Radiology 3 Flashcards
What’s abnormality?

X-ray:
High-density line arching out L side → track-line calcifications = very dilated abdominal aorta; as shadows of dilation are uneven on both sides → patient is acutely bleeding
CT: very dilated aortic aneurysm with calcifications around the edges + blush of contrast going outside of the aorta and opacification within peritoneum = active bleed from the aorta

Difference between arterial phase CT and portal venous phase
Arterial phase → contrast is given and goes through the R side of the heart → into pulmonary arteries → into L side of the heart → and then through the arteries (if CT scan at that time, then contrast is within the arteries = good contrast views of the arteries)
Portal venous phase → if we wait a bit later (after arterial phase = contrast in the arteries) → blood comes back → good enhancement of bowel, liver (portal veins) etc.

Role of imaging in acute pancreatitis
It’s really a clinical and biochemical diagnosis

Do we do CT early in acute pancreatitis?
Doing CT early won’t change management anyway as we won’t operate during the acute stage (because there will be lots of proteases released and we do not want them to get to different organs)

What’s that?

CT of severe, necrotising pancreatitis
- the pancreas is really swollen
- necrotic areas within the pancreas
- inflammatory changes surrounding the pancreas
Describe finding on imaging and if to request further one

Chest X-Ray:
- gas/air under diaphragm → pneumoperitoneum = bowel perforation
- we therefore need a better look into the abdomen → portal phase CT (as we want to look at the bowel wall)
What abnormalities can you see?


Describe abnormalities

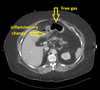
Hx of abdo pain, raised CRP and amylase

Perforated duodenum
(lack of enhancement of duodenal wall)
e.g. due to perforated ulcer

What imaging to request

Sounds like acute appendicitis

Ultrasound findings of appendicitis


Diagnosis

Enlarged R ovarian cyst
What imaging Ix to request?

?renal calculi
(she was at risk of dehydration due to ultramarathon)
Imaging Ix: unenhanced CT KUB
*no contrast due to the risk of masking calculi with a contrast

What further Ix (imaging) to choose?

?PE
Ix: CTPA

Spot abnormality + likely diagnosis


What further imaging Ix would you order?

- Normal CXR
- if we suspect PE and D-dimer is raised we would normally request CTPA
- however, this is a young female (breast tissue is v sensitive to CT radiation)
- Therefore we would rather do VQ scan

DO we do any further imaging Ix? If yes, what kind?

We suspect PE
- we can do USS of the leg

What’s a better imaging modality in pregnancy CTPA or V/Q scan?
CTPA → bad for mum as hypersensitive breast tissue in pregnancy
V/Q scan → bad for foetus (as it goes around the blood)


