adrenal Flashcards
what are teh 2 parts of the adrenal glands?
cortex (outer, lgr)
medulla (inner)

what is the largest portion of gland (90%)
–
Arises from_____ which also gives rises to the sex organs.
–
Completely covers the____
–
Secretes a range of steroid _____
cortex
mesoderm
Medulla
hormones i.e. a steroid that acts like a hormone.
the ____ arises form the ____, which also gives rise to the autonomic nervous system which is a division of the peripheral nervous system.
–
what does it secrete ?
medulla
ectoderm
epinephrine and norepinephrine
the autonomic nervous system controls _____ body function.
it is divided in 2 parts:
1) fight or flight aka _____
2) rest & digest aka _____
involuntary (e.g. peristlisis of the bowel)
sympathetic (thoracolumbar)
parasympathetic (craniosacral)

_____ tumors affect certain hormones of the sex organs
cortical
the tumors that affect fight and flight systems and may produce the below symptoms are _____
name 3 possible symptoms…
medullary
Acceleration of heart and lung action
Inhibition of stomach and upper-intestinal action (digestion slows down or stops)
Constriction of blood vessels in many parts of the body
Liberation of nutrients for muscular action
Dilation of blood vessels for muscles
Inhibition of Lacrimal gland (responsible for tear production) and salivation
Dilation of pupil (mydriasis)
Relaxation of bladder
Evacuation of colon
Inhibition of erection
Auditory Exclusion (loss of hearing)
Tunnel Vision (loss of peripheral vision)
Acceleration of instantaneous reflexes
Shaking
where are the adrenal glands located?
compared teh kidney
the ivc?
the duodenum?
the rt liver lobe
the aorta?
Anterior, Medial, Superior to Kidneys
–
Rt. medial portion
•
Posterior to IVC
–
Rt. lateral portion
•
Posterior to duodenum
•
Posterior and medial to Rt. liver lobe
–
Lt. lateral or slightly posterior to AO.
•
Splenic artery/vein pass between pancreas and lt. adrenal gland

what are teh rt and lt adrenal glands shaped like?
RT. is more triangular and caps the upper pole of the kidney.
–
LT. is semilunar in shape sits on the medial portion of the kidney and extends from the upper pole to the hilum
what is the normal size of the adrenals?
–
3-6 cm in length
–
3-6 mm thick
–
2-4cm wide
where do the adrenals get there supply from?
3 arteries supply each adrenal gland
–
Suprarenal branch of the inferior phrenic
–
Suprarenal branch from the AO
–
Suprarenal branch of the renal artery
are teh adrenal glands endocrine or exocrine?
endocrine (cortex - steroid hormones, medulla epinephrine/norepinephrine)
whar are the steriod hormones produces by the cortex (3) and what do they do?
–
Mineralocorticoids
primary: Aldosterone - Regulate electrolyte metabolism
–
Glucocorticoids
primary: Cortisone/ Hydrocortisone (antihistamine)
Help in carbohydrate metabolism (affects weight)
–
Sex hormones
Small amounts of Androgen / Estrogen
Characteristics (ambiguous genitilia)– Libedo/Drive
* Gonads produce more of these and other sex hormones
what is ACTH?
where is secreted from?
what does it control?
how is is stimulated and inhibited?
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Secreted from pituitary gland
•
Controls adrenal cortical hormones through feedback mechanism
A decrease in serum glucocorticoids will stimulate the secretion of ACTH. Increased cortical hormone activity inhibits further ACTH secretion
the _____ is made of_______ cells which are neuroendocrine cells and they secrete epinephrine/norepinephrine
–
there is ___ x as much epinephrine as norepinephrine
–
medulla, Chromaffin
4
Increase heart rate, Increase respiration, Dilate pupils, Dilate coronary vessels, Constricts visceral vessels, allowing flow to muscles to be increased are all examples of _________________ .
Fight / Flight response
_______ acts in order to energize the body systems and is often referred to as “flight or fight” hormone while norepinephrine has psychoactive effects on the brain.
–
_______ converts glycogen to glucose while increases the catabolism of glycogen.
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
what do you need to remember w/ adulat eval?
No Prep – but NPO wouldn’t hurt
Vector or Curved array
Difficult in larger adult patients (w/i gerota’s fascia - can see the area where it sits but it’s surrounded by soo much fat too hard to see)
Small size – normal gland
Location - medial retroperitoneal
Perinephric fat -
Roll pt. into decubitus position
Normal gland is thin and flat
Area of the glands generally well seen
what plane is this?

trans. the below is long

describe the cortex and medulla echogenicity
Cortex: thick, hypoechoic
–
Medulla: thin, hyperechoic
*can’t differentiate b/t medulla and cortex after childhood.

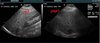
what is demonatrated here?

adenoma (notice how round the gland is)
what is a common adrenal gland variant?
ageneisis (congenital)
What are the below?
Aldosterone
Cortisol
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Catecholamines – are sympathomimetic “fight-or-flight” hormones (if high, possibly hyperthyroidism)
–
Total metanephrines - are metabolites of epinephrine
–
Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) - is a metabolite of norepinephrine,
lab values when dealing w/ any hormonal or endocrine gland, they tell you a lot!
indications for doing an adrenal gland exam (3)
Decreased hematocrit –Newborns can have large adrenal bleeds
–
Hypertension – Tumors of the medulla
–
Virilism – Tumors of the cortex
All of the following pertain to the adrenal glands EXCEPT.
a. exocrine gland
b. endocrine gland
c. cortex and medulla
d. retroperitoneal location
a







