers 2) blood vessels
the Pituitary gland is composed of two lobes ________________ and _______________.
1) ANTERIOR PITUITARY 2) POSTERIOR PITUITARY
The pituitary Fossa sits in the ____________
Sella turcica
infundibulum is like a

funnel that connects the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
Hypothalamus is an _____________, so it is innervated by the brain, and derived from _____________.
1) outgrowth of brain
2) neural ectoderm
Posterior Pituitary is made out of neural tissue so that’s why it is called _____________. it is an outgrowth of hypothalamus so it is derived from neural ectoderm.
1) Neurohypophysis
2) hypothalamus
Anterior Pituitary is made of Glandular tissue so that’s why it’s called ______________. it develops as a superiorly directed outgrowth of ____________, derived from ____________.
1) Adenohypophysis
2) roof of mouth
3) ectoderm ( comes from epithelium –> stratified squamous epithelium )
HYPOTHALAMUS and PITUITARY GLAND
INNERVATION: ______________
Arterial Supply: __________________
Venous Drainage: _________________
1) BRAIN
2) circulus arteriosus cerebri ( Cerebral arteriole circle ) (any brain structure)
3) cavernous venous sinus ( Cavernous sinus )
Hypothalamic hormones are enclosed in vesicles that move down the axon and accumulate near terminal ends that are touching the _________________________
capillaries of the posterior pituitary
NOTE we aare talking about the posterior pituitary
In response to an action potential– hormones are released from vesicles (much like a neurotransmitter), into_______________ instead of synaptic clefts.
venous capillaries
______________ and _____________ are manufactured in the hypothalamus, but released in the posterior pituitary
1) Oxytocin
2) Vasopressin
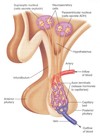
Hypothalamic hormones that are Released by Adenohypophysis are enclosed in vesicles that move down the axon and accumulate near terminal ends that are close to the ___________________
pituitary stalk (infindibulum) NOT THE CAPPILLARIES.
NOTE WE ARE TALKING ABOUT THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY
In response to an action potential– hormones are released from vesicles (much like a neurotransmitter), in this case into a circulatory structure called the______________( also known as ____________________m)
1) pituitary portal system
2) hypophyseal portal system
ALSO KNOWN AS the hypothalmic hypophyseal portal system
the Pituitary portal system is connected to a cappilary bed located in the

INFINDIBULUM
Most hormonal interactions of the hypothalamus-pituitary(anterior) complex follow a common pattern:
- A hypothalamic hormone effects control over the secretion of an ____________________;
- The corresponding anterior pituitary hormone controls secretion of the hormone of another _____________; and
- That secretion of that gland affects other target ___________.
1) anterior pituitary hormone
2) endocrine gland
3) tissues/organs
Hypothalamic hormones can have the effect of ___________ or _____________ the release of anterior pituitary hormones.
Called _____________ or __________________.
1) stimulating
2) inhibiting
3) RELEASING HORMONES
4) INHIBITING HORMONES
HORMONES MANUFACTURED IN THE HYPOTHALAMUS and their (FUNCTIONS) pt 1
OXYTOCIN - 1)_________, 2)_____________, 3)___________.
VASOPRESSIN (ADH) – 4)___________________
RELEASING HORMONES – 5)____________________
INHIBITING HORMONES – 6)______________________
1) initiates labor
2) stimulates mammary glands to release milk
3) Stimulates uterine contractions in activities other than labor
4) decreases urine output by increasing DCT and collecting duct permeability.
5) stimulate release of anterior pituitary hormones.
6) inhibit release of anterior pituitary hormones.
Oxytocin and Vasopressin are manufactured in the ___________, but released in the _______________.
1) hypothalamus
2) posterior pituitary
GROWTH HORMONE (GH) is manufactured & released by the ______________ – regulates growth; affects protein, _____________________.
1) adenohypophysis
2) fat and carbohydrate metabolism
THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) – controls _____________________________________.
secretion of thyroxin from the thyroid gland
ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE (ACTH) – controls secretion of hormones released by ___________, specifically ________________.
1) adrenal cortex
2) glucocorticoids
FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE (FSH) –
Females: stimulates __________ ; stimulate the release of ________
Males: stimulates _______________ maturation.
