Fatty Acid Metabolism, Synthesis, and Nucleic Acids Flashcards
What are the three steps of Fatty Acid Processing?
- Mobilization from fat storage
- FA activation and transport to mitochondria
- Metabolism to acetyl CoA to feed into CAC
What happens for the G-protein Signal for Fat Mobilization?
- Epinephrine and glucagon act on a 7TM receptor (Chapter 13).
- Adenylate cyclase forms cAMP and activate PKA.
- PKA activates perilipin A and hormone sensitive lipase.
How are Fatty Acids carried through the bloodstream?
Fatty Acids are not soluble in blood but are carried throughout the bloodstream by binding to serum albumin.
How is triacylglgerol broken down?
Lipases
converts MAG to fatty acid + glycerol
Monoacylglycerol (MAG) Lipase
converts DAG to MAG
Hormone Sensitive (HS) Lipase
converts TAG to DAG
Adipose Triglyceride Lipase (ATGL)
What is this Molecule?

Glycerol
What is this Enzyme?

Glycerol Kinase
What is this Molecule?

Glycerol 3-Phosphate
What is this Enzyme?

Glycerol Phosphate Dehydrogenase
What is this Molecule?

Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
What is this Molecule?

D-Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
How can Fatty Acids enter cell membranes?
Both passive diffusion and specific protein mediated transporters
Name a Fatty Acid Transporter
CD36, plasma membrane-associated fatty acid-binding protein (FABP(pm)), and a family of fatty acid transport proteins (FATP1-6)
How many carbon units in Fatty Acid Degradation, and what does it produce?
2 Carbon Units
Acetyl CoA
What does Fatty Acid Degradation involve, what is it called, and why?
involves oxidation steps and is called (beta)-oxidation based on the FA numbering scheme.
After each round of (beta)-oxidation the FA is 2 carbons shorter
What is this Molecule?
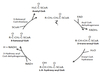
Acyl CoA
What is this Molecule?

2-trans-enoyl-CoA
What is this Molecule?

L-3-hydroxy Acyl CoA
What is this Molecule?
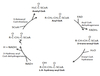
3-ketoacyl CoA
What is this Molecule?

Acetyl CoA
What is this Enzyme?

Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase
What is this Enzyme?
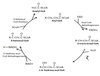
Enoyl CoA hydratase
What is this Enzyme?

3-Hydroxy Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase
What is this Enzyme?

3-ketoacyl CoA thiolase
What is this molecule?

Acyl CoA
What is this molecule?

Δ2-Enoyl-CoA
What enzyme catalyzes this reaction?
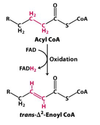
acyl CoA dehydrogenase
What is this molecule?
Δ2-Enoyl-CoA
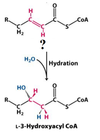
What is this molecule?

L-3-Hydroxyacyl CoA
What enzyme catalyzes this reaction?

enoyl CoA hydratase
What is this molecule?
L-3-Hydroxyacyl CoA
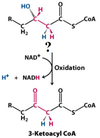
What is this molecule?

3-Ketoacyl CoA
What enzyme catalyzes this reaction?

L-3-hydroxacyl CoA dehydrogenase
What is this molecule?
3-Ketoacyl CoA
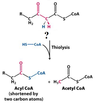
What is this molecule?

Acetyl CoA (shortened by 2 Carbon Atoms)
What is this molecule?

Acetyl CoA
What enzyme catalyzes this reaction?

β-ketothiolase
What enzyme catalyzes this reaction?
acyl-CoA synthetase
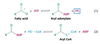
What is this molecule?

Fatty Acid
What is this molecule?
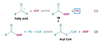
Acyl Adenylate
What is this molecule?

