signal transduction 3 Flashcards
Hydrophobic hormones
ligand for intracellular receptor
NT
ligand for Ligand-Gated Ion Channel and G pro coupled receptor
GF
ligand for EnzymeLinked and cytokine receptor
hormones and GF
ligand for EnzymeLinked receptor
Cytokines Growth factors
ligand for cytokine receptor
Hormones Cytokines
ligand for G-ProteinCoupled
only receptor on cytoplasm/ nucleus
intracell receptor (all others are on cel surface)
Dimeric/tetrameric complex of transmembrane polypeptides with intracellular catalytic domain
intracell receptor
Activates autophosphorylation
intracell receptor
Single polypeptide with 7 trans- membrane domains
G-ProteinCoupled
Activates trimeric G protein
G-ProteinCoupled
Multimeric ring-like complex of 3-5 polypeptides with multiple transmembrane domains
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel
tf Ligand-GatedIon Channel lack transmembrane domain
F has it
Opens internal water-filled pore
Ligand-GatedIon Channel
Polypeptide dimer with DNA- binding domains
intracell receptor
Binds as dimer to DNA sequence
intracell receptor
Activates cytoplasmic enzymes
cytokine receptor
Multimeric complex of trans- membrane polypeptides lacking intrinsic catalytic activity
cytokine receptor
Tf cytokine receptor has intrinsic cat. activity
F lacks it
SH2 domain
2 α-helices flanking β-sheet (antiparallel)
β-barrel (antiparallel) followed by C-term α-helix Binds in cleft between helix and strands
PTB domian
Binds in deep pocket lined with + residues
SH2

Binds in cleft between helix and strands
PTB domain

SH3 domain
Binds in shallow hydrophobic pocket

β-barrel fold (2 antiparallel β-sheets)
SH3 domain
2 perpendicular β-sheets (antiparallel) followed by C-term amphipathic α-helix
PH domain
PH domain
Binds in cleft between loops connecting strands

binding affinity phos. tyrosines
sh2 and ptb
bidning affinity of prolines
SH3 domain
phos. inositol PL binding affinity
PH domain
Receptors have an appropriate—- —– (dissociation constant, KD ) for the signaling molecule in order to detect it at the likely ——- in the vicinity of the cell.
Receptors have an appropriate binding affinity (dissociation constant, KD ) for the signaling molecule in order to detect it at the likely concentration in the vicinity of the cell.
criteria 1 of receptors
Receptors transmit the —- of the signaling molecule by modulation of further—– in the signaling cascade.
Receptors transmit the message of the signaling molecule by modulation of further components in the signaling cascade.
Criteria 2 of receptor
Receptors display ——- by detecting only those signaling molecules which the cell wants to perceive.
criteria 3 of reeptors
Receptors display specificity by detecting only those signaling molecules which the cell wants to perceive
criteria 3 of receptor
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
cationic selective
subunits of nicotinic ach receptor
Subunit with 4 transmembrane domains – M1, M2 (amphipathic), M3, and M4 – and 2 intracellular loops
tf both the N and C terminal in the nicotinic ach receptor is in the extracell space
T
termination of ligand gated ion channel
Diffusion away from the receptor and synaptic gap Degradation by enzymes on the cell surface (e.g., acetylcholinesterase)
Re-uptake into the pre-synaptic neuron
Formation of an —— ligand—— state (non—– form of receptor inactivation) ensures very —- periods of signal transduction.
Formation of an inactive ligand-bound state (noncovalent form of receptor inactivation) ensures very brief periods of signal transduction.
ligand gate ion channel term.


