Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles lecture 6 Flashcards
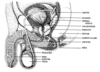
Sperm production takes place in the ____________. Each testis contains ~500 coiled tubules called ________________ – that produce hundreds (thousands?) of sperm each second in healthy males.
1) testes
2) SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
The inner lining of each tubule is lined with germinal tissue ( germinal means it’s gonna create something) – germinal tissue includes two kinds of cells knowns as
1)
2)
1) Germ cells
2) SUSTENTACULAR (Sertoli or Nurse) CELLS
•GERM CELLS goes through _________, these cells produce haploid sperm cells. All four resultant cells are viable sperm cells.
1) meiosis
•SUSTENTACULAR (Sertoli or Nurse) CELLS – nourish and __________________. They also secrete lubricating fluid to aid outward movement of sperm as they exit testis via ______________ and eventually epididymis. Also produces AMH (__________________), which regulates other hormones (e.g. testosterone, estradiol)
1) protect germ cells (so they can undergo meiosis)
2) efferent ductules
3) anti-Mullerian hormone
After it’s secreted by the sustentacular cells, the _______________ causes the “regression تراجع” of the paramesonephric duct.
anti-Mullerian hormone
Between seminiferous tubules there are clusters of endocrine cells called ____________ (aka ‘LEYDIG’) CELLS.
INTERSTITIAL
These cells secrete male sex hormones – ANDROGENS, the most important of which is __________________.
TESTOSTERONE
Sperm cells are amongst the smallest in the body (~1/20 mm).
Simple construction: __________________.
Tail is a flagellum – whipping motion provides ____________.
Base of tail contains a coiled _______________ to provide power for movement.
1) head and tail
2) motility
3) mitochondrion
Sperm Head contains nucleus and an organelle called an _____________ which contains digestive enzymes that helps sperm to penetrate egg (if present).
1)ACROSOME (a combination of vesicles diffused together)
Seminiferous tubules lead into straight tubules, then into larger set of tubules called _______________.
RETE TESTIS
Rete testis ultimately drains into larger tubules called ______________, which in turn drain into ____________.
1) efferent ductules
2) EPIDIDYMIS
Epididymis includes _________, ________ , and TAIL.
Tail of epididymis dilates (expands) into _______________.
1) HEAD
2) BODY
3) DUCTUS DEFERENS
Epididymis is a site of __________ storage
sperm (it’s not motile)
Epididimis secretes an enzyme that ___________________ of sperm that it can’t move.
Prevents the capacitence
DUCTUS DEFERENS passes up spermatic cord, and into body through _______________.
Inside body, right and left ductus deferens pass __________ over ureters, then loops _________ to them behind the urinary bladder.
1) inguinal canal
2) cranially
3) dorsal
As each duct passes behind (dorsal to) bladder, it has appended to it a gland called the ________________.
SEMINAL VESICLE
Just prior to attachment of the seminal vesicle, the ductus enlarges into an ________, which is a position of sperm storage prior to ejaculation.
AMPULLA
Notice how the spermatic cord loops ventral to (“in front of”) the attachment of the ureter of the bladder.
SEMINAL VESICLE has the enzyme which causes ______________ of the sperm
the capacitence
SEMINAL VESICLE
- Plastered up against the dorsal side of ____________.
- Exocrine glands - provide secretions that make up most of _____________.
- Fluid lubricates path of exiting sperm.
- Fluid is energy-rich (sugar rich) , providing food for sperm which is called _________.
1) urinary bladder
2) seminal fluid
3) Fructose
SEMINAL VESICLE Secretions is slightly __________. it helps to neutralize slightly acidic environment of vagina.
alkaline
_______________ promotes uterine contractions to help facilitate sperm movement up uterus into fallopian tubes.
___________ forms a temporary clot in vagina.
Once beyond the seminal vesicle, ductus is referred to as the ejaculatory duct. These are paired structures which empty into the prostatic urethra.
1) PROSTAGLANDINS
2) Fibrinogen
- Ejaculatory ducts come together to join the urethra within the mass of the ____________.
- Prostate is a single, midline gland just ________ to urinary bladder.
- Prostate is a mass of ____________, glandular tissue, and _____________.
1) prostate gland
2) inferior
3) connective tissue
4) smooth muscle
Prostate gland secretes Prostatic fluid that acts on the _____________ that is inside the seminal fluid that causes the clot in Females Vagina, after the temporery Clotting enzyme, the ____________ will break the clot down.
1) Fibrinogen
2) profibrinolysin
BULBOURETHRAL GLANDS is located in the ______________.
Cranial body wall
BULBOURETHRAL GLANDS is a Pair of glands at the base of prostate. it Secrets _____________ (pre-ejaculatory fluid that Lubricates the urethra & glans of penis.
Alkaline mucus
ERECTION
- Primarily a PARASYMPATHETIC function segments __________
- Parasympathetic function stimulates dilation of penile blood vessels – causing __________ of penis with blood. (A muscular hydrostat). Parasympathetic action potentials also stimulate glands to _____________ (e.g., bulbourethral).
1) sacral outflow (S2, S3, S4) (Autonomic control)
2) engorgement
3) secrete fluids
- An erection is Initiated by sensory stimuli, including sensations conveyed via _____________
- Conscious thoughts (cerebral cortex) can either ________________ erection center in hypothalamus.
- Also in part a sacral reflex (spinal cord injuries do not preclude sexual activity)
1) pudendal nerves
2) stimulate or inhibit
EJACULATION
- A ____________ FUNCTION!!
- Sympathetic fibers innervate smooth muscle of ____________.
- Produces forceful ____________ contractions of smooth muscle of ductus deferens.
- Peristalsis _________ sperm and seminal fluid out distal end of urethra.
1) SYMPATHETIC
2) ductus deferens
3) peristaltic
4) propels
GONADOTROPIN RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH) – (hypothalamus) stimulates secretion of _________________ and
___________________ from ant. pituitary .
1) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
2) Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE (FSH) and LUTEINIZING HORMONE (LH) are both produced by anterior pituitary and are Responsible for stimulating ____________ and ___________ secretion.
1) spermatogenesis
2) testosterone
TESTOSERONE – stimulates development of male sex organs, as well as secondary sexual characteristics. Participates in feedback loop involving _________. Also inhibits secretion of ___.
1) GONADOTROPIN RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH)
2) LH
INHIBIN – secreted by __________ cells, in response to sperm production. Inhibits secretion of _____.
1) sustentacular
2) FSH
Hypothalamus passes down to the Anterior Pituitary Gland through the _________________.
Pituitary portal system.
VERY IMPORTANT

