spine and skull Flashcards
(209 cards)
1
Q

A
1st rib
2
Q

A
ankylosing spondytis
3
Q

A
ankylosing spondytis
4
Q

A
ankylosing spondytis
5
Q

A
ankylosing spondytis
6
Q

A
anterior arch of the atlas
7
Q

A
atlanto-occipital dislocation
8
Q

A
atlanto-occipital joint
9
Q

A
atlas
10
Q

A
axis
11
Q

A
body of cervical vertebra
12
Q

A
body of th axis
13
Q

A
burst fracture
14
Q

A
burst fracture
15
Q

A
burst fracture
16
Q

A
C7
17
Q

A
cervical facets
18
Q

A
A) vocal cord
B) intervertebral space
C) trachea
D) transverse process
E) spinous process
F) pedicle
19
Q

A
cervical transverse processes
20
Q

A
chance fracture
21
Q

A
clay shovelers
22
Q

A
compression fracture
23
Q

A
compression fracture
24
Q

A
compression fracture
25

dens
26

first rib
27

hangmans fracture
28

hangmans fracture
29

heart shadow
30

jefferson fracture
31

jefferson fracture
32

red: clay shovelers
blue: burst fracture with associated swelling
33

red: lipping
blue: calcification
green: spondlylolithesis
34

spondylolisthesis C4-5
lipping C5-6
35

abnormal lines in the cervical vertebral body and lamina
36

body, lamina, spinous process lines
37

latearl cervical MRI
38

soft tissue edema
39

A) atlanto-occipital joint
B) dens
C) posterior arch of the atlas
D) inferior facet of C2
E) transverse process
F) superior facet of C3
G) lamina of C5
H) intervertebral disc space
I) pedicle
J) spinous process of C6
K) C7
40

A) C1
B) body of the axis
C) posterior arch of the atlas
D) spinous process
E) transverse process
F) C7
41

lateral lumbar
42

thoracic body
43

thoracic pedicle
44

transverse process
45
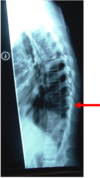
spinous process
46

lumbar oblique
47

Left: thoracic scoliosis
right: lumbar scoliosis
48

pedicle
49

S1
50

spinous process
51

transverse process
52

lumbar body
53

lumbar burst fracture
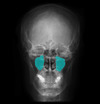
54

CT
55

CT
56

lamina
57

body
58

pedicle
59

spinous process
60

metastatic disease
61

metastatic disease
62

metastatic disease
63

metastatic disease
64

metastatic disease
65

oblique C Spine
66

A) pedicles
B) intervertebral foramen
C) superior articulating facets
D) spinous processes
E) inferior articulating facets
F) 1st rib
67

odontoid fracture
68
open mouth CT
69

A) odontoid process
B) inferior facet of C1
C) atlanto-axial joint
D) superior facet of C2
E) spinous process
70

