Signal Transduction, Metabolism, PDH Complex, Citric Acid Cycle Flashcards
Why is epinephrine released?
“Fight or Flight” Stimulus
Why is glucagon released?
low glucose levels
Why is insulin released?
High glucose levels
What are the steps for the G-protein system?
Binds to activated Receptor
GDP replaced with GTP
GTP-active protein binds to GTP-activated enzyme
cellular response
What is a primary messenger?
Example: a hormone, released directly from environmental stimulus
What is a secondary messenger?
A relay molecule that responds and reacts to the primary messenger
What is involved with the β-adrenergic receptor and G protein?
Epinephrine
cAMP functions as a second messenger activated by…
adenylate cyclase
What does cAMP activate?
Protein Kinase A
What does DAG activate?
Protein Kinase C
What does IP3 activate?
Ca2+ to release from ER
Only active as a dimer. Once dimerized, the subunits autophosphorylate one another
Tyrosine kinases (like insulin)
How do signals get terminated?
- Deactivate the secondary messenger
- Deactivate the subunit responsible for synthesizing the secondary messenger
- Dissociate the primary messenger from the receptor
How does our body use free energy?
For movement
For molecular transport into and out of cells
For synthesis of bio-macromolecules
Note that all of these processes require ATP
Exergonic reaction, cell respiration, hydrolysis of ATP
Catabolism
Endergonic reaction, cell movements, active transport, synthesis of ATP
Anabolism
What is the reaction for Keq?
𝐾eq = [products]/[reactants]
What is the reaction for ∆G°′?
∆G°′ = −RT 𝑙n ([products]/[reactants])
R is the gas constant
T is the temperature in Kelvin
If energy is released, and the reaction is spontaneous, then Keq is…?
>1
If energy is added, and the reaction is not spontaneous, then Keq is…?
<1
____ is intermediate in phosphoryl transfer potential, it can easily be replenished using compounds with higher phosphoryl transfer potential
rapidly consumed and replenished
ATP
The oxidation of carbon fuels
catabolism
An electron carrier in metabolism
NAD+
Involved mainly in fatty acid synthesis
NADPH
An electron carrier in metabolism, usually lower energy
FAD+
A carrier of acyl groups
Co-enzyme A
Derived from B Vitamins
Co-enzymes
How are metabolic processes regulated?
- Control the amount of enzyme (kinetics)
- Control the catalytic activity of the enzyme (allosterism, phosphorylation, etc.)
- Control accessibility of substrates (membrane compartmentalization)
What are the fates of pyruvate?
the fate of pyruvate can be lactic acid or ethanol (depending on organism) if cell is anaerobic or acetyl CoA if the cell is aerobic.
What are the 3 Steps for conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
1) decarboxylation, 2) oxidation, 3) CoA transfer
At what point is conversion of Pyruvate irreversible?
When it’s converted into acetyl CoA
E3 complex activation
Inhibited by NADH; Activated by NAD+
E2 complex activation
Inhibited by Acetyl CoA; Activated by CoA
E1 complex: PDK/PDP activation
Inhibited by ATP; activated by ADP via phos/dephos
What cofactor accepts the acetyl group from pyruvate?
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
What cofactor transfers the acetyl group from TPP to CoA?
Lipoic Acid
What are E3 cofactors?
FAD, NAD+
E2 is allosterically inhibited by
high acetyl-CoA
E3 is allosterically inhibited by
high NADH
The E1 subunit of the PDC is regulated through
phosphorylation/dephosphorylation
What is the overall reaction for the CAC?
acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + ADP + Pi → 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + FADH2 + ATP
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 1
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?

Citrate Synthase
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 2
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?

Acconitase
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 3
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?

isocitrate dehydrogenase
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 4
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?

a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 5
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?

succinyl CoA synthetase
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 6
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?
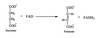
succinate dehydrogenase
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 7
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?

fumarase
What step in the citric acid cycle is this?

Step 8
What enzyme is used in this step of the citric acid cycle?

malate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase activation
activate with ADP and NAD+/inhibit with ATP and NADH
a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activation
activate with ADP and NAD+/inhibit with ATP and NADH and succinyl CoA
Where in the citric acid cycle is ATP produced?
Step 5
Where in the citric acid cycle is NADH produced?
Steps 3, 4, & 8
Where in the citric acid cycle is FADH2 produced?
6
The primary control points within CAC are which two enzymes that catalyze oxidative decarboxylations?
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Why isn’t the first step (ie. citrate to isocitrate) a regulatory step?
- This step is readily reversible
- Citrate is a signal molecule that can go into cytoplasm to inhibit PFK
- Citrate also serves as source of Acetyl-CoA in fatty acid synthesis