those three makes up the???????
•Mesovarium
•Mesosalpinx
•Mesometrium
BROAD LIGAMENT
MEIOSIS IN FEMALES
- (Recall that in males, each germinal cell produces four haploid cells – each of which becomes a viable sperm cell.)
- In females, only ______ of the resulting cells will be viable and the other ______ degenerate.
1) one
2) Three
Before first meiotic division in females, each germinal cell remains in suspended development. That is called _____________(diploid).
PRIMARY OOCYTE
1st meiotic division is not completed until puberty, when ________________ cycle.
FSH triggers ovarian
After 1st meiotic division, the remaining largest cell is the ________________ (haploid).
SECONDARY OOCYTE
2nd meiotic division is not completed until _________________ (haploid).
thta oocyte is fertilized
Each primary oocyte is packaged in an epithelial vesicle called a ___________.
FOLLICLE
It is within a follicle that the 1st meiotic division is completed to create _______________.
secondary oocyte
Ovarian cycle has 2 basic stages which are
1) _________________
2) _________________
1) Follicular phase (preovulatory phase)
2) Luteal phase (postovulatory phase)
Follicular phase (preovulatory phase) – _________________ of primary oocyte into secondary oocyte within follicle. Release of _______________.
1) development and maturation
Luteal phase (postovulatory phase) – degeneration of empty __________ and preparation of uterus for ___________.
1) follicle
2) pregnancy
what are the steps for Follicular phase ?
PRIMORDIAL FOLLICLE —-> PRIMARY FOLLICLE —-> SECONDARY FOLLICLE —-> TERTIARY FOLLICLE (VESICULAR OVARIAN FOLLICLE, GRAFFIAN FOLLICLE)
PRIMORDIAL FOLLICLE – not yet ____________.
PRIMARY FOLLICLE – develops _________ & thecal cells and zona _________
SECONDARY FOLLICLE – follicular fluid develops between ______ and ________ layers of follicle
1) growing
2) granulosa
3) pellucida
4) inner & outer
TERTIARY FOLLICLE (VESICULAR OVARIAN FOLLICLE, GRAFFIAN FOLLICLE) – fluid fills the _________, and primary oocyte matures into secondary oocyte, almost _____________.
1) antrum
2) ready to be released
what are the steps for Luteal phase?
CORPUS LUTEUM —-> CORPUS ALBICANS
CORPUS LUTEUM – what is left of follicle after ________. Corpus luteum secretes some _________ and mostly __________, both of which are important in regulating female menstrual cycle.
•CORPUS ALBICANS – degenerated __________.
1) ovulation
2) ESTROGEN
3) PROGESTERONE
4) follicle
•____________ is the release of a secondary oocyte from a mature follicle.
•Occurs in response to high concentrations of __________, primarily LH.
•Secondary oocyte is “_________” from ovary directly through mass of ovarian wall.
Fimbria directs oocyte into ______________, preventing movement into coelom.
1) OVULATION
2) Gonadotropins
3) ejected
4) fallopian tube
VERY IMPORTANT SO AFTER MASTERING THE OTHER CARD COME BACK AND MAKE CONNECTION