1) maturation of egg cells
2) nurse cells for sperm
LUTENIZING HORMONE (LH) –
Males- stimulates secretion of___________________.
Females, stimulates release of ____________________.
1) testosterone by testes
2) ovum by ovary
MELANOCYTE-STIMULATING HORMONE (MSH) – along with _____________, affects pigment (color) release in __________.
1) Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH)
2) skin
PROLACTIN (PRL) –
stimulates __________________.
milk production
PINEAL GLAND
- Location and Development: outgrowth of the roof of the ____________. Found near the posterior margin of the ___________, slightly cranial and superior to cerebellum.
- Innervation: brain.
- Arterial Supply: _________________
- Venous Drainage: __________________
- Function: produces __________ – amino acid derivative thought to have connection with ______________.
1) diencephalon
2) corpus callosum
3) circulus arteriosus cerebri
4) cavernous venous sinus
5) MELATONIN
6) regulating sleep cycle
THYMUS GLAND
- Location: Located just deep to ____________ and just ventral to great ____________. Until puberty, a large structure, after which it begins to atrophy and gets replaced with ______________.
- Development: from ____________ derived from __________ of third pair of visceral pouches (3rd gill slit pouch).
1) sternum
2) vessels of heart
3) adipose tissue
4) epithelial cells
5) endoderm
THYMUS GLAND
- Innervation: _______________
- Arterial Supply: _____________________ (branch of subclavian that is ventral to body wall).
- Venous Drainage: ____________ to brachiocephalic vein.
- Function: produce 4) ____________, 5)______________, 6) ____________ – convert embryonic lymphocytes into ___________.
1) Vagus Nerve (X)
2) branches from internal thoracic artery
3) thymic veins
4) THYMOSIN
5) THYMUS HUMERAL FACTOR
6) THYMOPOIETIN
7) T-cells
THYROID GLAND
Location: Located close to thyroid cartilage. Has ___________ connected by _____________ medially. Isthmus covers cricoid cartilage in ventral view.
Development: first endocrine gland to appear during development. Develops from ____________ thickening in floor of early pharynx and epithelium of 3rd and 4th ____________.
Starts out _________ to tongue, but ultimately comes to be wrapped around laryngeal cartilages.
1) two lateral lobes
2) thyroid isthmus
3) endodermal
4) pharyngeal pouches.
5) caudal
THYROID GLAND
Innervation: ______________
Arterial Supply: __________________________
Venous Drainage: _________________________. These are tributaries of internal jugular veins (superior & middle) and left brachiocephalic vein (inferior) respectively.
Functions:
- THYROXIN – _____________________
- CALCITONIN – _________________________
1) Vagus Nerve (X)
2) superior and inferior thyroid arteries.
3) Superior, middle, & inferior thyroid veins
4) regulate rate of metabolism
5) decreases levels of calcium in the blood by inhibiting osteoclasts (dissolve bones) and increasing calcium excretion
PARATHYROID GLAND
Location:
- Usually __________.
- Very small (less than 5 mm).
- Called parathyroid glands because of their position on _____________ of outer surface of thyroid gland.
Development: Like thyroid gland, develop from __________________ in floor of early pharynx and epithelium of _______________ gill slit pouches
1) paired
2) posterior margins
3) endodermal thickening
4) 3rd and 4th
PARATHYROID GLAND
Innervation: ________________
Arterial Supply: _______________________
Venous Drainage: ______________________________
Function:
PARATHYROID HORMONE (Parathormone or PTH) – _____________________________, and promoting calcium reabsorption by the kidneys.
1) Vagus Nerve (X)
2) superior and inferior thyroid arteries.
3) Superior, middle, & inferior thyroid veins
4) raises the level of calcium in the blood, by inhibiting osteoblasts and promoting osteoclasts
ADRENAL GLAND
Location : _____________________(“suprarenal” gland). Have inner medulla and outer cortex.
Development:
Adrenal cortex – _________________________.
Adrenal medulla – _________________________________.
Innervation: adjacent sympathetic fibers. ______________ parasympathetic innervation.
