Retroperitoneum Flashcards
(32 cards)
what does the retroperitoneum contain?
where is it located?

containing the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, duodenum, ascending colon, descending colon, pancreas and the large vessels and nerves.
b/t the posterior portion of the parietal peritoneum and posterior abdominal wall muscle

what are teh borders of the retroperitoneum?
The space extends from the diaphragm to the pelvis. Note the posterior abdominal muscles, psoas and quadradus lumborum muscles are posterior to the retroperitoneum.

what are the abdominal retroperitoneal spaces and what do they have inside of them?
Peri = around - think of the perimeter of something.
Para = Alongside
I think of the 2 letter a’s running alongside the r.

what are the 3 abdominal retrpoeritoneal spaces?
Anterior Pararenal space – bound anteriorly by the posterior parietal peritoneum and posteriorly by the anterior renal fascia (Gerota’s)
–
Perirenal space – is the space surrounded by Gerota’s fascia (surrounds kidney)
–
Posterior Pararenal space – The small area between the posterior renal fascia (Gerota’s) and the transversalis muscle

identify the 3 abd retrperitoneal spaces


what are the 4 subdivisions of the pelvic retrop?
Prevesical
•
Rectovesical
•
Presacral
Bilat. – pararectal/paravesical

where does the pelvic retrop lie?
Lies between pubis and sacrum. From A/P
–
Lies between pelvis peritoneal reflect and pelvic diaphragm i.e. muscles of the pelvic floor. From S/I

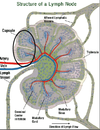
The ______ is part of the immune system, made up of a network of conduits that carry a clear fluid called___.
lymphatic system, lymph
_______ associated with the lymphatic system is concerned with immune functions in defending the body against the infections and spread of tumors.
what does it consist of ?
Lymphoid tissue
It consists of connective tissue with various types of white blood cells enmeshed in it, most numerous being the lymphocytes
where are lymph nodes found?
ina number of areas w/i the body
http: //www.youtube.com/watch?v=qEIV6c61kx4&feature=related
http: //www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZdYxx4CHb-A&feature=related
are all lymphatic retrop?
no, some are intraperitoneal *similar appearance despite location
what moves lymph?
muscles
are lymph nodes seen in a healthy adult?
who might you see these in?
generally not – it is covered by body fat
children or thin adults
_____ are lymphatics chain follows AO from thoracic to abdominal cavities and Iliac arteries
paraortic nodes


what is the normal size of a lymph nodE?
what is it’s sonographic appearance?
<1 cm
•
Homogeneous, ovoid, smooth borders, well defined
•
Hilum – echogenic due to fatty tissue
•
Hypoechoic
•
Nodes will not change shape or move like bowel will

When lymph nodes are enlarged they cause a _____ to become evident. this is when an organ is being pushed upon by some type of mass lesion.
“mass effect”
what do you see int he top lt image?

mass effect
what are these examples of?

retroperitoneal lymph nodes
what are these examples of?

peripancreatic lymph nodes (pt has history of lymphoma)
same below

what are these examples of?

paraortic lymph nodes (pt has history of AIDS)

what do you need to remember when scanning lymph nodes?
sometimes slow motion will not allow you to see it.
The space between the parietal peritoneum and the muscles and bones of the posterior abdominal wall. “
This phrase best describes
a. The peritoneal space
b. The retroperitoneal space
c. Morrison’s pouch
d. Pouch of Douglas
e. B and C
b
- All of the following anatomy is found in the retroperitoneal space EXCEPT.
a. periaortic lymph nodes
b. kidneys
c. antrum of the stomach
d. ureters
c