Life, Water, Amino Acids, Proteins Flashcards
What is the more complex of the cell types?
Eukaryotes
Enclosed organelles
Both have rhibosomes
What causes hydrogen bonding?
Electronegativity difference (dipoles)
What are the four weak forces?
- Hydrogen Bonds
- Van der Waals Forces
- Hydrophobic Interactions
- Electrostatic/Ionic Interactions
Which atom pulls the electron cloud towards itself resulting in a partial charge and giving rise to a dipole?
The more electronegative atom
Two atoms attract one another until they get too close
Van Der Waals foreces
Any interactions where there is a charge differential leading to an attractive force
electrostatic interaction
In an aqueous environment, non-polar molecules will gather together to reduce their surface area
Hydrophobic Interactions
These are used as buffers
weak acids or weak bases
proton donor
acid
proton acceptor
base
The _____ Ka is, the stronger the acid
larger
The _____ pKa is, the stronger the acid
lower
What is the equation for Ka?
HxA/HA
What is the equation for pKa?
-logKa
What is the equation for pH?
-log H
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
R group is nonpolar
Hydrophobic/Nonpolar
R group has electronegative atoms that are not charged at normal pH ranges
Polar-Neutral
R group has electronegative atoms that are positively charged at physiological pH
Polar Charged/Positive
R group has electronegative atoms that are negatively charged at physiological pH
Polar Charged/Negative
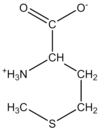
What Amino Acid is this?
Polarity?

Glycine
Gly
G
Nonpolar
What Amino Acid is this?
Polarity?

Alanine
Ala
A
Nonpolar
What Amino Acid is this?
Polarity?

Valine
Val
V
Nonpolar
What Amino Acid is this?
Polarity?

Leucine
Leu
L
Nonpolar