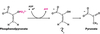Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis Flashcards
What is the net reaction for glycolysis?
glucose + 2 ADP + 2 NAD+ → 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH
What reaction is occurring here?

Phosphorylation
What Enzyme is this?

Hexokinase
What molecule is this?

Glucose
What molecule is this?

Glucose 6-Phosphate
G-6P
What reaction is occuring here?

isomerization
What Enzyme catalyzes this reaction?
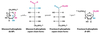
Phosphoglucose Isomerase
What molecule is this?
Glucose 6-Phosphate
G-6P
What molecule is this?

Fructose 6-phosphate
F-6P
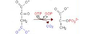
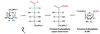
What reaction is occuring here?

phosphorylation
What Enzyme is this?
Phosphofructokinase
What molecule is this?

Fructose 6-Phosphate
F-6P
What molecule is this?

Fructose 1, 6-Biphosphate
F-1,6BP
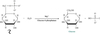
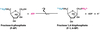
What reaction is occuring here?

Cleavage
What Enzyme is this?

Aldolase
What molecule is this?

Fructose 1, 6-Biphosphate
F-1,6BP
What molecule is this?

Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
DHAP
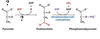
What molecule is this?

Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
GAP
What reaction is occuring here?

isomerization
What Enzyme is this?

Triose Phosphate Isomerase
What molecule is this?

Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
DHAP
What molecule is this?

Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
GAP
What reaction is occuring here?

oxidation and phosphorylation
What Enzyme is this?

GAP Dehydrogenase