Carbohydrates, Lipids, Membranes Flashcards
individual sugar unit with formula (CH2O)n.
Monosaccharide
2-10 sugar units
Disaccharide, tri-, tetra-, etc
greater than 10 sugar units
Oligosaccharide
larger polymer 10’s to 1000’s, may be linear or branched
Polysaccharide
What is the term for a sugar with a carbonyl group on the endmost carbon atom?
Aldose
What is the term for a sugar with a ketone group on one carbon atom?
Ketose
What makes a molecule alpha or beta?
Alpha- OH is up on the next carbon from the attached oxygen when moving clockwise
Beta - that same OH is down
How do you name sugars by carbon atoms?
triose, tetrose, pentose, hexose, etc.
Rich in hydroxyl (OH- ) groups
Carbohydrates
Tend to have the general formula of (CH2O)n where n ≥ 3
Carbohydrates
Single most abundant form of biomolecule found in nature
Carbohydrates
What are the cellular functions of carbohydrates?
energy storage and metabolism
cellular structure
linkers with other biomolecules (glycolipids, RNA/DNA, glycoproteins)
recognition molecules between cell types and cell structures
What is this?

Ketose
What is this?

Aldose
What is this?

Aldohexose
What is this?
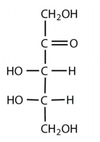
Ketopentose
What is this?
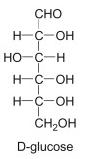
D-Glucose
What is this?

L-glucose
What is this?
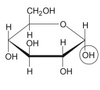
alpha D-glucose
What is this?

Beta D-glucose
What is this?

Beta L-glucose
What is this?

D-Fructose
What is this?

L-fructose
What is this?

alpha D-fructose
What is this?

Beta D-fructose
What is this?
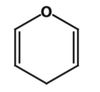
Pyranos
What is this?

Furanos
What is this?
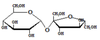
Sucrose
What is this?
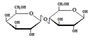
Lactose
What is this?

Maltose
What kind of linkage is this?

alpha-1,4
What kind of linkage is this?

alpha-1,6
What is the term for something with non-superimposable mirror images?
Enantiomer
What is the term for something with multiple chiral centers, not mirror images?
Diastereomers
What is the term for diastereomers that differ at only one chiral center?
Epimers
What is the term for two molecules, aldoses and ketoses, with the same formula but different structure?
Constitutional Isomers
How many carbons form the ring in Glucose?
6
How many carbons form the ring in Fructose?
5
Unbranched α-1,4 linked glucose units
Amylose
Primarily protein with O- or N- linked carbohydrate
Glycoprotein
α-1,4 linked glucose units with α-1,6 branches
Amylopectin
Unbranched β-1,4 linked glucose units
Cellulose
α-1,4 linked glucose units with α-1,6 branches
Glycogen
A protein with long carbohydrate chains such as cartilage
Proteoglycan
What is a lipid?
Lipid is a generic term for any biological molecule that has low water solubility.
Generally consist of long chains of numerous reduced carbons (alkanes and alkenes)
Lipids
May be either hydrophobic or amphipathic (polar and nonpolar parts)
Lipids
Don’t polymerize to a great extent, aggregate through non-covalent interactions
Lipids
What are the cellular functions of lipids?
Energy storage and metabolism
Membrane structure
Signaling molecules
How many carbon atoms in Dodecanoic acid?
12
How many carbon atoms in Tetradecanoic acid?
14
How many carbon atoms in Hexadecanoic acid?
16
How many carbon atoms in Octodecanoic acid?
18
How many carbon atoms in Lauric acid?
12
How many carbon atoms in Myristic acid?
14
How many carbon atoms in Palmitic acid?
16
How many carbon atoms in Stearic acid?
18
What’s the difference between a saturated fatty acid and an unsatruated fatty acid?
Double bonds… saturated is a straight chain, unsaturated has double bonds.
What are trans fats?
Rather than kinking the structure like cis orientations in unsaturated fatty acids, they fold it instead, leaving everything rigid and inflexible (solid).
What is this?

glycerol
What is this?

Fatty Acid
What is this?

Triacyclglycerol
What is the general structure for a steroid?
Three hexagonal rings and a pentagonal ring.
What is the natural state of a saturated fatty acid at room temperature?
Solid
What is the natural state of an unsaturated fatty acid at room temperature?
liquid
What is this?

Phospholipid base
What is a membrane?
- An organized array of lipids and proteins whose hydrophobic nature acts as an effective barrier to polar molecules.
- Effectively serves to partition the cellular components from the outside.
What are the roles of membranes?
- Excludes Toxins
- Allows passage and accumulation of nutrients
- Key role in energy transduction
- Function for cellular locomotion
- Role in reproduction
- Role in signal transduction process
- Role in molecular recognition and cell-cell recogntion
What is a Micelle?
A membrane with heads outward, tails inward.
What is a Liposome?
A membrane with two layers, heads out, tails in.
- These proteins do not penetrate the lipid bilayer to any significant degree
- Associate with membrane surface via ionic interactions and H-bonds
- Are readily dissociated from the membrane w/ salt and pH change
Peripheral Proteins (also known as extrinsic proteins)
- have hydrocarbon surfaces that penetrate the lipid bilayer
- have polar ends that are in contact w/ aqueous
- may insert partially or fully through lipid bilayer
- can only be removed w/ detergent that breaks up bilayer
Integral Proteins (also known as intrinsic proteins)
do not associate with membrane themselves but have a hydrophobic lipid tail that does.
Lipid linked proteins
Movement down a concentration gradient
Simple Diffusion
Spontaneous passive transport of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins
Facilitated diffusion
one type of molecule gets transported
Uniport
movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration gradient
Active Transport
2 different types of molecules being transported in the same direction
Symport
2 different types of molecules being transported in opposite directions
antiport
Example of simple diffusion
Water across a membrane, from high to low concentration.
Example of Uniport Facilitated Diffusion
Glucose into a eurythrocyte via a specific transporter
Example of Symport
Glucose/Sodium Transporter
Example of Antiport
Sodium-Potassium Pump
A protein moves along a membrane, but stays on its plane
Lateral Diffusion, fast
A protein moves in a membrane, switching to the opposite side
Transverse Diffusion, slow
What three things make a molecule more likely to be taken up by a membrane?
Nonpolar
Small
Uncharged
What is this?

phosphatidyl serine