Acyl CoA
What is the yield from the degradation of Palmitate?
8 acetyl CoA
7 FADH2
7 NADH
What is the overall ATP yield from Fatty Acid Degradation?
106
an alternate, water-soluble fuel source
Ketone Bodies
What happens with Unsaturated Fatty Acids for odd numbered double bonds?
- Normal oxidation occurs until you hit the double bond.
- The “normal” cis double bond is isomerized to trans by cis D3-enoyl CoA isomerase
- Normal oxidation continues but at the 2nd step (you would not get an FADH2)
What happens with Unsaturated Fatty Acids for even numbered double bonds?
- Normal oxidation occurs until you form the diene. Which stops the process.
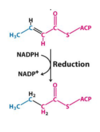
- The even numbered double bond is removed (reduced to alkane) by a reductase which requires NADPH. And shifts the double bond to the three (odd number) position.
- The double bond at the 3 position moved to the 2 position by the cis D3-enoyl CoA isomerase as in the odd numbered oxidation process.
- Oxidation continues as with the odd numbered.
What is key in regulation of Fatty Acid Synthesis?
Regulation at fat cell activation of perilipin A and lipase by epinephrine and glucagon
What are the three stages of Fatty Acid Synthesis?
–Transfer of Acetyl CoA precursor units to cytoplasm from mitochondria
–Activation of acetyl CoA to form malonyl CoA (3C)
–Attachment of acyl carrier protein w/ 2C unit addition
What is the Movement of Acetyl CoA from Mitochondria to Cytoplasm and back?
The 2C units of acetyl CoA that will become a fatty acid are moved out of the mitochondria as Citrate (6C), converted to oxylacetate, to malate, then to pyruvate to cross the membrane again
The two carbon Acetyl CoA unit is regenerated from citrate using what enzyme?
ATP citrate lyase (which requires ATP for energy)
What does Fatty Acid Synthesis require?
2 NADPH for each 2C unit added
What happens during Formation of Malonyl CoA as Template for Repeating FA unit?
The enzyme acetyl CoA carboxylase adds a carboxylic acid to the 2C acetyl CoA to make the 3C malonyl Co A. Requires ATP
What protien is required to begin Fatty Acid Synthesis?
Acyl Carrier Protein
What happens during Condensation of Acetyl-ACP and Malonyl-ACP?
Acyl-malonyl ACP condensing enzyme adds the 2C acetyl CoA to the 3C malonyl CoA with the loss of CO2 to make a 4C product.
What is the blue Molecule?

Acetyl-ACP
What is the pink Molecule?
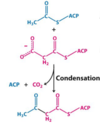
Malonyl ACP
What is the product molecule?

3-ketoacyl ACP
What Enzyme is used in this reaction?

acyl-malonyl ACP condensing enzyme
What is the top molecule?

3-ketoacyl ACP
What is the bottom molecule?
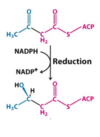
D-3-hydroxyacyl ACP
What Enzyme is used in this reaction?

β-ketoacyl ACP reductase
What is the top Molecule?

D-3-hydroxyacyl ACP
What is the bottom Molecule?
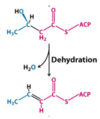
Δ2-enoylacyl ACP
What Enzyme is used in this reaction?

3-hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase
What is the top molecule?

Δ2-enoylacyl ACP
What is the bottom molecule?
Acyl ACP
What enzyme is used in this reaction?