Small ligands bind in pocket.
Large ligands bind to extracellular loops.
GPCR
GPCR has – transmembrane alpha helixes
7
tf the N terminal is on ext side and C terminal in on the int. side in GPCR.
T
glycosylation ; phosphorylation in GPCR
N; C terminal in GPRC
rhodopsin recptor
GPCR
Largest subunit in gpcr
alpha
phillic to phobic on gpcr
alpha; betay on gpcr
Guanine nucleotide-binding site (GDP, GTP) and GTPase activity
alpha subunit of GPCR
GPCR portion that interacs with effector protein
alpha subunit
BY unit of GPCR
cov attach to membrane with some int. with effector protein
after ligand bidns GPCR —- —–,
GDP/GTP exchange causes—– with —– to dissociate
conf change
alpha subunit with GTP
(GPCR)
seconary enzyme in GPCR
will bing alpha subunit with GTP
and intrinsic GTPase activation cause Hydrolysis of GTP to GDP and release of alpha GDP

major mechanism of desensitization of GPCR
Receptor phosphorylation by protein kinases
Protein kinase A (PKA) receptor
protein kinases (GRKs) receptor
+/- ligand GPCR-specific
+ ligand
Extracellular enzymes —– or —- many of the small ligands.
Extracellular enzymes metabolize or inactivate many of the small ligands.
GPCR inact
—— —— endocytosis accounts for some desensitization
Receptor-mediated endocytosis accounts for some desensitization
GPCR inact.

Extracellular enzymes metabolize or inactivate many of the small ligands.

Receptor phosphorylation by protein kinases
GPCR termination
Caffeinated Alcohol Drinks
—– Binds to allosteric binding site on GABA-bound receptor
ethanol
TF in : Caffeinated Alcohol Drinks
EToh bidning to GABA receptor keeps it closed
F keeps it open
Effect of EToh on GABA bidning site
Causes membrane potential to become more negative
Increases GABA’s suppression of neural activity
Increases dopamine release

GABA Ligand-Gated Ion Channel
Anion-Selective (Inhibitory)
Adenosine G-Protein-Coupled Receptor thru caffiene stimulant
① Blocks adenosine binding site (antagonist)
Normally Adenosine G-Protein-Coupled Receptor
Suppresses neural activity; increases blood flow
Allows increased neural activity Leads to blood vessel constriction, epinephrine release, and increased level of alertness
Caffiene blocking
Individual feels sober when highly intoxicated.
end result of cafffiene alcohol drinks
Each subunit is a single polypeptide chain consisting of: Large extracellular N-terminal domain for binding ligand Single transmembrane domain
Intracellular C-terminal domain with catalytic domains
Enzyme-Linked Receptor
dimer; tetramer
RTK; SER threonine kinase
RTK
Ligand binding Dimerization Kinase activation
then
Autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues (cross-phosphorylation)

GF binding to RTK
act of RTK bidning of adaptor pro.
then
RAS act protein

RAS GDP
attaches to membrane
and is converted to active RAS (GTP) upon act of RTK by GF
RAS act protein phos it.
(serine/threonine kinase
MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase
MAP Kinase – Effector Protein
MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase
act by RASGTP
threonine/tyrosine kinase)
MAP Kinase Kinase
effect of MAP Kinase – Effector Protein

Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinase
Ligand binding to type –
Dimerization with type –
Kinase activation
and cross-phosphorylation (Ser/Thr residues) of type —
Ligand binding to type II
Dimerization with type I
Kinase activation
and cross-phosphorylation (Ser/Thr residues) of type I

upon act of receptor Serine/Threonine Kinase
SMAD binding and
phosphorylation
SMAD unfolding
and act
after act of SMAD
dissociation and dimerization with diff SMAD subtypes
translocate to nucleus to alter gene expression
binding of act SMAD to another SMAD
Exposure of nuclear localization signal (NLS)
Termination of Enzyme linked receptor
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis (Down-Regulation)
clustering
adaptin binding
clathrin binding
adaptin binding
clathrin binding
clustering

clathrin polymerization accompanied by
vacuole formation in Enzyme-Linked Receptor term.
Release of — —-vesicle into cytoplasm
Shedding of ——- ———
Fusion of vesicle with ——– (internal —– ph)
Release of clathrin-coated vesicle into cytoplasm
Shedding of clathrin coat Fusion of vesicle with endosome (internal acidic ph
3rd step in Enzyme-Linked Receptor