Hypothalamus releases GnRH that acts on the adenohypophysis and makes it produce and secrete ____________
FSH & LH
The target of FSH in the female is to produce ______________, which has two functions. LIST THEM
- Release ____________
- THey start to mature, which will cause the _________________________
1) granulosa cells
2) granulosa cells
2) OOCYTE to mature and develope
what happens at the luteal phase?
the uterine cycle shows the endometrium which is the

1) the hormone secreted changes
2) inner linning of the uterus
FSH levels are higher than LH levels from day 0-14 to _______________
stimulate the development
Bleeding the first day on your period represent the ___________________________ if and only if there is no pregnancy.
Destruction of the endometrium
While the previous Cycle’s endometrium degenerates, the next Cycle’s folecels are being produced, what does that tell us about the estrogen levels?
it is usually low,
(when the endometrium develops, the estrogen level rises)
“HYPOTHALAMUS RELEASES GONADOTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH). Pay attention to the pulse rate. This stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH.”
Hormones are not released at a ______________.
at the this starting point, our GnRH pulse frequency is usually ____________.
and FSH is released at _____________
1) steady rate
2) medium
3) higher levels
FSH STIMULATES MATURATION OF _______________.
PRIMARY FOLLICLE

Developing follicles secrete slowly increasing amounts of _____________. Eventually, ___________ will affect FSH levels.
1) estrogen & inhibin
2) inhibin

MATURING FOLLICLE SECRETES ESTROGEN. Estrogen: (A) at low levels, inhibits secretion of ____; (B) as it increases, builds the uterine wall (___________________).
1) LH ( low levels means that oocyte is not mature )
2) endometrium (prepares it for the possibility that implantations can occur)

RISING LEVELS OF INHIBIN DECREASE FSH LEVELS. This dip in FSH levels, separates the _____________ from the rest.
dominant follicle

HIGH CONCENTRATION OF ESTROGEN LEADS TO __________ SECRETION. There is a change in GnRH pulse rate and the effect on LH is reversed.
THE GnRH pulse freaquence is ___________
1) INCREASE IN LH ( estrogent has to stay high for 3 days then LH will be secreted )
2) high