pagets disease
71

posterior arch of the atlas
72

scheurmans kyphosis
73

scottie dog
74

spondylolisthesis
75

spondylosis
76

swimmers
77

swimmers
78

C7
79

pedicle
80

thoracic scoliosis
81

C7 to T12
82

spinous process
83

transverse process
84
what views are used in the cervical spine
1. AP
2. lateral
3. swimmers
4. oblique
5. flexion
6. extension
85
what three views are used in cervical trauma
1. AP
2. cross table lateral
3. odontoid
86
how should vertebrae look on x ray
stacked marshmellows
87
what three alignments should be checked on an AP or lateral
1. body alignment
2. lamina alignment
3. spinous process alignment
88
how should the lateral edges of the spine look on edge
smooth rolling lines
89
what are seven features to look for on a cervical xray
1. size and symmetry of bodies
2. normal alignments x3
3. smooth lateral edges
4. no fractures
5. normal axis and atlas
6. no large soft tissue mass
7. normal disc spaces
90
what three vertebrae must be included on a cervical X ray
C1, C7, T1
91
soft tissue at C2 should be no thicker than \_\_\_\_\_
soft tissue at C6 should no thicker than \_\_\_\_\_
6mm
2cm
92
when should a swimmers view be done
when the shoulder doesn;t allow a clear picture of C7-T1
93
when would someone do a cervical oblique
when there is a suspected facet issue
94
when would someone use an open mouth view
to see the dens
95
what are some issues to look for in an open mouth xray
is the dens a normal size
are there equal and normal spaces around the dens
96
what are two reasons someone might do a lateral flexion/extension view
1. checking for rheumatological disease
2. checking to see if the patient can be intubated
97
what two view are normally done in the thoracic spine
AP and lateral
98
when examining a thoracic x ray what are five issue to look for
1. step deformity
2. midline spinous processes
3. spinous processes eqidistant from both pedicles
4. evenly space sternoclavicular joints
5. equal disc spaces
99
what structures should be included in a thoracic xray
C7-L1, all transverse process, at least part of all the ribs
100
what is a lateral thoracic useful for
looking for scoliosis and compression fractures
101
what five views are used in the lumbar spine
1. AP
2. lateral
3. oblique
4. flexion
5. extension
102
what structures should be included in a lumbar xray
L1-S1
103
what is the oblique lumbar view used for
to look for spondylolysis
104
par interarticularis
the portion of the lamina between the superior and inferior articular processes
105
what is CT used for in the spine
1. look for bony abnormalities
2. rule out C spine fracture
3. when MRI is not an option
106
what is MRI useful for in the spine
1. look for soft tissue deformity
2. no radiation
107
T/F contrast should be used on an MRI if the patient has undergone surgery or there is a history of cancer/chemotherapy
true
108
what are some metallic implants that would not permit MRI
1. aneurysm clips
2. pace makers
3. ocular foreign bodies
4. metal cardiac valves
109
what are seven unstable cervical spine fractures
1. atlanto-occipital dislocation
2. facet joint dislocation
3. hangmans
4. hyperextension fracture
5. burst
6. jeffersons
7. odontoid
110
what are the stable fractures of the cervical spine
1. clay shovelers
2. wedge
111
what are the unstable fractures of the lumbar and thoracic spine
1. chance fracture
2. burst fracture
112
what are the stable fractures of the lumbar and thoracic spine
1. wdge
2. spinous process fracture
3. spondylolysis
4. spondylolisthesis
113
three types of facet joint dislocation
1. subluxed
2. perched
3. locked
114
what is the difference between subluxed, perched, locked facets
subluxed is just some slippage
perched means complete subluxation but not jumped
locked means the superior facet has slid anterior over the inferior facet
115
what happens in a hangmans fracture
there is bilateral pedicle fracture at C2 which pushes C2 anteriorly
116
what will a hangmans fracture feel like on palpation
a step off at C1-2
117
what happens in a jeffersons fracture
the atlas "smooshes" due to an axial force applied to the top of the head
118
what will a jefferson fracture look like on imaging
a C1 with splayed out lateral masses and too much space around the odontoid
119
what are the three grades of an odontoid fracture
1. just the tip
2. through the odontoid
3. fracture through the base of the odontoid into the body of C2
120
what kind of odontoid fracture is most unstable
grade two
121
what is a clay shovelers fracture? how is it caused
a spinous process fracture at C6 or 7
commonly found secondary to a flexion injury
122
what is the key indication of a burst fracture
parts of the body will be pushed back
123
T/F an xray is all that is needed to assess burst fracture
false, if a burst fracture is suspected a CT should be done
124
what two fractures are common with a patient who jumped from a height and landed on their feet
lumbar burst fracture and calcaneus fracture
125
how can a compression fracture be differentiated from a burst fracture
they are less traumatic and the defect doesnt push the body back
126
what are four possible conditions that wold lead to a compression fracture
1. osteoporosis
2. osteomalacia
3. pagets disease
4. multiple myeloma
127
osteomalacia
inadequate phosphorus, calcium, and vitamin D in blood that leads to softening of bone
128
pagets disease
a nonmetabolic bone disease that is characterized by excessive bone destruction and repair
129
what will pagets disease look like on xray
vertebrae with white streaks of hypertrophied bone next to areas of decreased bone density
130
multiple myeloma
malignant neoplasm of the bone marrow, usually looks like a punched out lesion in bone
131
T/F multiple myeloma often present with compression fracture
true
132
chance fracture
a fracture through the spinous process into the vertebrae
133
how do chance fractures hapen
hyperflexion with the leg immobilzed (child with a lap belt)
134
how will a chance fracture look on a lumbar AP
a missing spinous process
135
spondylolysis
a defect in the pars interarticularis that can cause sponylolisthesis
136
spondylolisthesis
a movement of one vertebrae in relation to the inferior vertebrae common in L5-S1
137
what sign is indicative of spondylolysis
a "scottie dog" with a collar or broken neck
138
how many grades of spondylolisthesis are there? what are they indicative of
4
1. grade 1: 1/4 slippage
2. grade 2: 1/2
3. grade 3: 3/4
4. grade 4: completely slipped off
139
sclerotic change to a disc
hardening and osteophyte formation
140
how will a calcified disc look on xray
hazy white instead of dark gray
141
lipping
osteophyte formation that forms a narrow disc space with lips
142
ankylosing spondylytis
a chronic inflammatory condition that results in the vertebrae growing together around disc spaces
143
what is the difference between ankylosing spondylitis on xray
lipping is osteophyte formation, AS will cause syndesmophyte formation with smooth edges
144
what sign is indicative of ankylosing spondylitis on xray
bamboo spine, squared vertbrea with smoothed disc spaces
145
scheurmans kyphosis
anterior wedging of the thoracic vertbrae, common in adolescent boys
146
what is the diagnostic criteria for scheurmans kyphosis
3 consecutive vertbrae with +5deg of wedging
147
what is the main factors determining what type of treatment is best for scheurmans kyphosis
how much time there is availible for bracing based on the patients age
148
how will metastatic disease present itself on xray
can be moth eaten or ivory vertbrae
149
what types of cancer metastases are common with ivory vertbrae
prostate and breast cancer
150
what types of metastases present with a moth eaten or punched out vertebrae
breast, multiple myeloma
151
1. what is this?
2. what is it indicative of?
3. what view is this in?