tf in Enzyme-Linked Receptor: Termination
Potential recycling of receptors to plasma membrane is not possible
F
recycling happens at end
and
Transfer of remaining contents to lysosomes for degradation
tf Cytokine cant recruit manyintracellular signaling proteins
F it can recruit a broad range because of itts great diversity
tf the intracellular enzymatic activity has no intrincic enzymatic activity
t
single polypeptide
cytokine receptor
Cytokine receptor
multimeric complexes
1st step of Cytokine Receptor action
Cytokine binding Dimerization
JAK activation and cross-phosphorylation Subunit phosphorylation

STAT binding
prompts Phos Jak to phosphorylate it
2 thing phos in cytokine receptor activation
JAKS and subunits
upon sTAT phosphorylation
STAT dimerize
AND
Translocation to nucleus Altered gene expression
Protein phosphatases remove —- phosphates from the receptor and/or activated —–
Protein phosphatases remove tyrosine phosphates from the receptor and/or activated STATs.
Cytokine receptor termination
SOCS (suppressor of cytokine signaling)
inhibit STAT phosphorylation by binding
inhibiting JAKs or competing with STATs for phosphotyrosine binding sites
Multimeric formation of the receptor after ligand binding triggers —– of the ligand-receptor complex.
Multimeric formation of the receptor after ligand binding triggers endocytosis of the ligand-receptor complex.
cytokine receptor termination
importin α5
subunit of importin α5-β complex
Ran-GTP
dissociates
STAT1 dimer (NLS) and importin α5 complex
(happens in nucleus)
after dissociation of STAT 1 and importin a5
the STAT1 dimer
binds to DNA targets
and causes Expression of antiviral response
VP24 protein from EBola
Competes with STAT1 dimer for binding site on importin α5 subunit
VB24 and importin α5 subunit complex
diffuse thru nuclear pore
and Dissociated by complex by Ran-GTP
Suppression of antiviral response
promoted by VP24 protein after Dissociation from complex by Ran-GTP
Small KD
Receptor has high affinity for ligand.
Kd=
koff/ kon
LR=
([R]o [L]o) /(KD + [L]o)
Bound
B max(Free/Free+Kd)
Free = KD,
then Bound = 0.5 Bmax
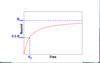
if free>Kd
bound= bmax
Negligible ligand depletion (bound < 10% of free) Negligible inactivation of ligand and receptor
2 conditions of saturation binding relation
tf 2 conditions of saturation bidning relation all ligand and receptor act and there are few cell surface interaction
F
Negligible inactivation of ligand and receptor
Negligible cell surface interactions
main condition of saturation plot
Equilibrium conditions
Homogeneous,——-(1:1) populations of ligand and receptor
Homogeneous, monovalent (1:1) populations of ligand and receptor
Saturation Plot
Label the saturation plot


If EC50 >KD
Cell expresses more receptors than required for effective biological responses.

F
expresses less
EC50 is Half-Maximal Effective Conc

advantage of scatchard plot
— evaluation is easy for checking original — (straight line) or comparing different — or receptors.
Visual evaluation is easy for checking original assumptions (straight line) or comparing different ligands or receptors.
—- on both axes magnifies experimental error.
“Bound” on both axes magnifies experimental error.
disadvantage of scatchard plot
what does this indicate abt parotid

KD are same but control has more Bmax than parotid
meaning;
binding characteristics of salivary gland muscarinic acetylcholine receptors of the parotid contribute to reduced saliva stimulation
what does this indicate abt SM gland

Diabetic has greater KD
but = B max
no conconclusion on whether
binding characteristics of salivary gland muscarinic acetylcholine receptors of SM gland contribute to reduced saliva stimulation or not?