enoyl ACP reductase
Where does the required NADPH for Fatty Acid Synthesis come from?
Note that each extension requires 2 NADPH
One comes from oxaloacetate recycling and one comes from the PPP
What releases the free fatty acid from the ACP?
thioesterase
What catalyzes extension of FA chains to stearate (C18)?
elongase
Where is the most common point of unsaturation in Fatty Acids?
- involves the placement of a double bond between carbons 9 and 10 (as in the conversion of palmitic acid to palmitoleic acid or the conversion of stearic acid to oleic acid, facilitated by the action of Δ9-desaturase). Other positions that can be desaturated in humans include carbon 4, 5, and 6, via Δ4-, Δ5-, and Δ6-desaturases, respectively.
- Humans cannot desaturate higher than carbon 9. Higher desaturated sites are obtained from diet.
How is Fatty Acid Synthesis Regulated?
Acetyl CoA carboxylase: phos inactive/dephos active via epinephrine/glucagon/insulin
Upregulated by citrate and downregulated by palmitoyl CoA
How is Fatty Acid Synthesis Regulated?
Primarily, Acetyl CoA Carboxylase
upregulated by citrate and insulin
downregulated by palmitoyl CoA and glucagon/epinephrine
Acetyl CoA carboxylase is further regulated through phosphorylation by AMP-Dependent Protein Kinase (AMPK)
What are nucleic acids made up of?
heterocyclic nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and one or more phosphates
What is the Role of Nucleic Acids in the Cell?
- Act as cofactors for many enzymes (ex NADH)
- Provide energy for the synthesis of other biomolecules (ex ATP)
- Store genetic and proteomic information (DNA and mRNA)
- Catalyze enzymatic reactions (ex rRNA)
What are the Purines?
Adenine
Guanine
What are the Pyramidines?
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
What is the geometry for nitrogenous bases?
Planar (sp2)
Constitutional isomers that exist in rapid equilibrium
Tautomers
How do you recognize a deoxyribose?
The second carbon has no oxygen - H on either side!
What is a nucleoside?
Nucleic acid base plus sugar
Ribose or deoxyribose
What are the deoxyribonucleoside Purines?
2’-deoxguanosine
2’-deoxyadenosine
What are the deoxyribonucleoside Pyramidines?
Thymidine (?)
2’-deoxycytidine
2’-deoxyuridine
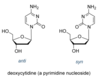
What is the difference between an anti and syn nucleotide bond?
Anti- extends outward
Syn-overlaps molecule
What is this Nitrogenous Base?

Adenine
What is this Nitrogenous Base?

Guanine
What is this Nitrogenous Base?

Cytosine
What is this Nitrogenous Base?

Thymine
What is this Nitrogenous Base?
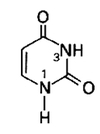
Uracil
What are the Deoxyribonucleosides?

What are the Ribonucleosides?

What is the Role of Nucleotides?
•NTP’s (where N is any or unknown base) are carriers of energy through phosphate or pyrophosphate transfer.
–ATP: general energy carrier
–GTP: energy for protein synthesis
–CTP: energy for phospholipid synthesis
– UTP: energy for carbohydrate synthesis
Almost always bound to Mg+
What is the polymer linkage for Nucleic Acids?
The linkage is made from the 3’ alcohol of the sugar (ribose or
deoxyribose) of one nucleotide to the 5’ phosphate of another sugar.
The directionality of the nucleic acid polymer is thus 5’-3’.
Defines the reading frame much like N-terminus to C-terminus in proteins.
Naming is similar to others: dinucleotide, trinucleotide….etc
Oligonucleotide (>10 nt) to polynucleotide
How would this structure be named?

5’-d[TpApCpG]-3’
or
5’-TACG-3’
How does a primary sequence of nitrogenous bases connect?
Fructose + Pi

How does the double strand get formed?
Making the double strand involves base pairing via hydrogen bonds
Chargaffs Rules:
A pairs with T (or U)
G pairs with C
Name a tertiary structure of DNA
G-quartet
Single-stranded G-rich DNA
G-quadruplex
How many Histones are there?
5
H1 is not part of bead, rest have 2 copies
What are the types of RNA?
mRNA (messenger RNA): single-stranded transcribed form of “coding” DNA which acts as the template for translation, degrades quickly in vivo
tRNA (transfer RNA): Highly folded RNAs which transfer a single amino acid to the ribosome during translation
rRNA (ribosomal RNA): The RNA component of the supramolecular machinery which catalyzes the synthesis of proteins
What type of RNA contains a lot of methylated and unusual nucleic acids?
tRNA
The Ribosome is comprised of approximately __% RNA
65%