1. air fluid interface in the left maxillary sinus
2. fluid or tumor in the right sinus
3. waters
152
1. what is this?
2. what is happening?

1. basilar skull fracture with hemotympanum
2. blood from the skull fracture is collecting behind the ear
153

basilar skull fracture
154
what is this? what might cause this

battle sign
basilar skull fracture
155
1. what is this?
2. what might cause this?
3. what bones are fractured to cause this

1. a blowout fracture
2. a blow to the orbit
3. the zygomatic/maxillary bone
156
1. what is this
2. name a two likely causes

1. a blowout fracture
2. a racquet ball to the face, MVA
157
what would make this happen?

a blowout fracture that traps the inferior rectus so it can't contract to move the eye up
158
what is happening here? how can you tell?

bony destruction caused by infection or neoplasm
because the septum and nasal concha are gone
159
what view is this

caldwell/AP
160

coronal suture
161

coronoid process
162

crista galli
163
what is this? what complications come from this?

depressed skull fracture
increased intracranial pressure and hemorrhage
164
what is this? how can you tell

epidural hematoma, because it is more lens shaped than flat
165

epidural hematoma
166

ethmoid
167
1. what are the arrow indicating?
2. why would this be abnormal?
3. what is causing this?

1. falx cerebri
2. they are deviating to the left
3. increased intracranial pressure
168

floor of the sella turcica
169

frontal sinus
170

greater wing of the sphenoid
171
what is this?
what would cause this?

hemotympanum
basilar skull fracture
172

inferior nasal concha
173

inferior nasal concha
174

lacrimal bone
175

lambdoidal suture
176

maxilary sinus
177

frontal sinus
178

right and left ventral horns
179

linear skull fracture
180

mandibular condyle
181
maxillary sinus
182
1. what are these?
2. what do they represent?
3. what is a common cause?

1. oil droplets
2. areas of bone destruction
3. multiple myeloma
183

optic sulcus
184

orbital roof
185
what view is this

panorex
186
what is this called? what might you suspect if you see this?

raccoons sign
basillar skull fracture
187

ramus of the mandible
188

sinusitis
189

scalp hematoma
190

sinusitis
191

sphenoid sinus
192

sphenoid sinus
193
what is this?
what is happening?

subdural hematoma
blood is collecting in the subdural space
194
what view is this? what is it used for?

townes
looking at the back of the skull
195
what view is this? what is it used for

waters
getting better look at the frontal and maxillary sinuses and the orbital floor

196

zygomatic bone
197
what are the maxillary sinuses hard to evaluated on an AP/caldwell?
because the beam has to pass through the skull and brain
198
what is a lateral skull xray best for?
looking for fracture lines
199
when taking a townes view, how is the head positioned
the head stay neutral but the beam is directed at an angle
200
how are the teeth numbered in a panorex view
top row, left to right, 1-16
bottom row, right to left, 16-32
201
what is the most common skull fracture? is it considered serious
linear
no, other than there may be a bleed associated with it
202
why are depressed skull fractures serious?
they are more likely to involved injury to the brain
203
what is the most serious type of skull fracture
basillar
204
what physical exam findings might indicate a basilar skull fracture
1. CSF leak from the nose or ears
2. hemotympanum
3. raccoon sign
4. battle sign
205
what should be in the maxillary sinus?
if there is an interface, what might you suspect is the cause
mostly air, no fluid interface
blood in the sinus, sinusitis, or tumor
206
what is the primary indication of sinusitis
thickened nasal concha
207
what are two possible causes of bony destruction of the septum or sinuses?
1. funal infection
2. cancer
208
how can you typically tell the difference between a epidural and subdural hematoma
epidurals are more of a lens shape
subdural is more of a crescent shape
209
what percent of epidural hematomas are associated with skull fractures? where are they most common?
95%
unilateral temporoparietal region