HIGH LEVELS OF ESTROGEN STIMULATE SECRETION OF LH BY ANTERIOR PITUITARY. Spike in LH causes _____________ of primary oocyte & ______________ of the secondary oocyte – leaving follicle without egg which is called (______________). (Approximately day 15.)
LH weakens the Outer wall of folicle
1) maturation
2) ovulation
3) the corpus luteum

Estrogen leads to the initial Development of _______________ and will handover those responsibilites to _______________, which will increase the vasculation and development of it (first blank), and also turn on the Secretion of __________________
1) endometrium
2) progestrone
3) Uterine Glands
_________________ SECRETES ESTROGEN ANDPROGESTERONE. This maintains the endometrium for 15-16 days and inhibits ___________.
Hight progestrone results with ______________ GnRH pulse frequency.
1) CORPUS LUTEUM
2) FSH & LH.
3) Very LOW
NOTE THAT FSH IS EVEN LOWER THAN LH.

HIGH PROGESTERONE LEVELS ____________ GnRH PULSE RATE. This change in pulse rate, coupled with inhibin secretion, keeps _____________ levels low.
1) DECREASE
2) Gonadotropin

(If oocyte is not _______________in the uterine wall) CORPUS DEGENERATES (TO _____________) AND STOPS PRODUCING ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE.
1) fertilized and implanted
2) CORPUS ALBICANS

DECREASE IN PROGESTERONE AND ESTROGEN. Low Progesterone & Estrogen levels allow GnRH pulse rate to _______________. This allows an ______________ secretion by pituitary again. The cycle is ready to repeat.
1) slightly increase.
2) increase in FSH

WITHOUT ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE, ENDOMETRIUM BREAKS DOWN – ______________ OCCURS. which is the sloughing off of the enlarged endometrial wall along with __________________. This physical event marks __________
_______.
1) MENSTRUATION
2) blood and mucous
3) the beginning of the cycle.

IF – SOMEWHERE BETWEEN:
HIGH LEVELS OF ESTROGEN STIMULATE SECRETION OF LH BY ANTERIOR PITUITARY. Spike in LH causes maturation of primary oocyte & ovulation of the secondary oocyte – leaving follicle without egg (the corpus luteum). (Approximately day 15.)
And
(If oocyte is not fertilized and implanted in the uterine wall) CORPUS DEGENERATES (TO CORPUS ALBICANS) AND STOPS PRODUCING ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE.
SPERM GETS TO EGG. THEN
1) FERTILIZATION CAN TAKE PLACE, AND ULTIMATELY, EMBRYO CAN BECOME IMPLANTED IN UTERINE WALL.
Females can store sperm for about ___________.
(Also, it turns out that unused oocytes are actively scavenged.)
With sex before ovulation, sperm can be stored for use. So, even though __________ hasn’t occurred, pregnancy can occur because the female is holding on to the sperm.
From point of ovulation (about day 15) to the point where the corpus luteum begins to degenerate (about day 25), fertilization can take place.
The potential for fertilization is highest during the ___________________________
1) four days
2) ovulation
3) first three days of this 10-day period.
HORMONAL REGULATION IN PREGNANT FEMALES
Developing embryo has _________________ membranes: chorion, amnion, yolk sac, and allantois.
Chorion is the embryonic contribution to placenta.
Chorionic portion secretes ______________________ (hCG).
hCG prevents _______________ from degenerating – thus it continues to secrete PROGESTERONE AND ESTROGEN.
This maintains integrity of uterine wall and inhibits subsequent _______________ (due to lack of FSH or LH).
Hormonal birth-control mimics these high estrogen & progesterone levels to trick the body into thinking it is pregnant and thus inhibiting ovulation.
1) extra-embryonic
2) HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN
3) corpus luteum
4) ovulation


