Surgery (3) Flashcards
Risk factors for colorectal carcinoma
- neoplastic polyps
- IBD (UC>CD)
- smoking
- previous cancer
- familial cancer syndromes (HNPCC, FAP)
Most common colorectal carcinomas
Type: adenocarcinoma (95%)
- rectum 45%
- sigmoid 25%
Pathophysiology of colorectal carcinoma
Mutations in WnT (pathway that regulates calcium inside the cell) → APC mutation → p53 → p53 x2 → malignancy
Spread of colorectal cancer
Most spread haematogenously to the liver via the portal system
Symptoms of R and L sided colorectal Ca
- Right-sided lesions: weight loss and IDA
- Left-sided lesions: PR bleeding, altered bowel habit or large bowel obstruction
What can be seen on examination of a patient with colorectal carcinoma
- General examination may show signs of iron-deficiency anaemia (pallor, koilonychia, angular stomatitis)
- Palpation may reveal hepatomegaly (metastases)
- PR examination may reveal a palpable mass
Ix for colorectal cancer
- Bedside – Faecal occult blood test
- Bloods – FBC (microcytic anaemia), LFTs (metastases), CEA (tumour marker)
- Imaging – Chest X-ray (metastases), USS Liver (metastases), CT/MRI (staging)
- Invasive – Colonoscopy (visualise lesion and biopsy).
Duke staging for colorectal ca
Duke A
Tumour confined beneath muscularis mucosae (90% Five year survival)
Duke B
Tumour extension through muscularis mucosae (65% Five year survival)
Duke C
Involvement of regional lymph nodes (30% Five year survival)
Duke D
Distant metastases (<10% Five year survival)
(4) types of surgery for colorectal Ca
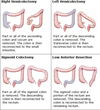
What R hemicolectomy is used for?
Right hemicolectomy for :
caecal, ascending and proximal transverse colon tumours
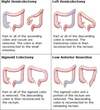
What Left hemicolectomy is used for?
Left hemicolectomy for distal transverse colon or descending colon tumours

What sigmoid colectomy is used for?
For sigmoid tumours

What anterior resection is used for?
Anterior resection:
- low sigmoid
- high rectal tumours
If concerns around the primary anastomosis, a loop ileostomy can be created and reversed in the future

What’s Total mesorectal excision used for?
Total Mesorectal Excision:
for rectal tumours with removal of surrounding fatty
tissue and nodes
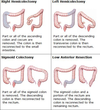
What’s abdominoperineal resection used for?
Abdomino-perineal (AP) resection
- low rectal tumours (
Results in an end colostomy

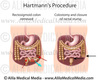
What’s Hartmann’s procedure used for?
Hartmann’s procedure
- patients presenting as an emergency with large bowel obstruction
- results in an end colostomy
- it is temporary and the two parts of the bowel are re-joined in a later surgery (6 months later)
Criteria for 2ww referral for colorectal cancer
2-week wait referral guidelines for
colorectal cancer:
- iron-deficiency anaemia >/60
- unexplained change in bowel habit >/60
- unexplained rectal bleeding >/50
- abdominal pain + weight loss >/40
What number of stoma openings are indicative of?
Number of openings:
2 = loop
1 = end
(3) types of stomas comparison
- location
- content
- opening
- indication

Complications of stoma (mnemonic)
FOUL SHITS
Fluid loss
Odour
Ulceration of skin
Leakage
Stenosis
Herniation
Ischaemia
Terminal ileum loss
Sexual and psychological problems