Arterial Supply: ____________
Venous Drainage: _____________
1) on cranial (superior) surface of kidney
2) mesoderm of posterior abdominal wall
3) neural crest cells that are derived from adjacent sympathetic ganglion
4) No significant
5) adrenal arteries
6) adrenal veins
Adrenal Cortex, Function :
- MINERALOCORTICOIDS – _____________________ (e.g. aldosterone).
- GLUCOCORTICOIDS – ___________________________
- ANDROGENS – ________________________________
1) regulate sodium retention and potassium loss
2) act as anti-inflammatory agents; affect metabolism of food.
3) regulates control over rapid growth spurts in preadolescents.
Adrenal Medulla, Function :
ADRENALINE (EPINEPHRINE) – _________________________
NORADRENALINE (NOREPINEPHRINE) – ________________.
1) increases heart rate and blood pressure.
2) constricts arterioles
PANCREAS
Location : inside notch of duodenum; _____________. Has body, and tail.
Development: diverticulum of embryonic foregut. _____________________ embryonic buds eventually fuse.
Innervation: foregut: sympathetic – _________________; parasympathetic – ______________
Arterial Supply: ______________________ (branches of celiac & superior mesenteric)
Venous Drainage: ______________________ is tributary of splenic vein
1) retroperitoneal
2) Dorsal and ventral
3) greater splanchnic nerve
4) Vagus nerve (X).
5) pancreaticoduodenal arteries
6) pancreaticoduodenal vein
PANCREAS
Function: pancreas is not only an exocrine gland for digestion.
GLUCAGON – from ________ cells of pancreatic islets, _________________________.
INSULIN – from ______ cells of pancreatic islets, _________________________.
1) alpha
2) raises blood glucose level
3) beta
4) lowers blood glucose level
OVARY
Location : near kidneys, anchored by _________ to uterus.
Development: ________________. Ovaries migrate somewhat caudally, retain position near kidneys.
Innervation: sympathetic – similar to hindgut, level ____, follows least splanchnic nerve; parasympathetic – ______________
Arterial Supply: ____________, branch of abdominal aorta.
Venous Drainage: ___________, dump into inferior vena cava.
1) fallopian tubes
2) intermediate mesoderm
3) T12
4) sacral outflow
5) ovarian artery
6) ovarian vein
OVARY
Function: ovaries produce ____ in regular cycle determined by hormonal secretions. Functions of ovarian hormones and their secretions are tied to secretion of ______ and ___ from anterior pituitary gland.
1) ova
2) FSH
3) LH
OVARY produces
ESTROGENS – _______________________________
PROGESTERONE + ESTROGENS – __________________
________________________________.
1) stimulate development of female sex organs and sexual characteristics.
2) regulate menstrual cycle; maintain pregnancy in presence of developing embryo or fetus
TESTES
Responsible for _______________ and synthesis of male sex hormones.
Location : in _____________, in scrotal sac, connected to inner workings of body by ______________.
1) sperm production
2) postnatal males
3) spermatic cord
TESTES
Development: from _________________.
- As transitory stage of kidney degenerates, a ligament called the _______________ descends on each side of abdomen from inferior pole of gonad.
- that ligament passes obliquely through developing anterior abdominal wall at site of future inguinal canal and attaches at internal surface of _______________ (future position of scrotum in males or labia majora in females).
- Gubernaculum is thought to guide descent of testes into scrotum, and ultimately anchors testis to scrotal wall.
1) intermediate mesoderm
2) GUBERNACULUM
3) labioscrotal swelling
TESTES
Innervation: sympathetic – similar to kidney, ________, follows least splanchnic nerve, hook a ride down spermatic cord via testicular blood vessels; parasympathetic – ____________.
Arterial Supply: _______________. Branches off of abdominal aorta, however developmental proximity of kidney means they sometimes branch off of renal artery. Arteries follow the developmental track of testes, and can thus be very long.
Venous Drainage: _______________, dump into inferior vena cava. Form the pampiniform plexus.
1) T10-T12
2) sacral outflow.
3) testicular artery
4) testicular vein
TESTES
Function: Responsible for sperm production and synthesis of male sex hormones.
produces TESTOSTERONE – stimulate development of______________, secondary sexual characteristics, and behavioral features. Functions of testosterone and its secretion is tied to secretion of ____ from anterior pituitary gland.
1) male sex organs
2) LH


