SM_219a: Bone Histology Flashcards
Types of bones are _____ and _____
Types of bones are flat bones and long bones
Flat bones include bones of the _____, _____, and _____
Flat bones include bones of the skull, face, and clavicle
(long bones are everything else)
_____ is the shaft of a long bone
Diaphysis is the shaft of a long bone

_____ is the end of a long bone
Epiphysis is the end of a long bone

_____ connects the diaphysis and epiphysis and includes the ______
Metaphysis connects the diaphysis and epiphysis and includes the epiphyseal plate

_____ sit on the surface and synthesize bone
Osteoblasts sit on the surface and synthesize bone

_____ are old osteoblasts that sit within lacunae and are connected bu canaliculi to diffuse nutrients and waste
Osteocytes are old osteoblasts that sit within lacunae and are connected bu canaliculi to diffuse nutrients and waste

_____ are multinucleated giant cells the resorb bone
Osteoclasts are multinucleated giant cells the resorb bone

Bone remodeling involves _____ and _____ of bone on the _____ by _____ and _____, respectively
Bone remodeling involves apposition and resorption of bone on the surface by osteoblasts and osteoclasts, respectively
Bone is composed of ______ and ______
Bone is composed of 70% inorganic material (hydroxyapatite) and 30% organic material (90% type I collagen)
(hydroxyapatite is a complex of calcium and phosphate)
Collagen is mineralize through ______
Collagen is mineralize through exocytosis of small vesicles containing alkaline phosphatase and pyrophosphatase from the osteoblasts into newly formed bone (osteoid) to initiate mineralization and bind Ca and P
Describe the role of Ca and PTH in bone metabolism
- Low serum Ca sensed by parathyroid gland
- Parathyroid gland secretes PTH
- PTH stimulates bone resorption
(PTH regulated through Vitamin D and kidney activation of Vitamin D)

_____ is found on the outside of long bones, while _____ is found inside long bones
Compact/lamellar bone is found on the outside of long bones, while trabecular/spongy bone is found inside long bones

____ is the structural unit of compact bone
Haversian systems (osteons) are the structural unit of compact bone
(osteocytes surround a central canal that carries blood vessels and nerve fibers, concentric rings around the canal are from layers of bone laid down by osteoblasts)

_____ extend out of _____ to connect osteocytes together, allowing them to _____ and _____
Canaliculi extend out of lacunae to connect osteocytes together, allowing them to acquire nutrients and excrete wastes

_______ is when new bone develops from and replaces hyaline cartilage and occurs in long bones, bones at the base of the skull, and short bones in the hands and feet
Endochondrial ossification is when new bone develops from and replaces hyaline cartilage and occurs in long bones, bones at the base of the skull, and short bones in the hands and feet
______ is when new bone develops directly from a capsule of undifferentiated connective tissue and occurs in the flat bones of a face, cranial bones, and clavicles
Intramembranous ossification is when new bone develops directly from a capsule of undifferentiated connective tissue and occurs in the flat bones of a face, cranial bones, and clavicles
Describe endochondrial ossification
Endochondrial ossification
- Primary ossification center in the shaft extends out both ways
- Secondary ossification center starts at epiphysis
- Ossification centers grow together until they meet
- Epiphyseal plate forms

Endochondrial ossificiation includes zones, namely _____, _____, _____, and _____
Endochondrial ossificiation includes zones, namely zone of ossification, zone of hypertrophy, zone of proliferation, and reserve cartilage

Intramembranous ossification involves bone forming out of ______ as ______ buld bone layer by layer outwards
Intramembranous ossification involves bone forming out of primitive connective tissue as osteoblasts build bone layer by layer outwards
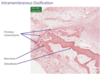
_____ forms the edge of woven/immature bone
Osteoid forms the edge of woven/immature bone
(lacks lamellar structure)

Lamellar/mature bone has _____
Lamellar/mature bone has organized lamellae of bone



